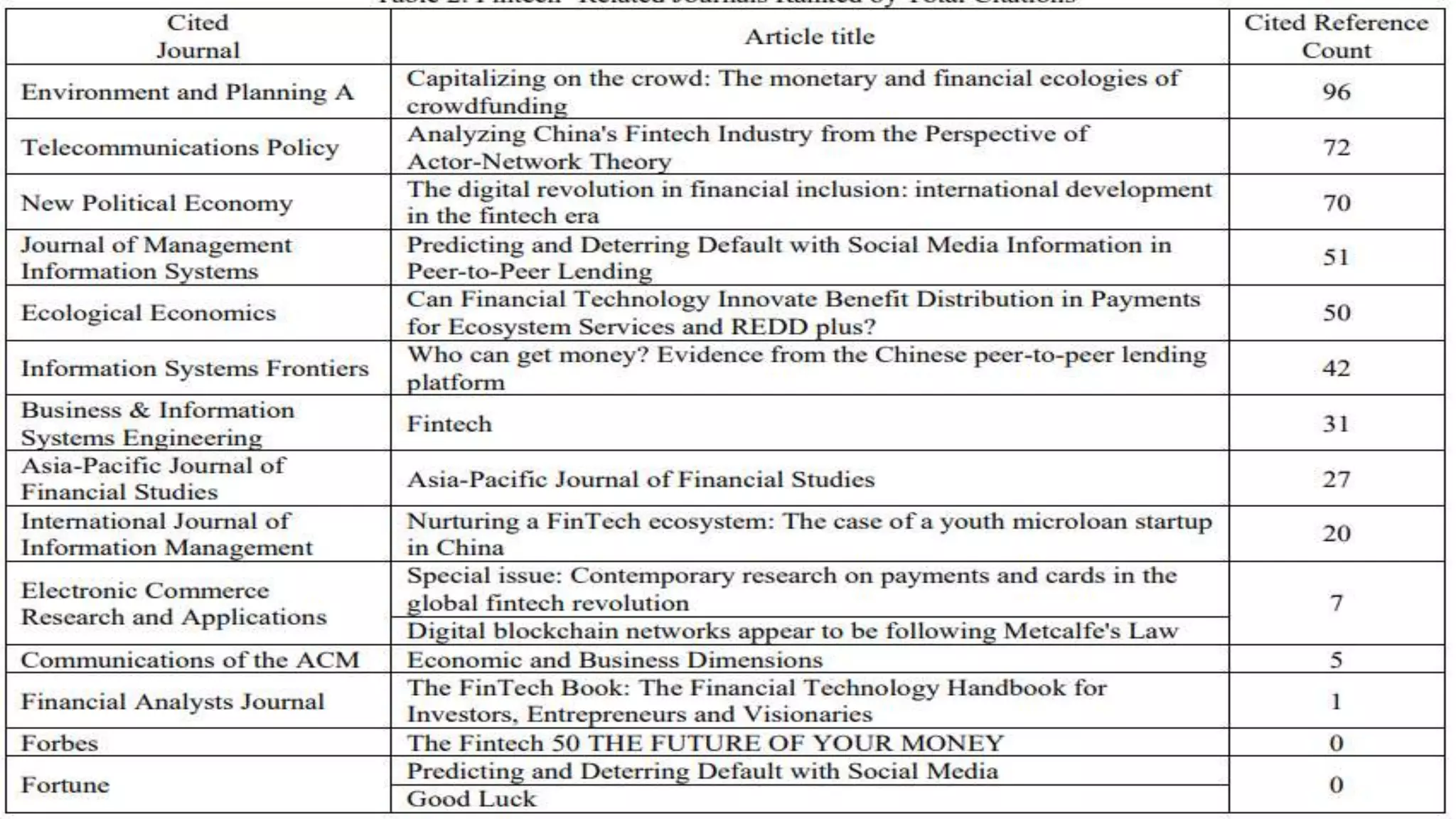
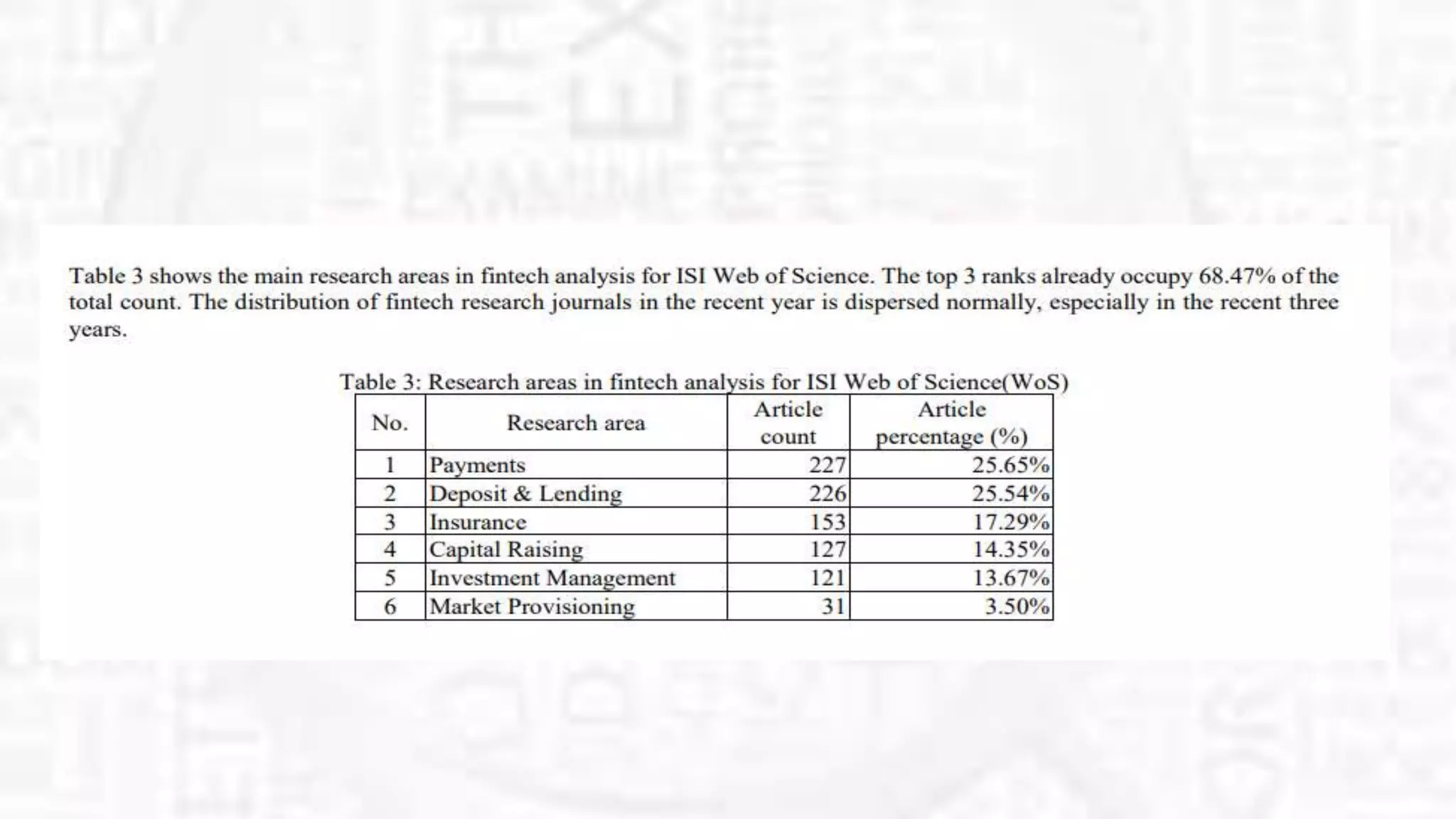
The document summarizes several research papers related to fintech. It begins by providing background on fintech and how it uses technology to support financial activities and efficiency. It then lists the top fintech journals based on total citations and some of the most popular fintech papers on SSRN, including papers on bitcoin and cryptocurrencies, blockchain technology, and initial coin offerings. One highlighted paper finds that purchases with tether, a cryptocurrency pegged to the US dollar, are timed after market downturns and result in increased bitcoin prices, indicating tether may be used for price manipulation.