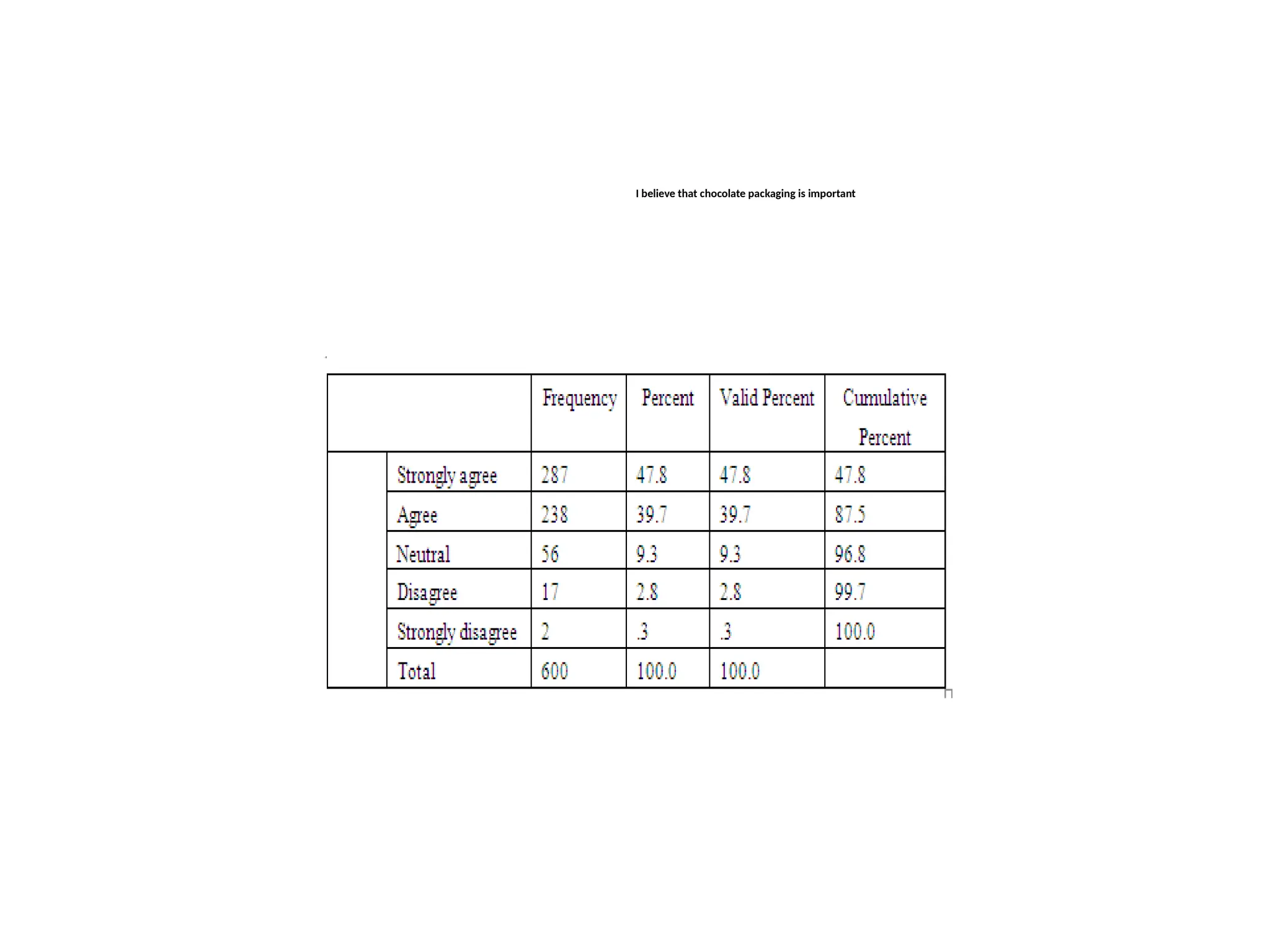
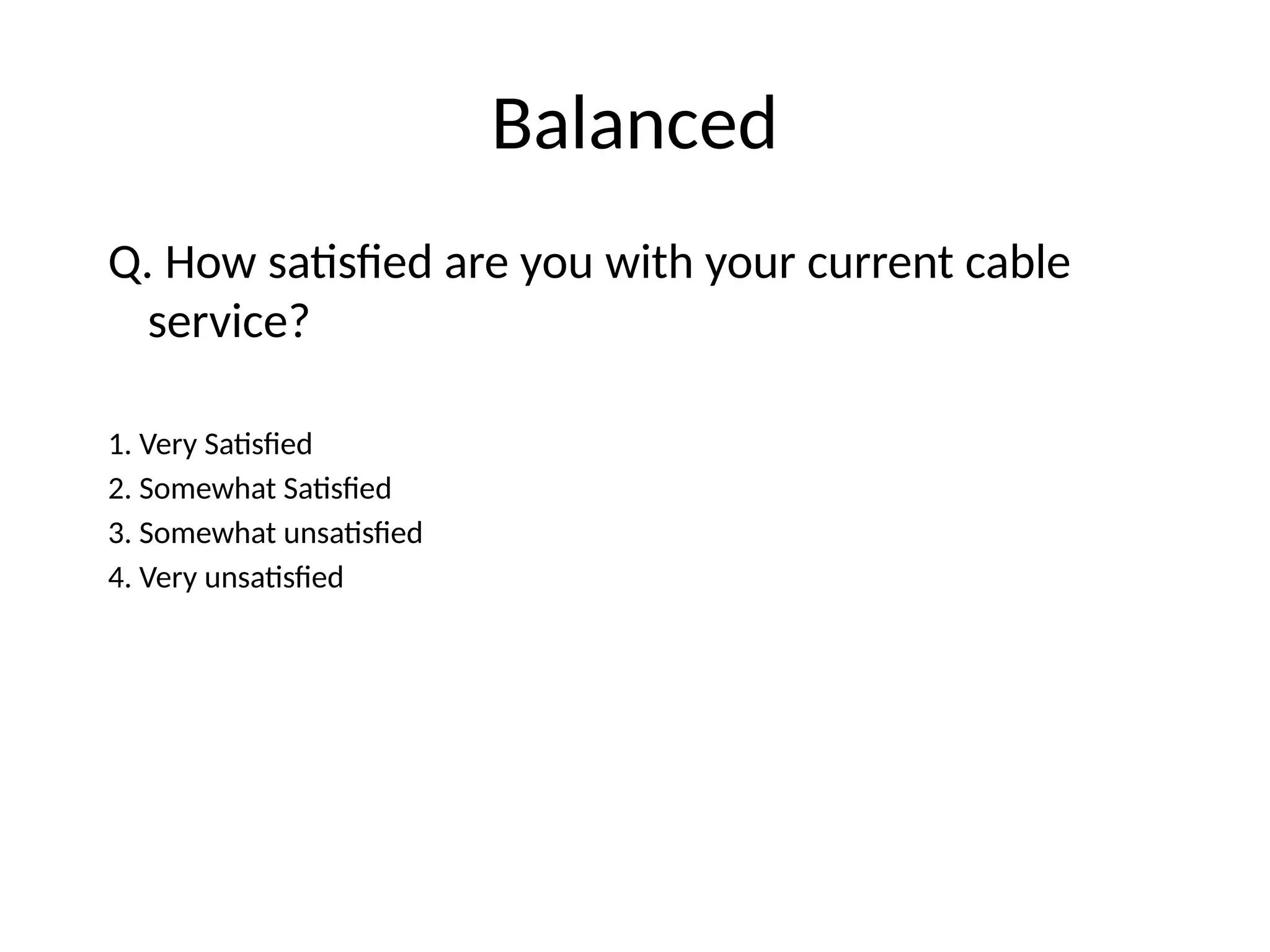
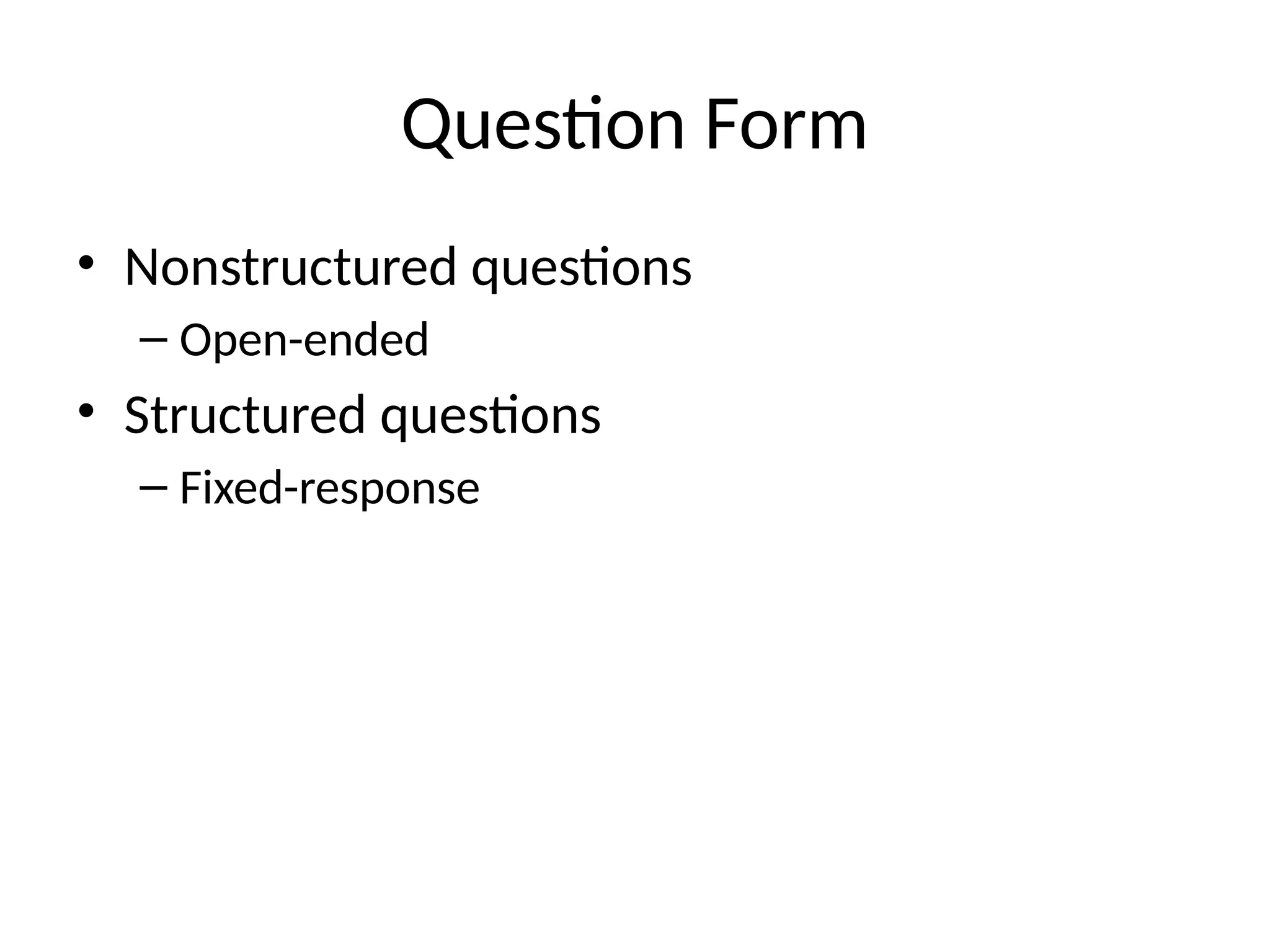
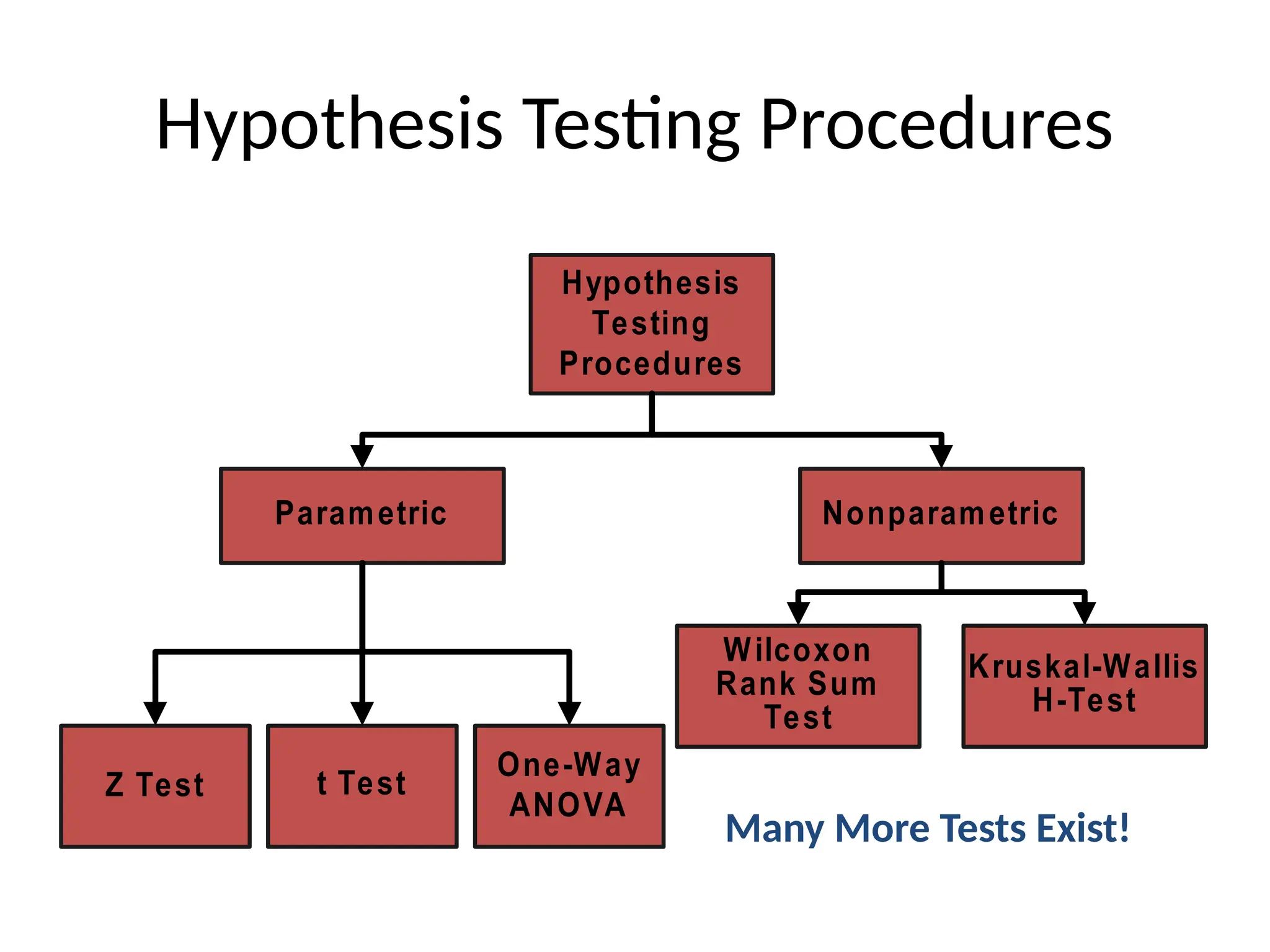
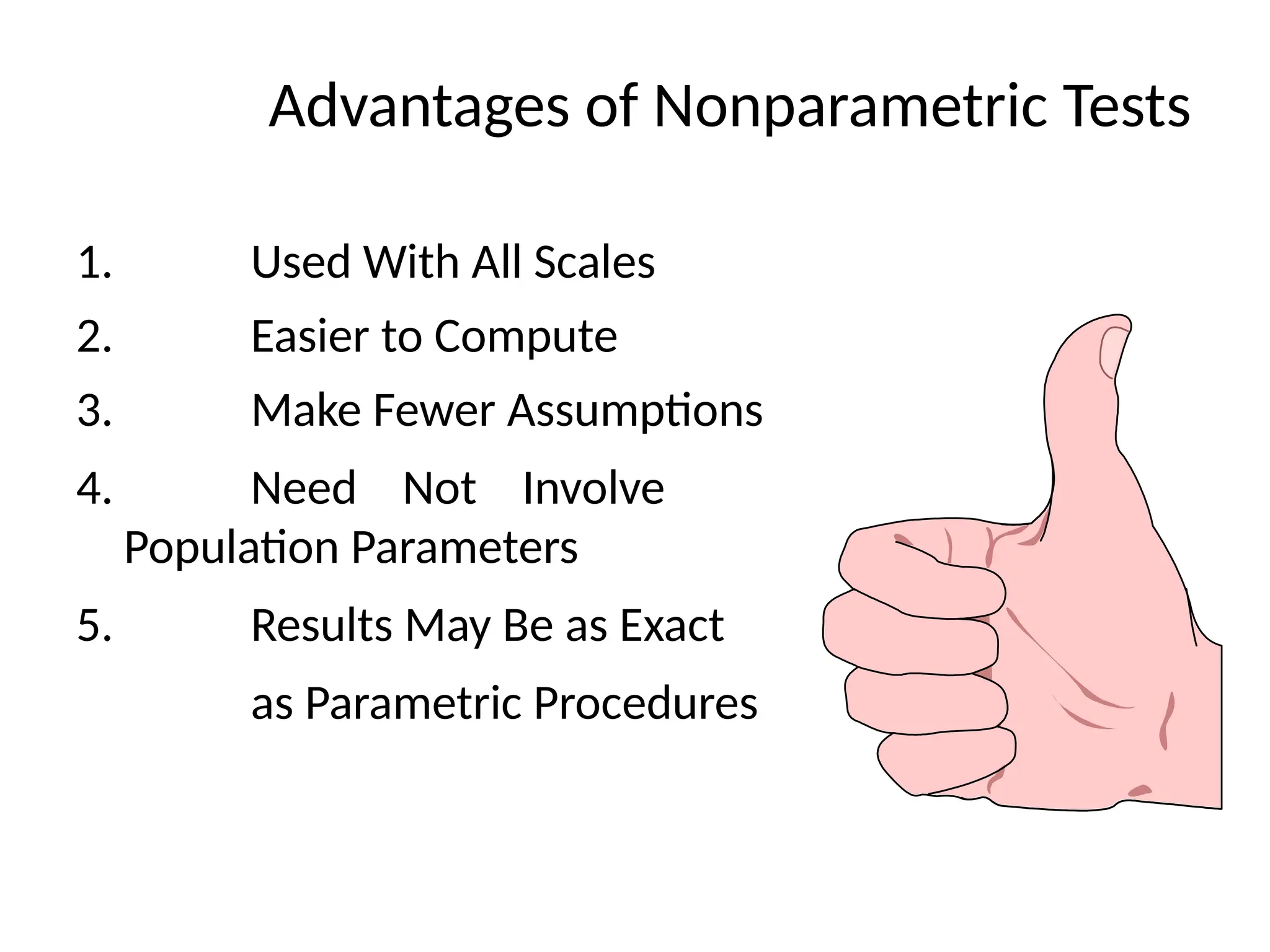
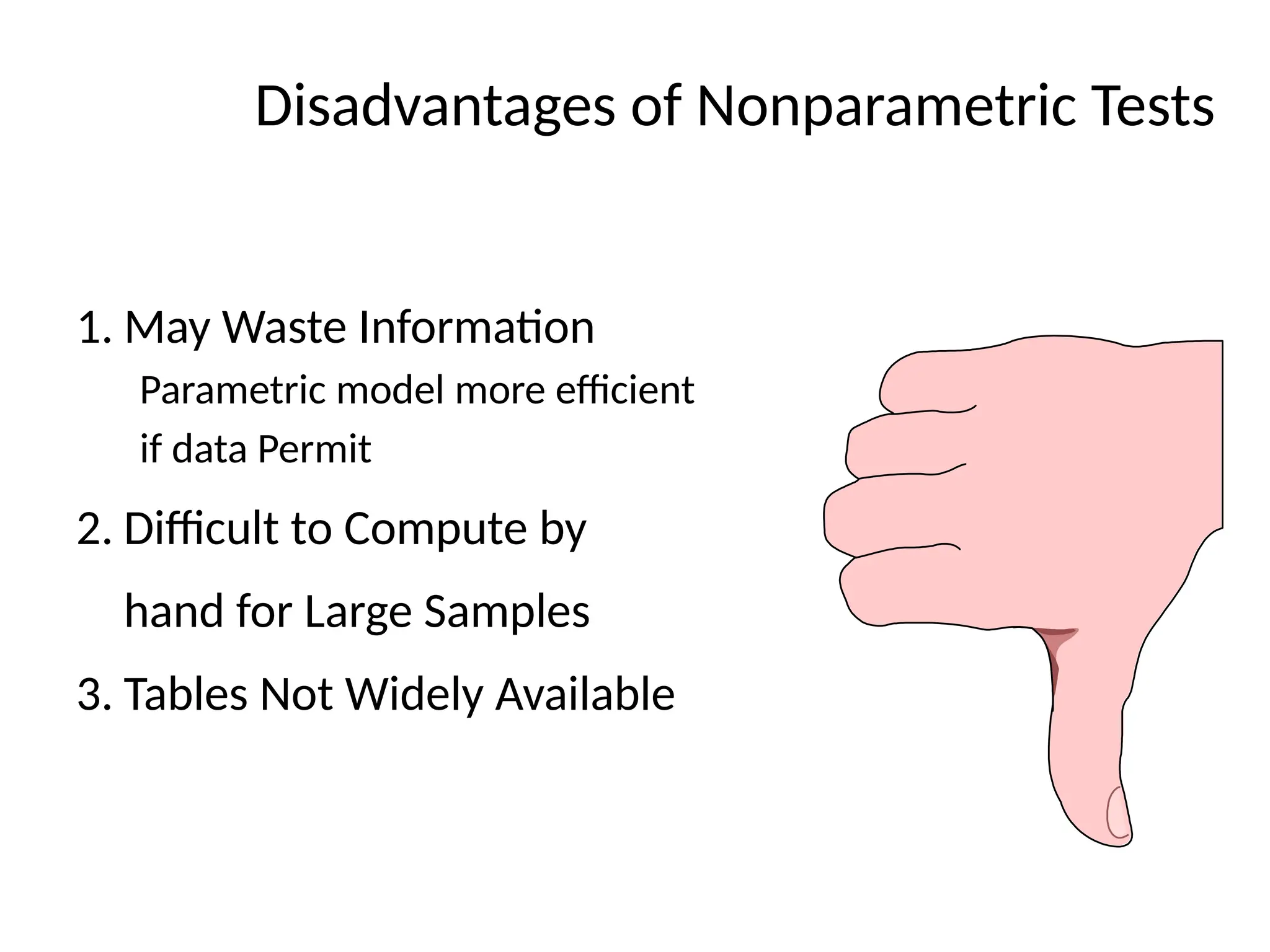
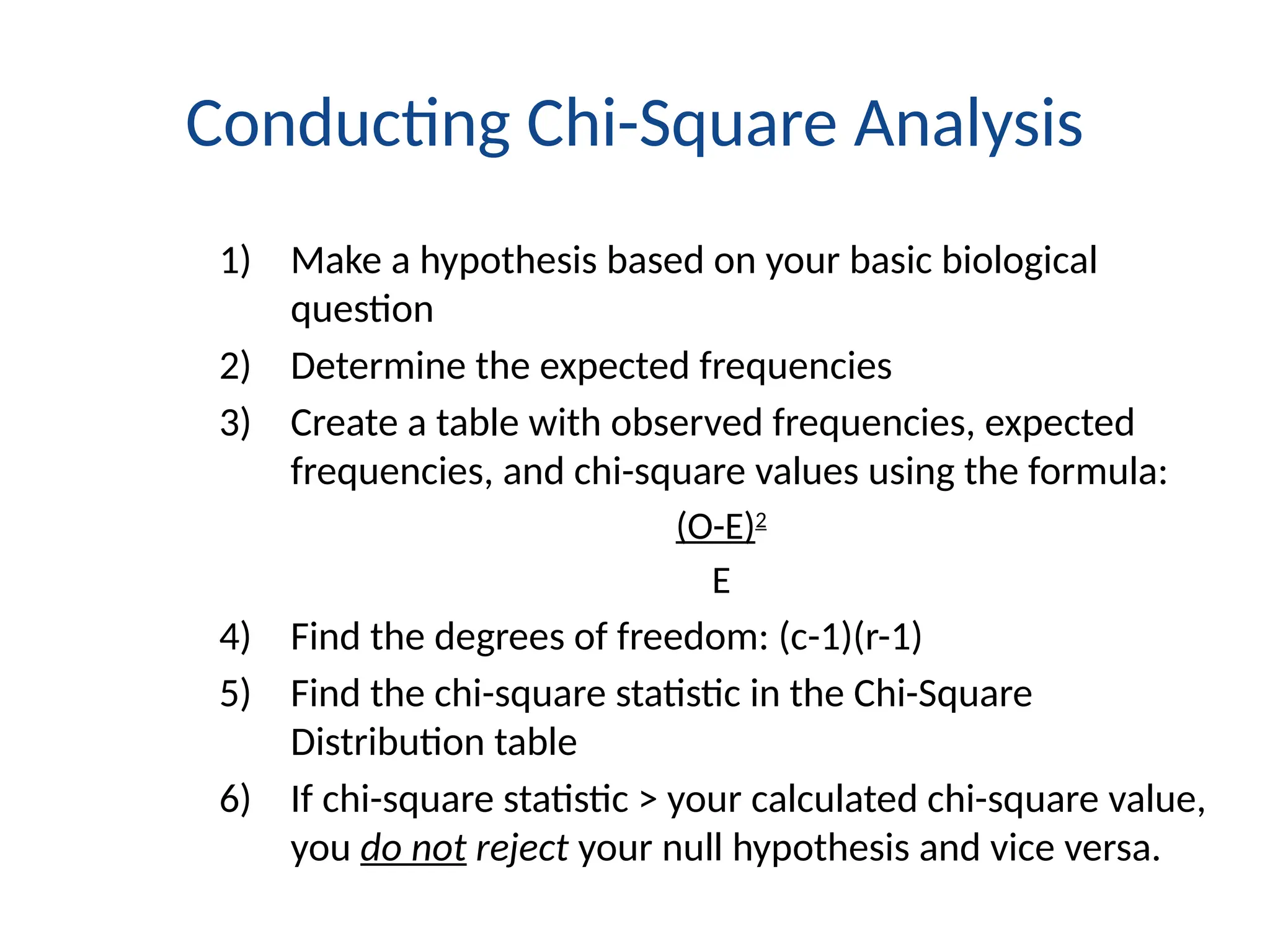
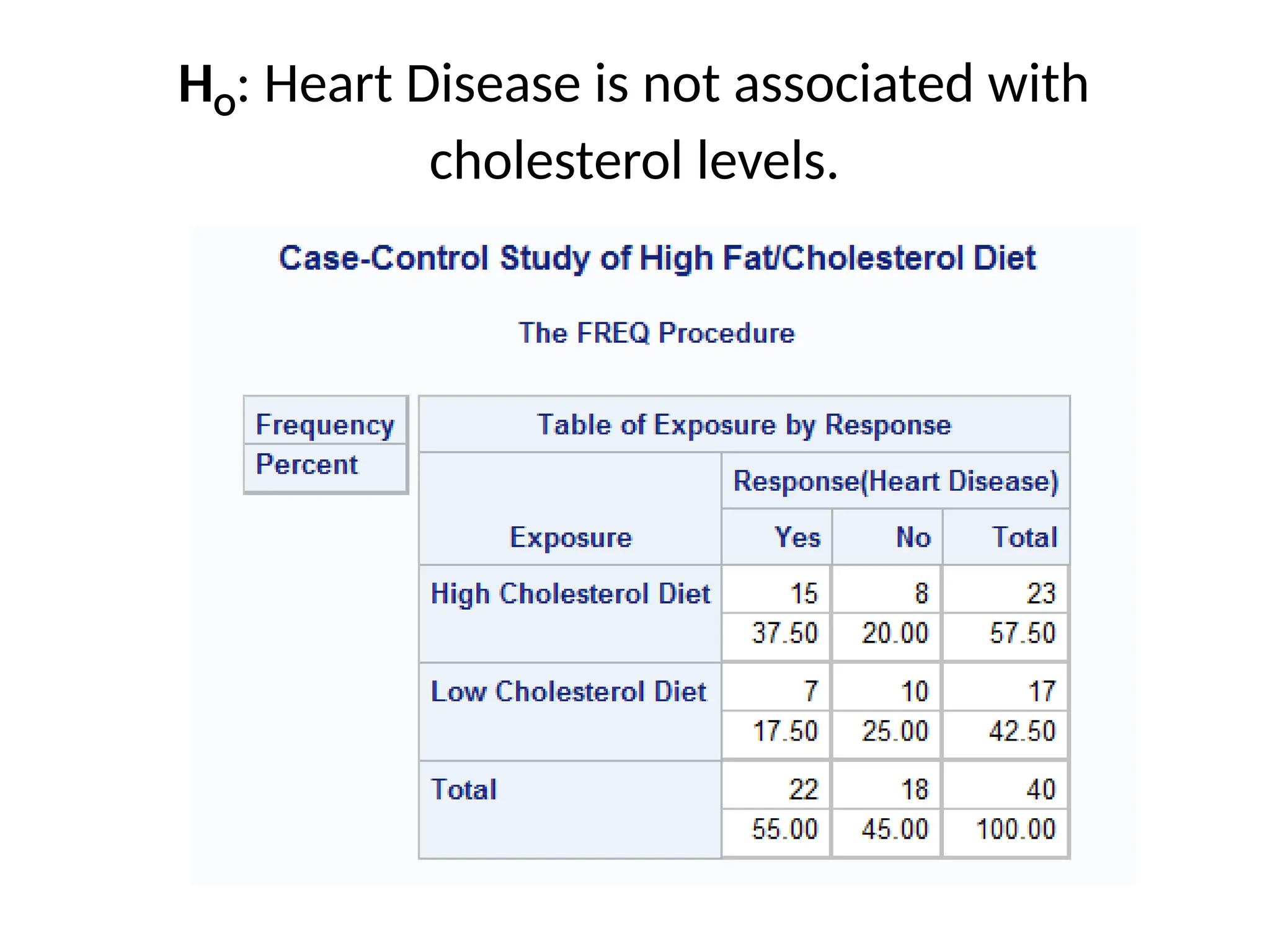
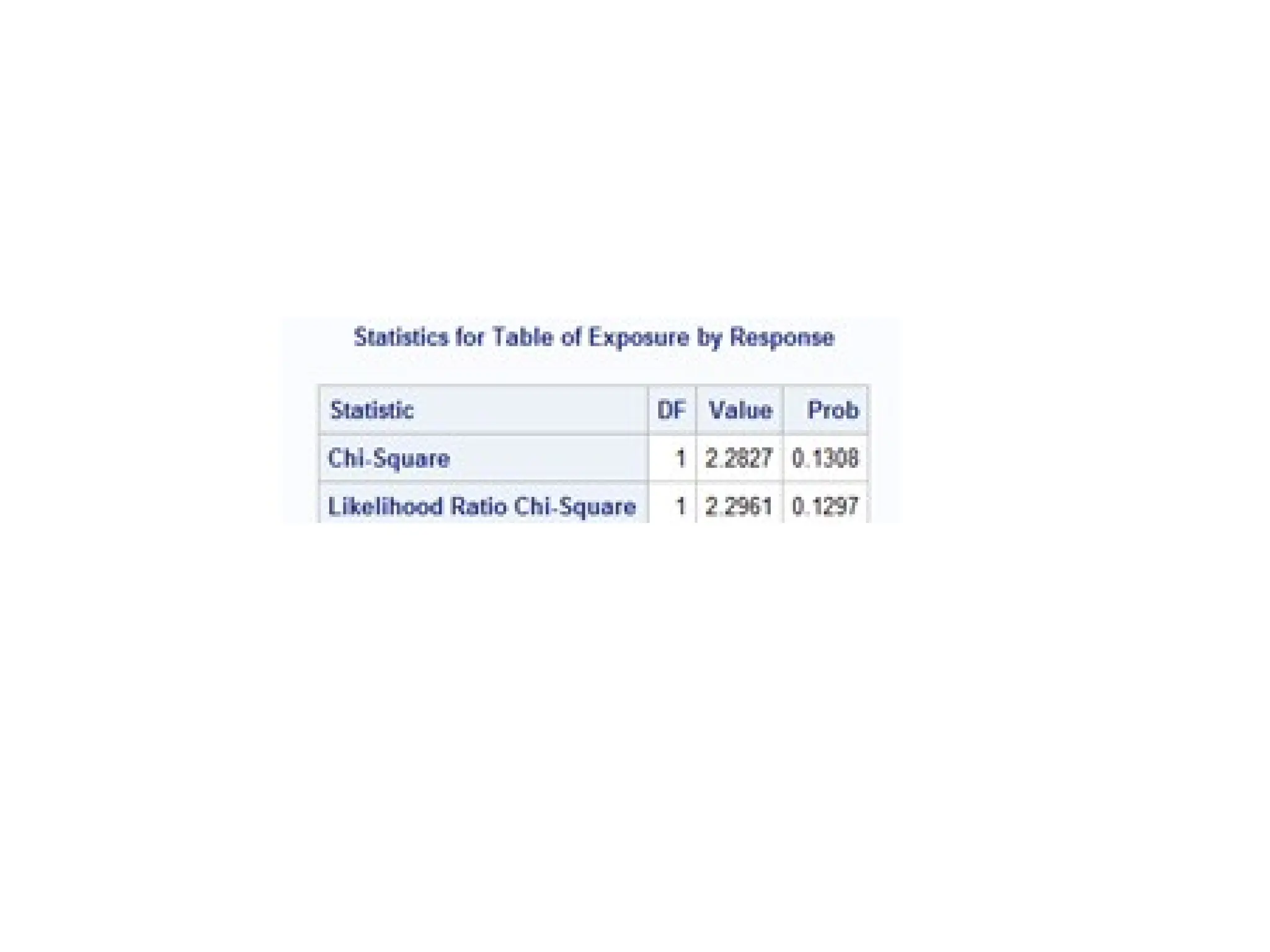
This document outlines various research methods in management, focusing on data collection techniques such as primary and secondary observation, interviews, questionnaires, and projective techniques. It emphasizes the complexity of questionnaire design, highlighting the importance of clear question phrasing, sequencing, and cultural considerations in international contexts. Additionally, the document discusses data analysis procedures, hypothesis testing, and formatting for report preparation.