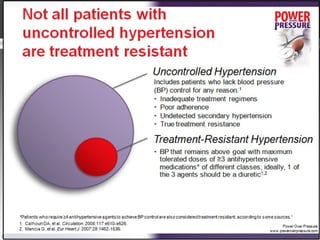
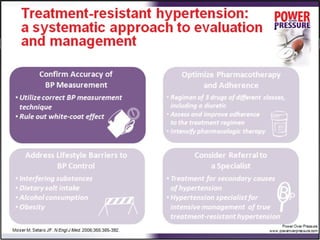
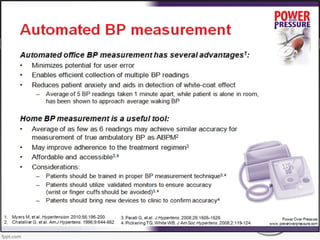
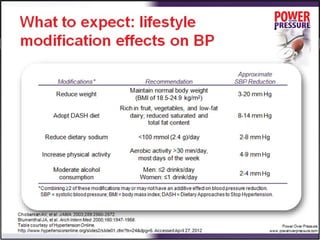
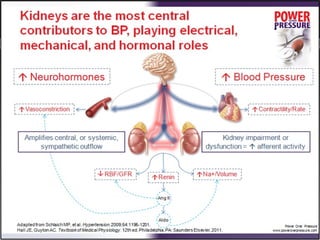
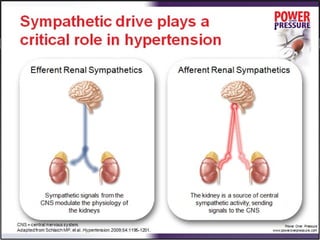
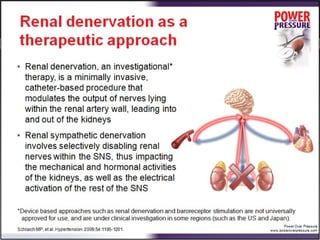
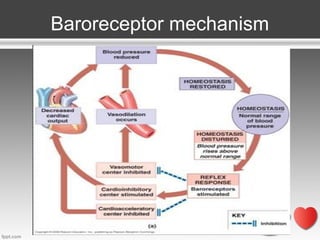
Resistant hypertension is defined as blood pressure that remains above goal despite treatment with three antihypertensive agents of different classes, one being a diuretic. Refractory hypertension is when blood pressure cannot be controlled despite four or more drugs at maximal doses. Pseudoresistant hypertension occurs when poor control is due to non-adherence or suboptimal treatment rather than true treatment resistance. Evaluation of patients with resistant hypertension includes screening for secondary causes like primary aldosteronism or renal artery stenosis through tests of electrolytes, renal function, and imaging studies. Treatment involves optimizing the current three-drug regimen before adding supplementary drugs like beta blockers or aldosterone antagonists.