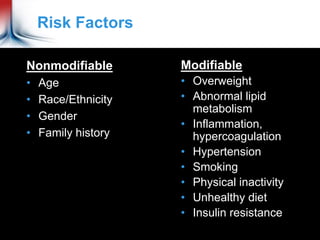
This document discusses cardiometabolic risk, which refers to the risks associated with metabolic changes that can lead to cardiovascular disease. It defines cardiometabolic risk and identifies both non-modifiable and modifiable risk factors such as obesity, dyslipidemia, hypertension, smoking, and physical inactivity. The document emphasizes the importance of early identification and management of risk factors through comprehensive patient assessment and targeted intervention to prevent diseases like cardiovascular disease and diabetes.