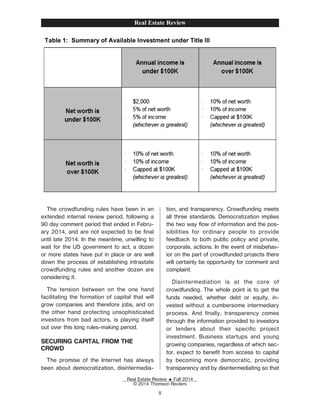
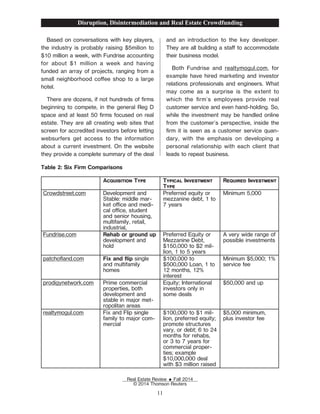
The document discusses the rise of crowdfunding and how it has disrupted and disintermediated traditional financial intermediaries. It describes how early crowdfunding platforms in the 2000s allowed people to donate or invest small amounts in projects and receive rewards. This led to the growth of major crowdfunding sites like Kickstarter and peer-to-peer lending platforms like LendingClub and Kiva. The document argues that crowdfunding has made it possible to access capital outside of traditional sources and will continue growing as a new funding mechanism, similar to how eBay and Amazon disrupted retail markets.