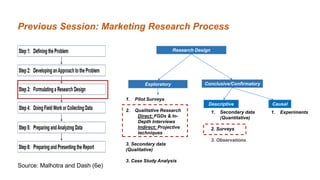
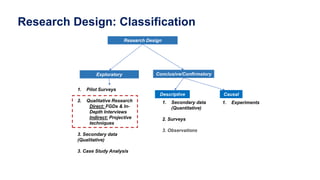
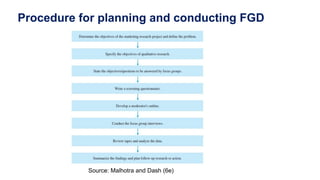
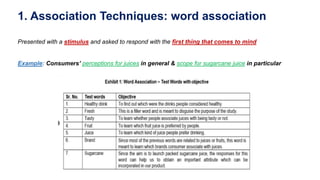
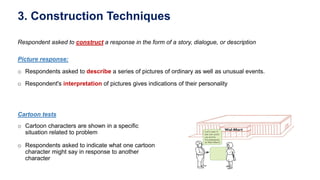
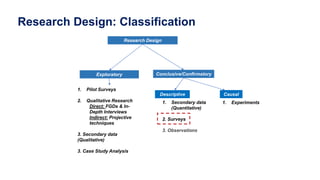
This document discusses qualitative marketing research methods. It begins by covering exploratory research design and then describes various qualitative research techniques in detail. These include focus group discussions, in-depth interviews, and projective techniques such as association techniques, completion techniques, construction techniques, and expressive techniques. For each technique, examples are provided of how they are conducted and the types of information they can provide for market research. The document aims to explain how qualitative methods can help understand consumers, generate new ideas, and interpret quantitative results.