The document discusses refrigeration and air conditioning systems. It describes vapor compression and vapor absorption refrigeration cycles. It covers commonly used refrigerants such as R-12, R-22, ammonia, and their properties. It defines performance parameters for refrigeration systems such as coefficient of performance, tons of refrigeration, and energy efficiency ratio. It also describes domestic refrigerators, window air conditioners, and split air conditioners as examples of refrigeration and air conditioning equipment.
























![26
CHAPTER : Refrigeration and Air Conditioning
BASIC MECHANICAL ENGINEERING (3110006)
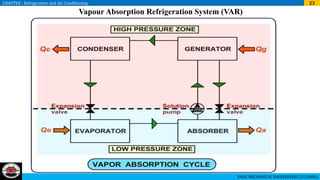
Working
• Low pressure and low temperature vapour ammonia coming from evaporator enters in
the absorber where ammonia is absorbed by weak solution coming from generator
through throttle valve.
• Due to absorption of NH3 in water, solution becomes strong. [In the mixture of NH3 and
water, if amount of NH3 is less than water is called weak solution and if amount of NH3
is more than the water is called strong solution.]
• During absorption process heat is released and rejected to cooling water.
• The strong solution from absorber is pumped into generator, where it is heated and NH3
vapour separated from solution.
• In generator is supplied from external source. The weak solution at point 4 is flowing
back to absorber through throttle valve.
• Again weak solution in absorber absorbs NH3 vapour coming from evaporator.
• NH3 vapour coming from generator passes through condenser and condensed in
condenser and reject heat to cooling medium. Then liquid NH3 throttled through
expansion device and it enters](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/refrigeration-air-conditioning-240118120549-030d8777/85/refrigeration-air-conditioning-training-ppt-26-320.jpg)









