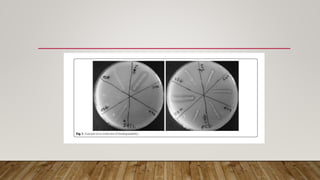
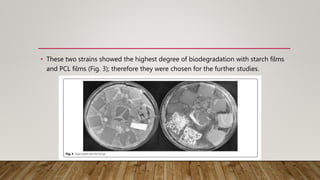
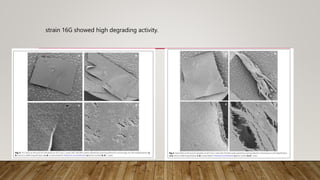
C. rosea strain 16G was able to decompose starch films by 100% within 16 days at 28°C and 65% within 30 days at 21°C. It decomposed PCL films by 52.91% at 28°C and 34.5% at 21°C within 30 days. Pseudomonas and Rhodococcus bacterial strains were able to degrade PCL emulsions. Trichoderma sp. strain 16H degraded starch films by 12.07% and PCL by 21.54% per month at 28°C in liquid culture. C. rosea strain 16G showed the highest degradation of bioplastic films and was most effective at lower temperatures.


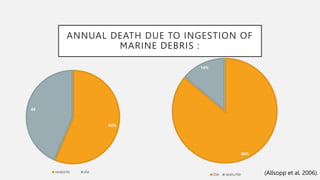
![• The plastic ingestion has been documented in over 100 species of seabird.
• researchers have been searching for new, alternative materials which can be used
as good substitutes for conventional plastics.
• One of them is production of biobased and biodegradable plastics [BP].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarreserach-221219161727-82bf7250/85/RESEARCH-PPT-4-320.jpg)








![MEDIA
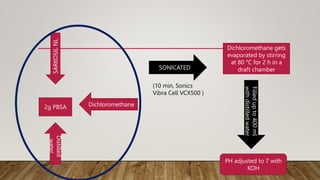
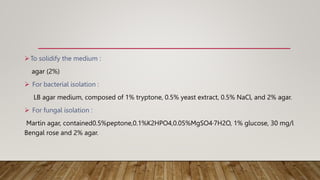
• Mineral minimum medium [MM] containing 0.1% emulsified polymers was
prepared.
composition was as follows:
FOR SOURCE OF CARBON :
0.2% NaH2PO4, 0.05% MgSO4·7H2O, 0.02% KH2PO4, 0.1% yeast extract and 0.1%
polymer emulsion (PBSA, PBS, PCL or PLA).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarreserach-221219161727-82bf7250/85/RESEARCH-PPT-15-320.jpg)
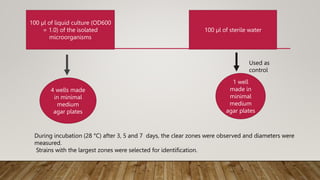
![CLEARANCE METHOD :
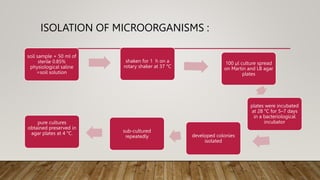
• Plastic-degrading microorganisms were identified.
• microbial colonies cultivated on plates were tested on mineral minimum [MM]
agar plates containing 0.1% emulsified polymers.
• bacterial biomass was inoculated as a scratch on agar plates.
• After incubation (2–3 days, 28 °C), the clear zones colonies forming clear zones
were selected as BP-degrading strains for further analysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarreserach-221219161727-82bf7250/85/RESEARCH-PPT-18-320.jpg)




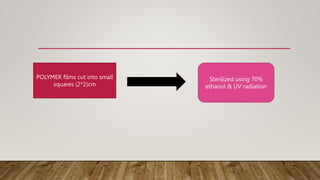
![LIQUID CULTURE METHOD FOR FUNGI:
0.1g plastic film+100ml
sterile [MM] in a conical
flask
Films sterilized by
washing in 70 % ethanol
+ UV radiation for 5 min
Medium inoculated with
the selected strain
incubated in rotary shaker
at 28 &21 celsius,200 rpm
for 1 month period
Control was maintained
with films in a microbe
free medium](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarreserach-221219161727-82bf7250/85/RESEARCH-PPT-24-320.jpg)