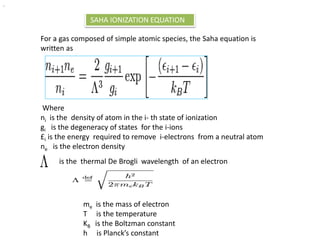
Meghnad Saha was an Indian astrophysicist born in 1893 in present-day Bangladesh who made significant contributions to astrophysics. He is best known for formulating the Saha ionization equation, which is a basic tool for interpreting stellar spectra and determining the ionization states of elements in stars based on their temperature. Saha helped establish several scientific institutions in India and was nominated for the Nobel Prize in physics. He died in 1956 after a distinguished career advancing science in India.