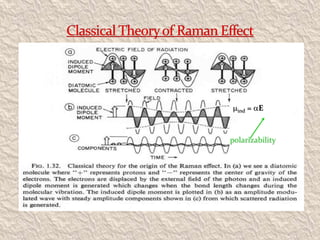
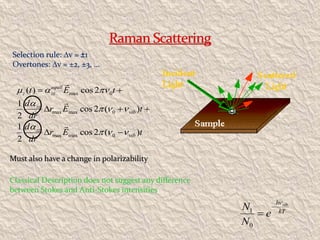
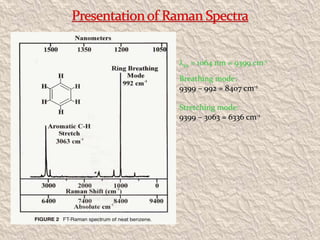
Sir C.V. Raman was an Indian physicist who won the 1930 Nobel Prize in Physics for his groundbreaking work on the scattering of light and discovery of the Raman Effect. He was born in India in 1888 and showed great academic aptitude from a young age, obtaining several advanced degrees before age 18. Raman conducted research on light scattering both during his career as an assistant accountant general and later as a physics professor. His discovery of new spectral lines when light interacts with matter, which came to be known as the Raman Effect, provided insights into molecular structure. Raman made many other contributions and established the Raman Research Institute in Bangalore before passing away in 1970.