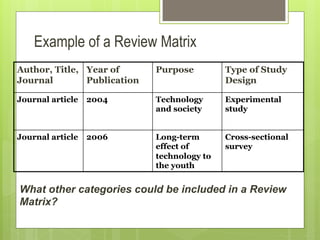
This document outlines the steps for conducting a literature review. It begins by defining research and the objectives of research such as gaining new insights or testing hypotheses. It then discusses what a literature review is and its purpose of analyzing existing research. The main steps covered are establishing a research focus, identifying relevant search tools and terms, searching databases using operators and wildcards, organizing findings, determining relevant literature, and analyzing and summarizing the evidence into a report. Examples and exercises are provided to illustrate each step in the literature review process.