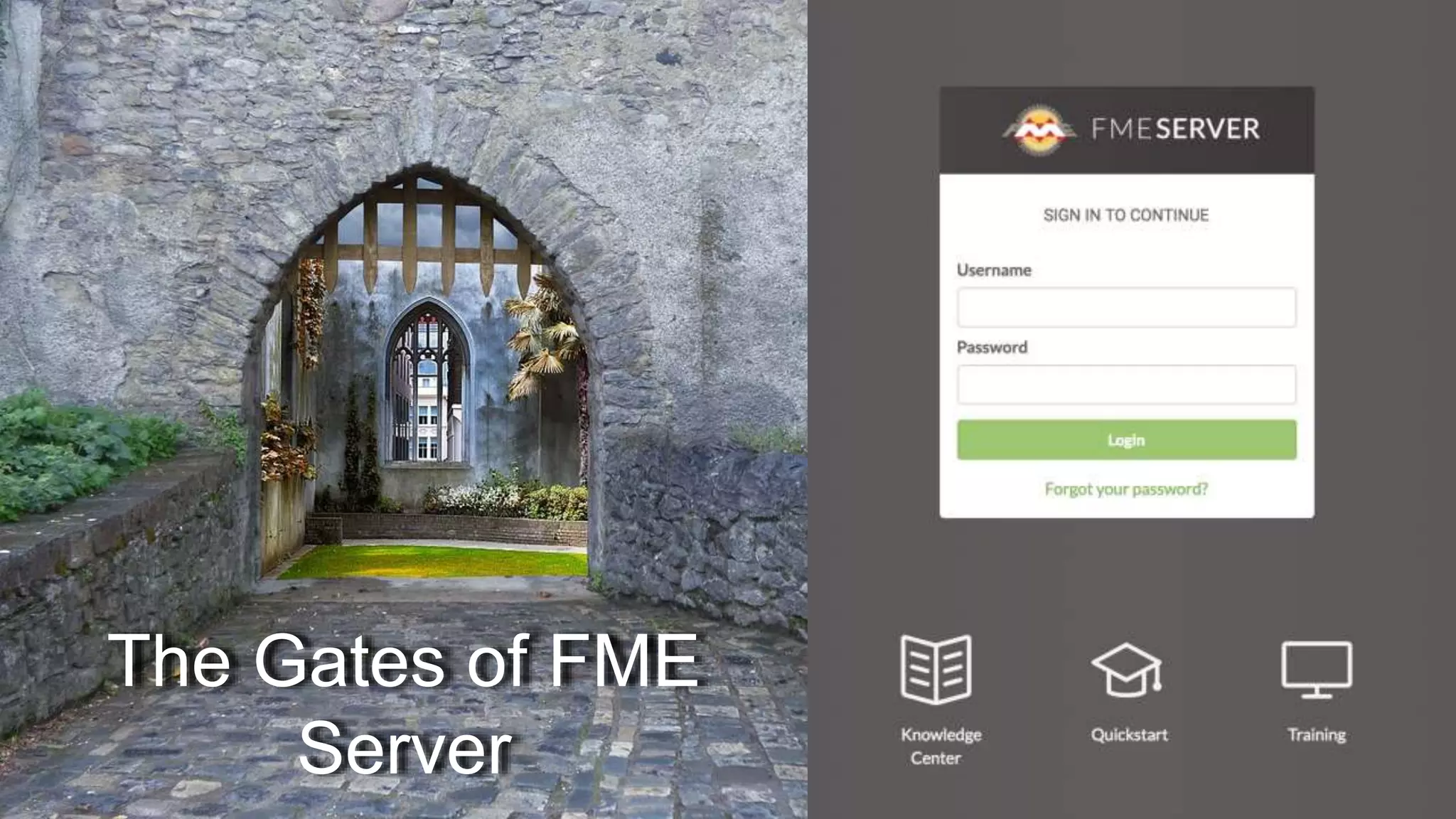
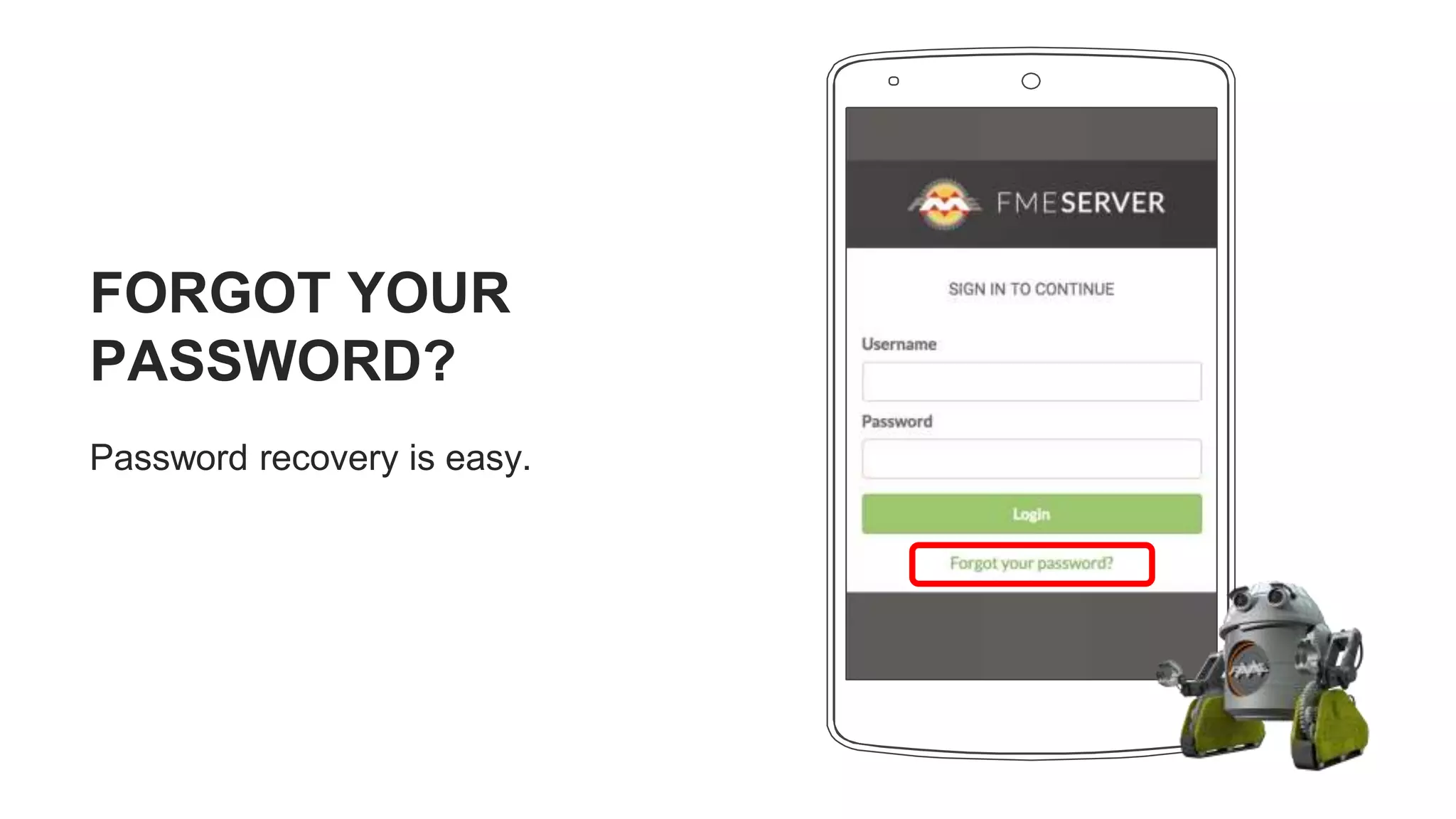
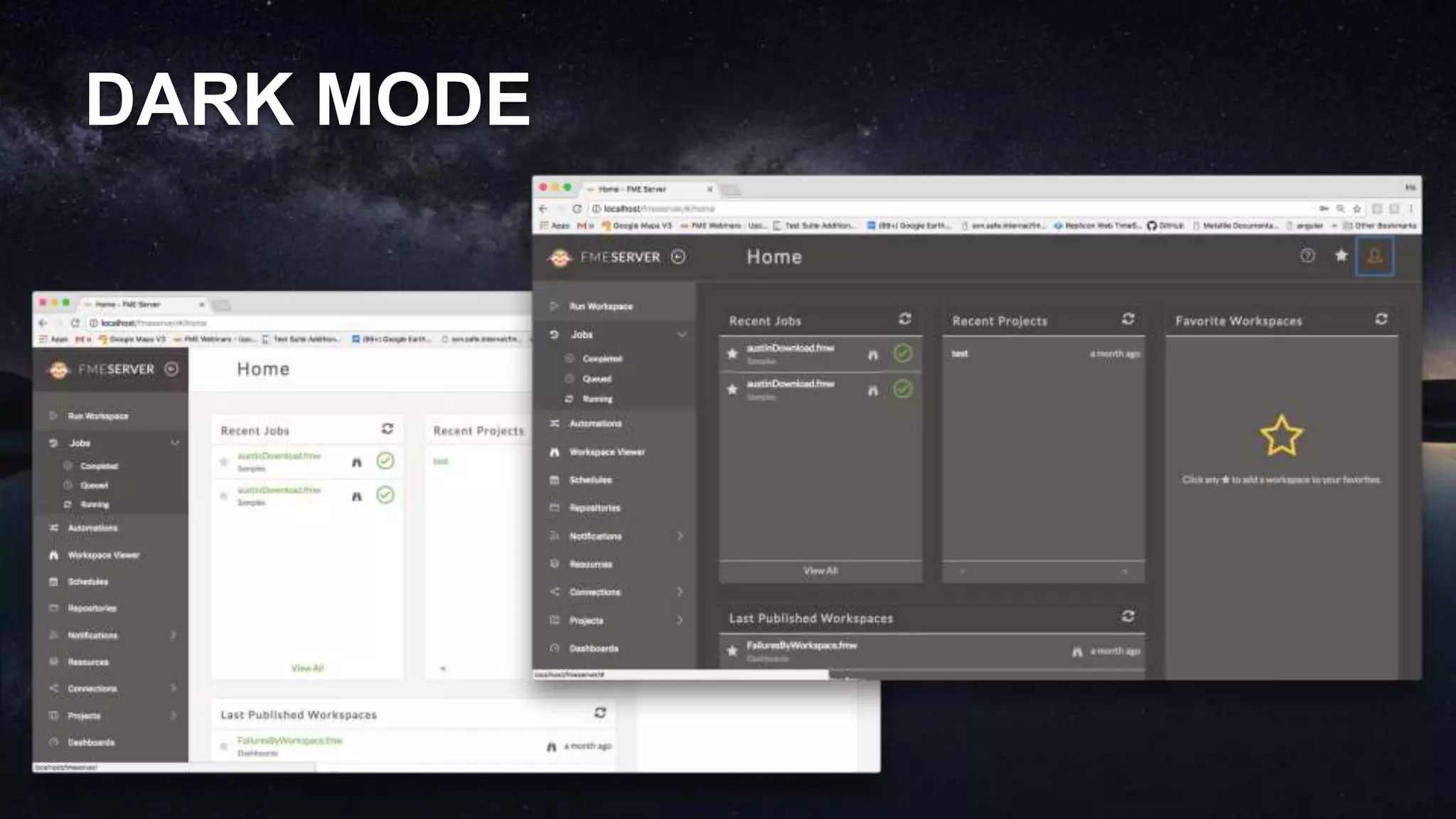
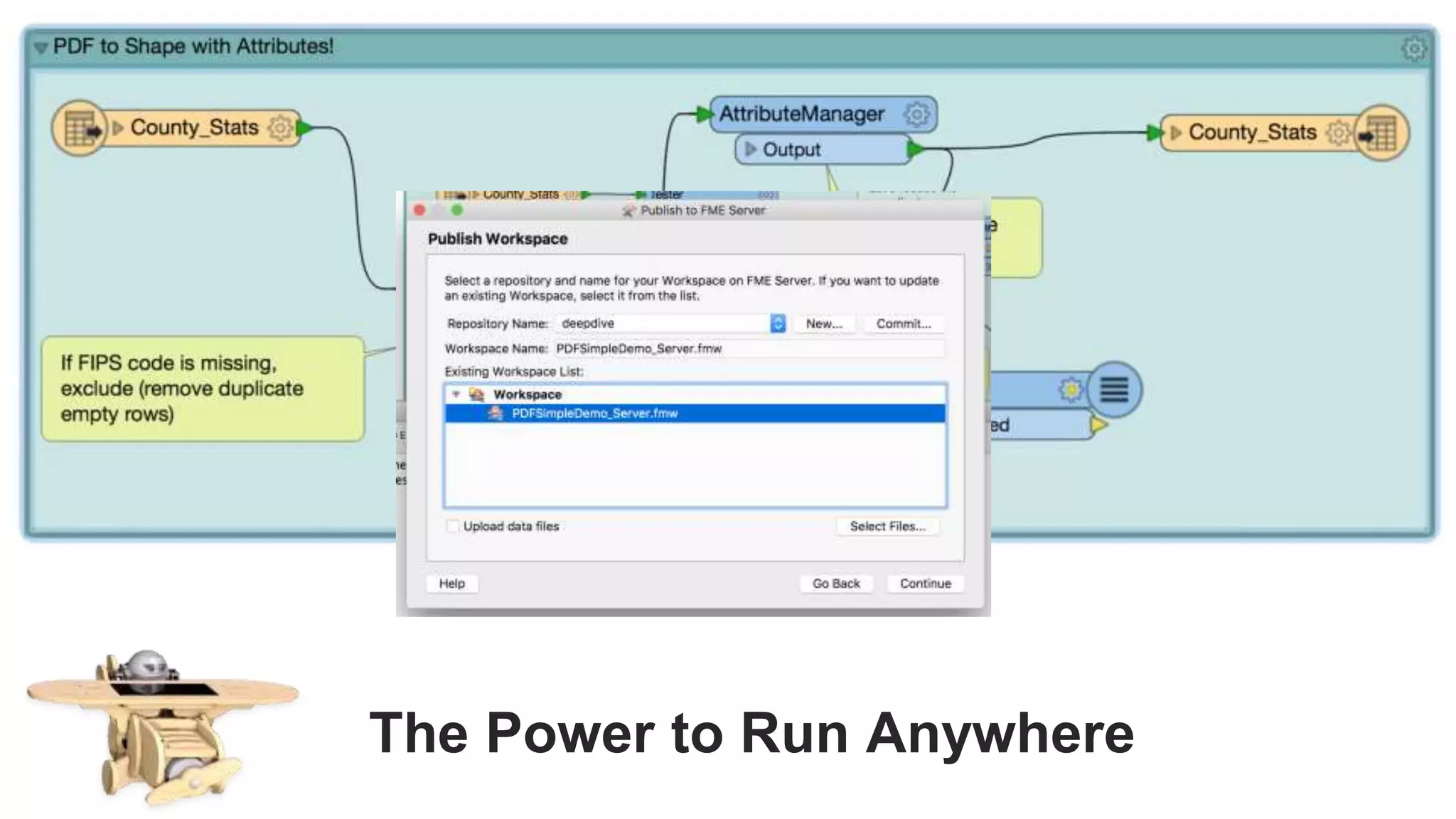
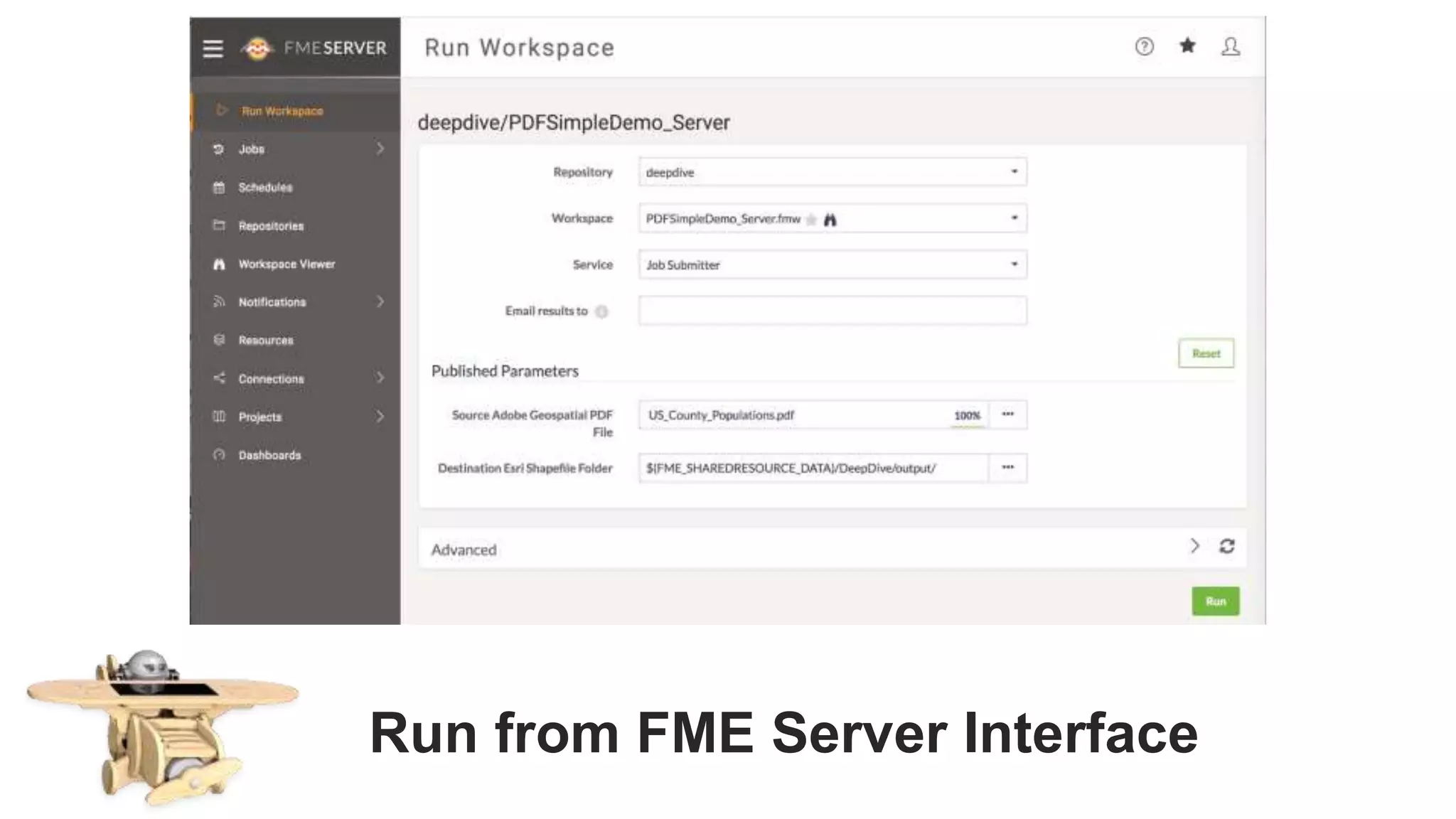
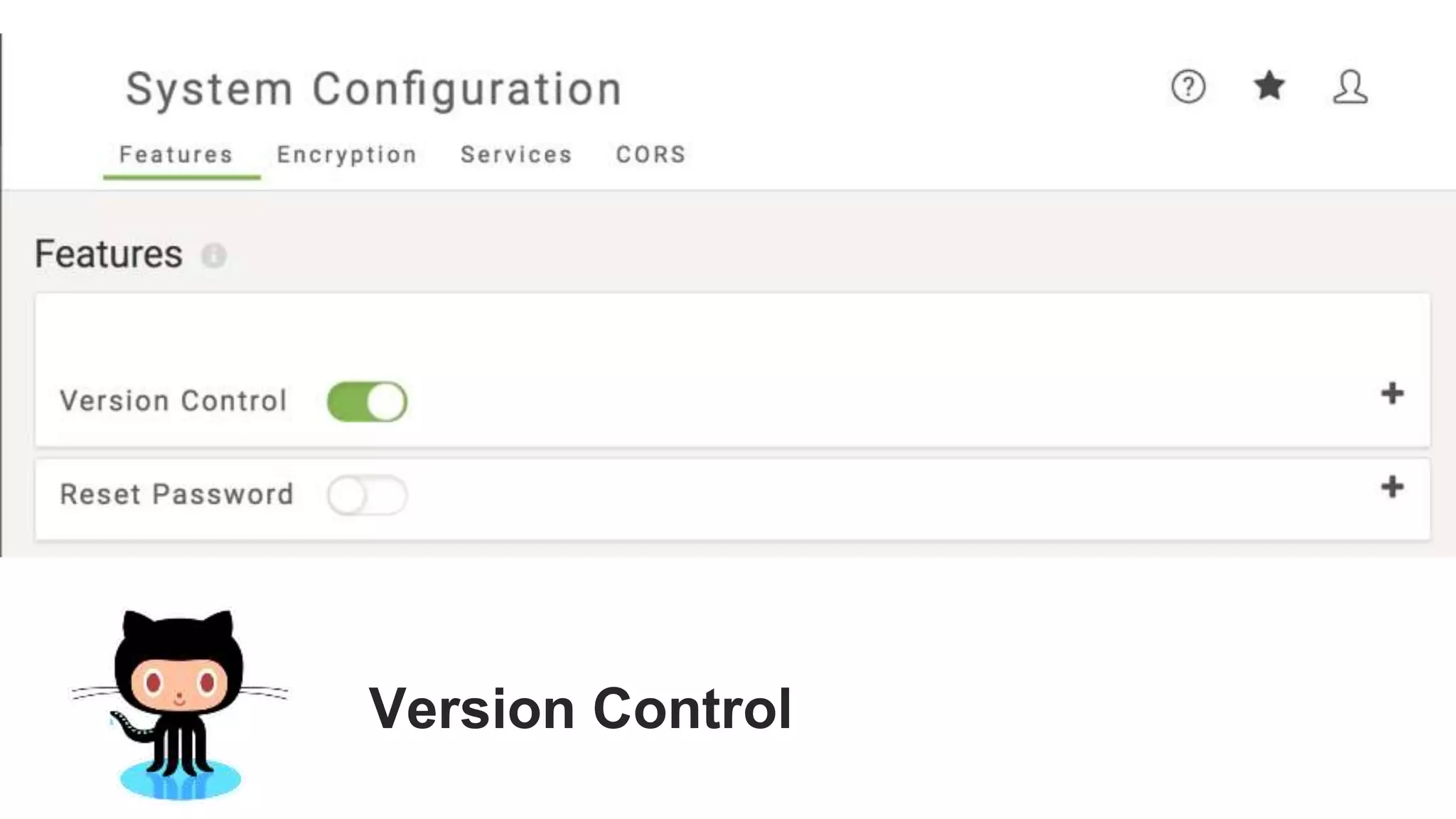
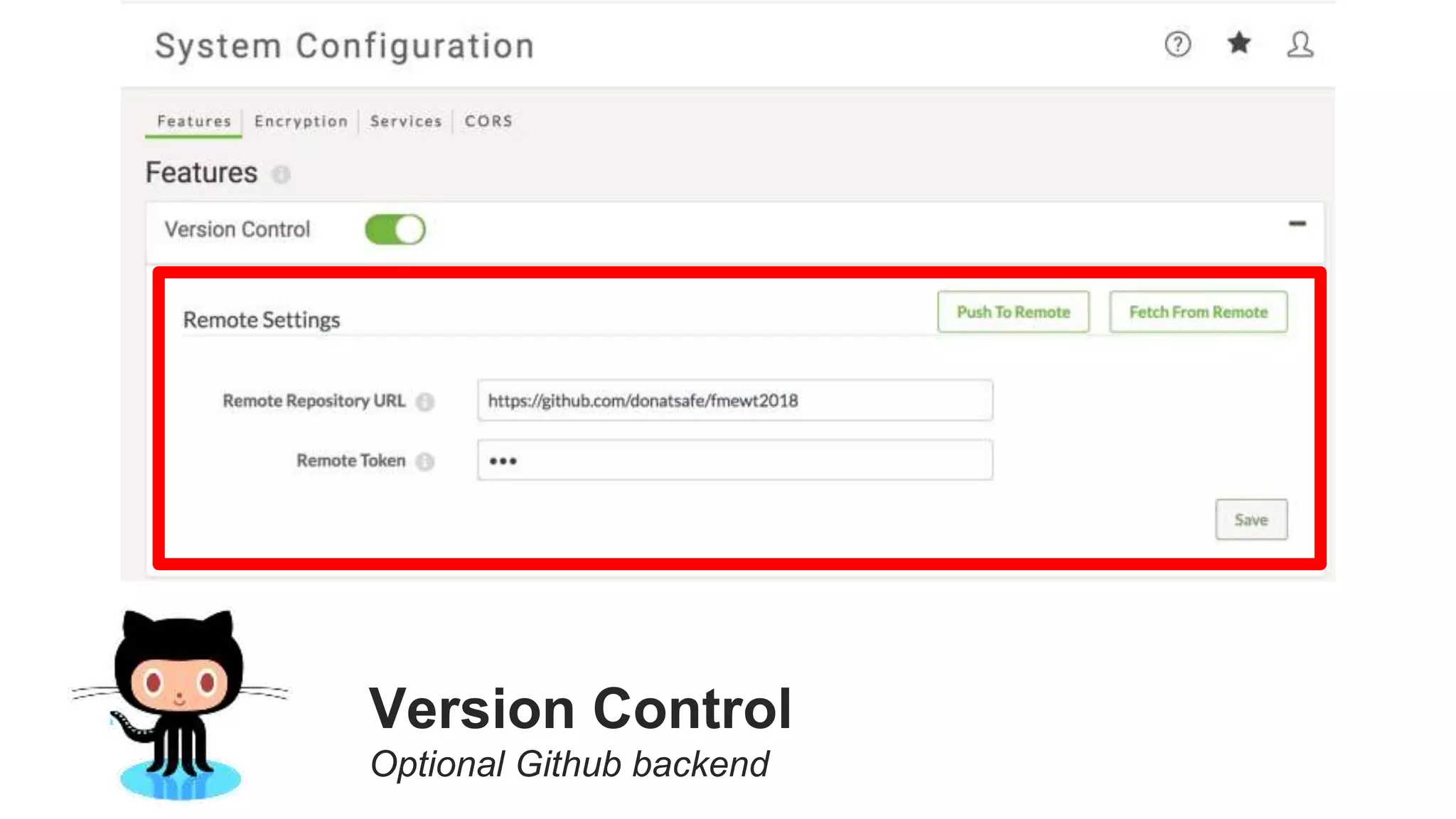
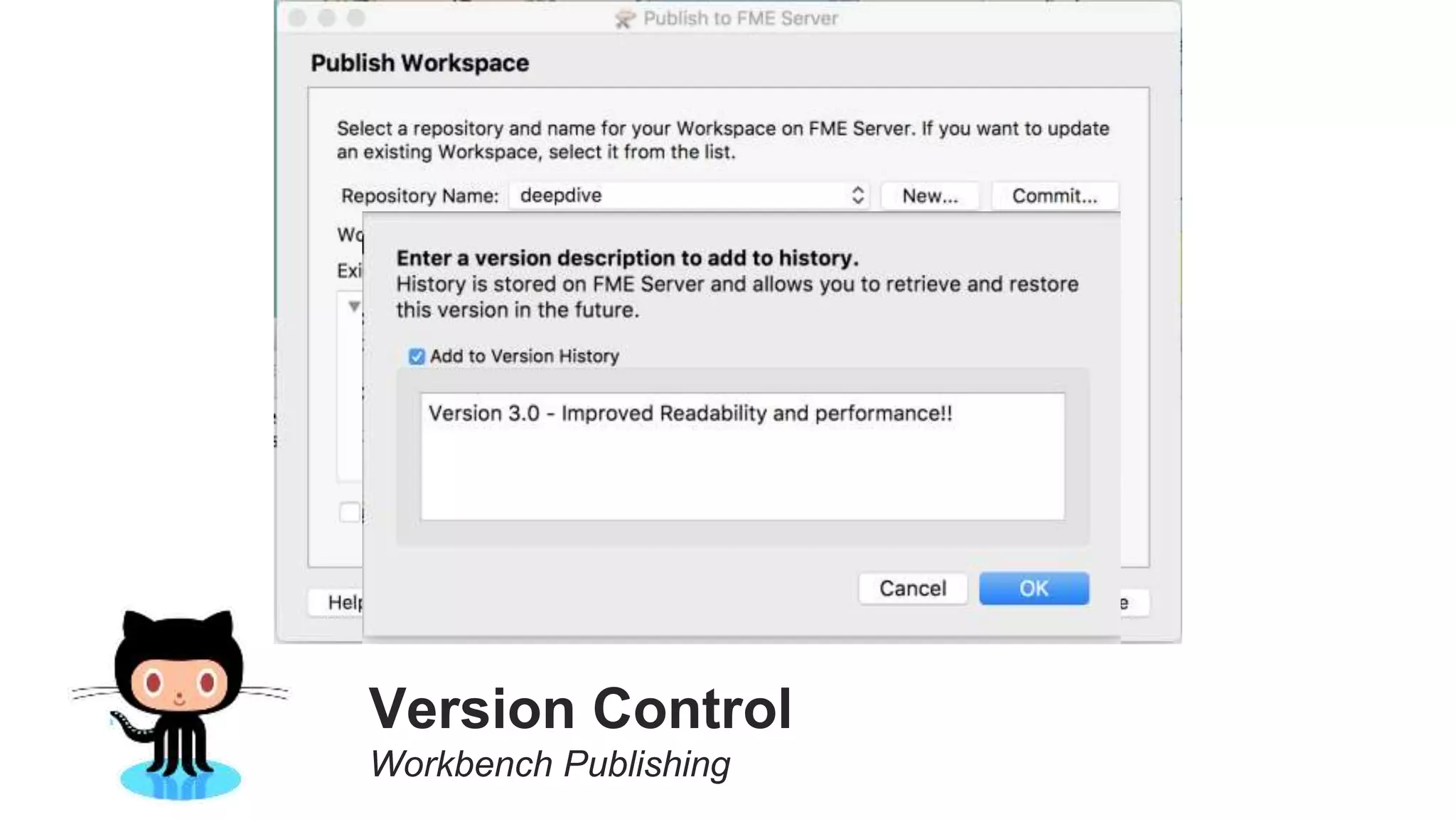
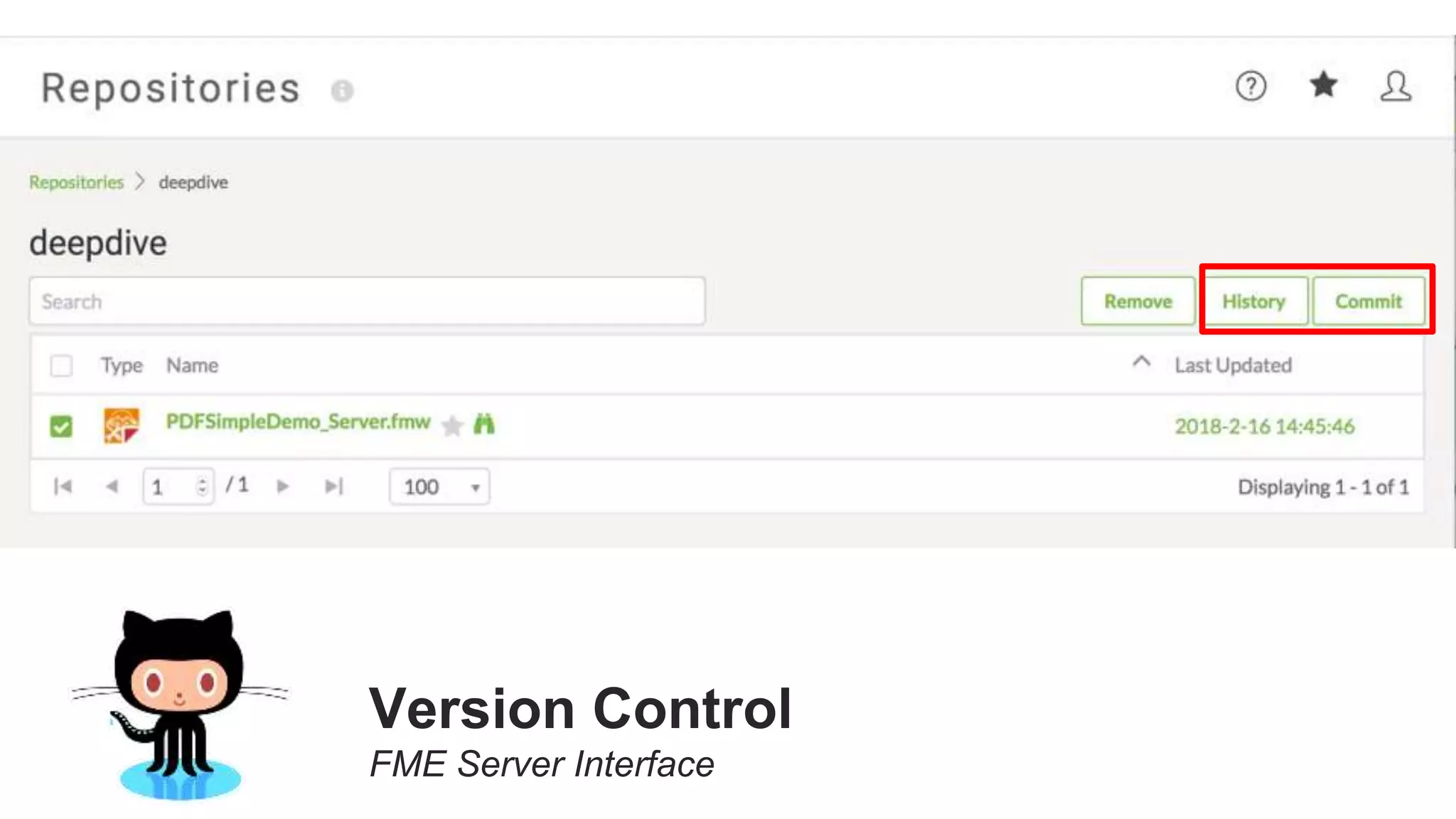
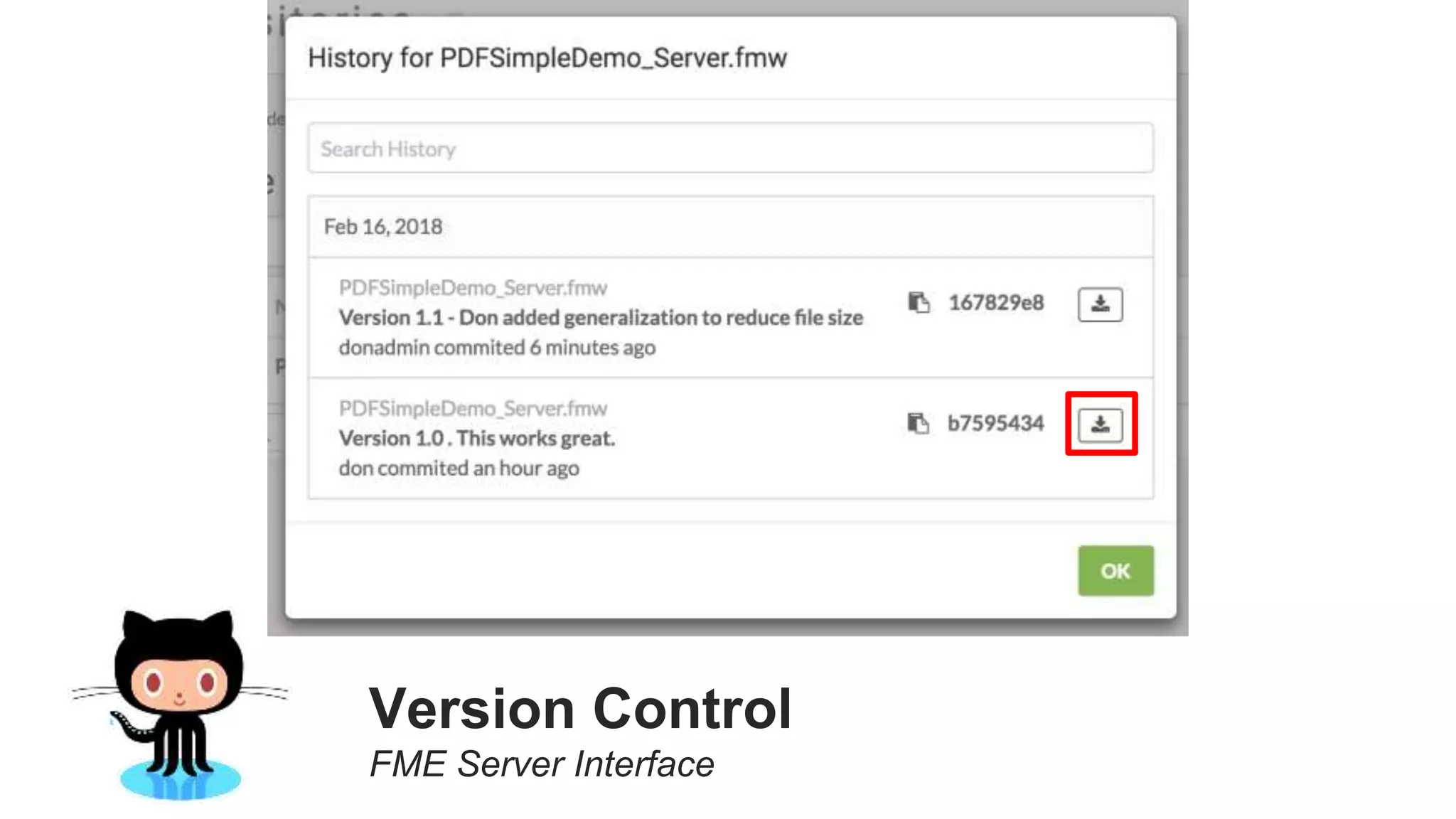
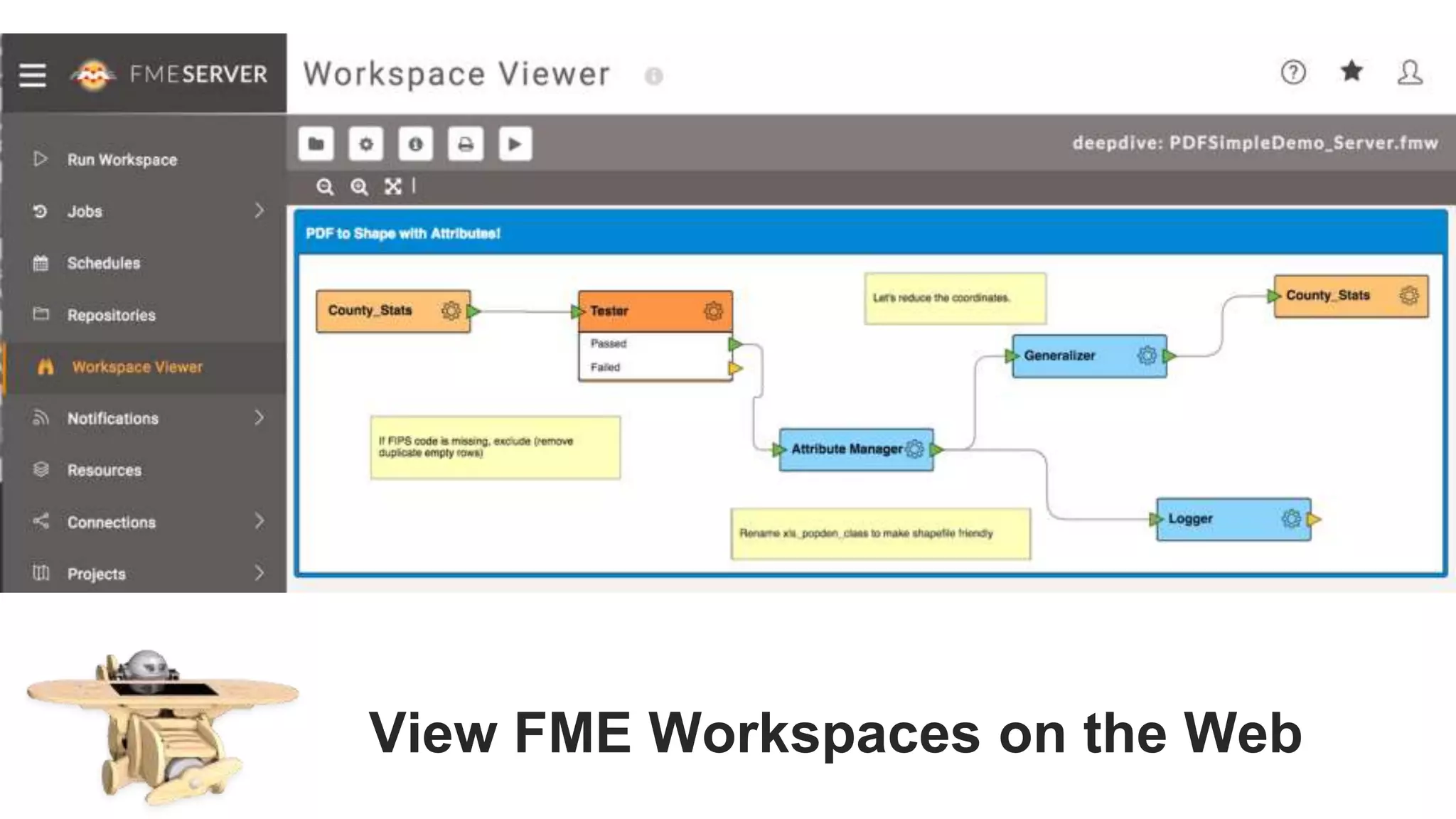
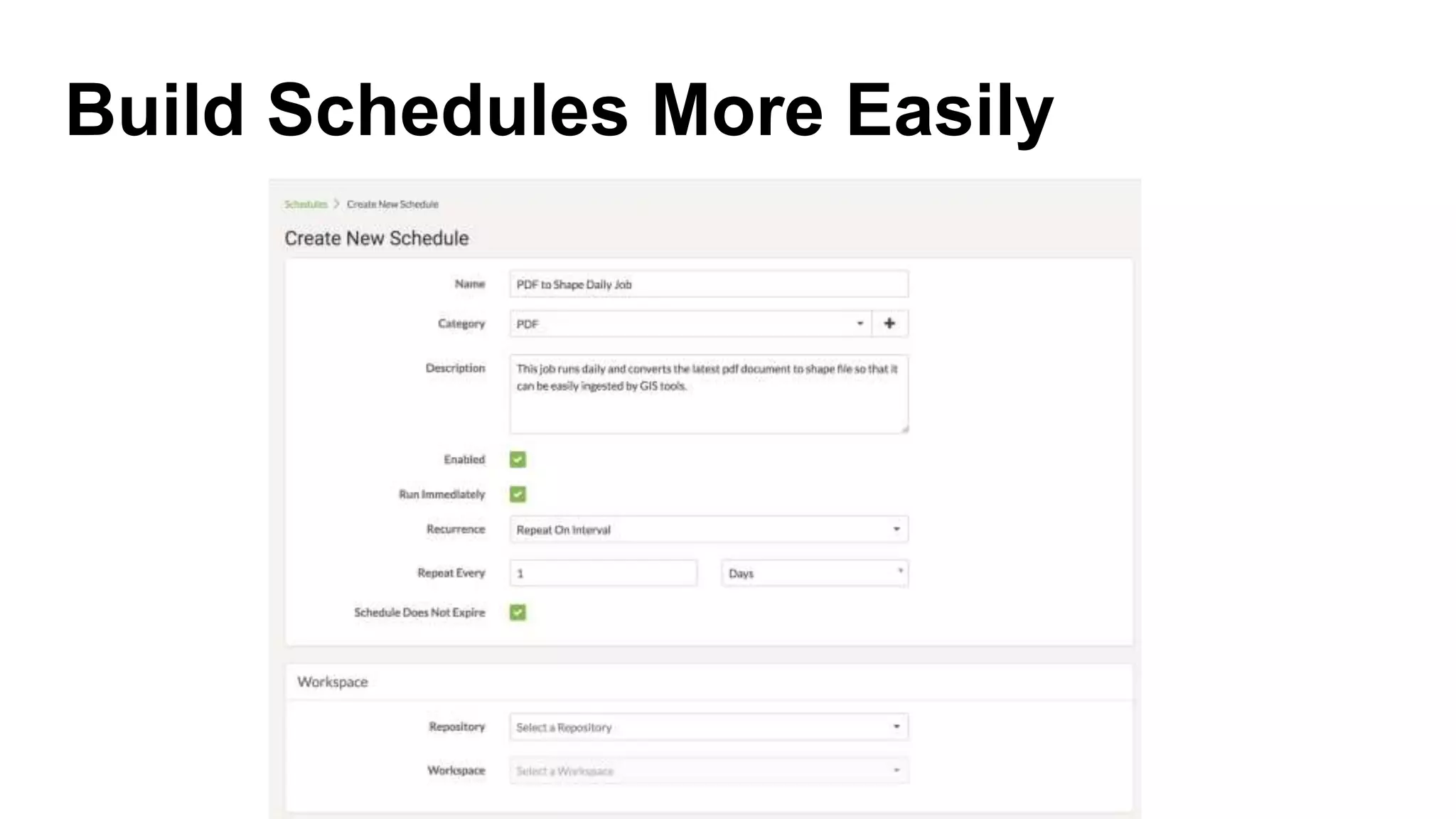
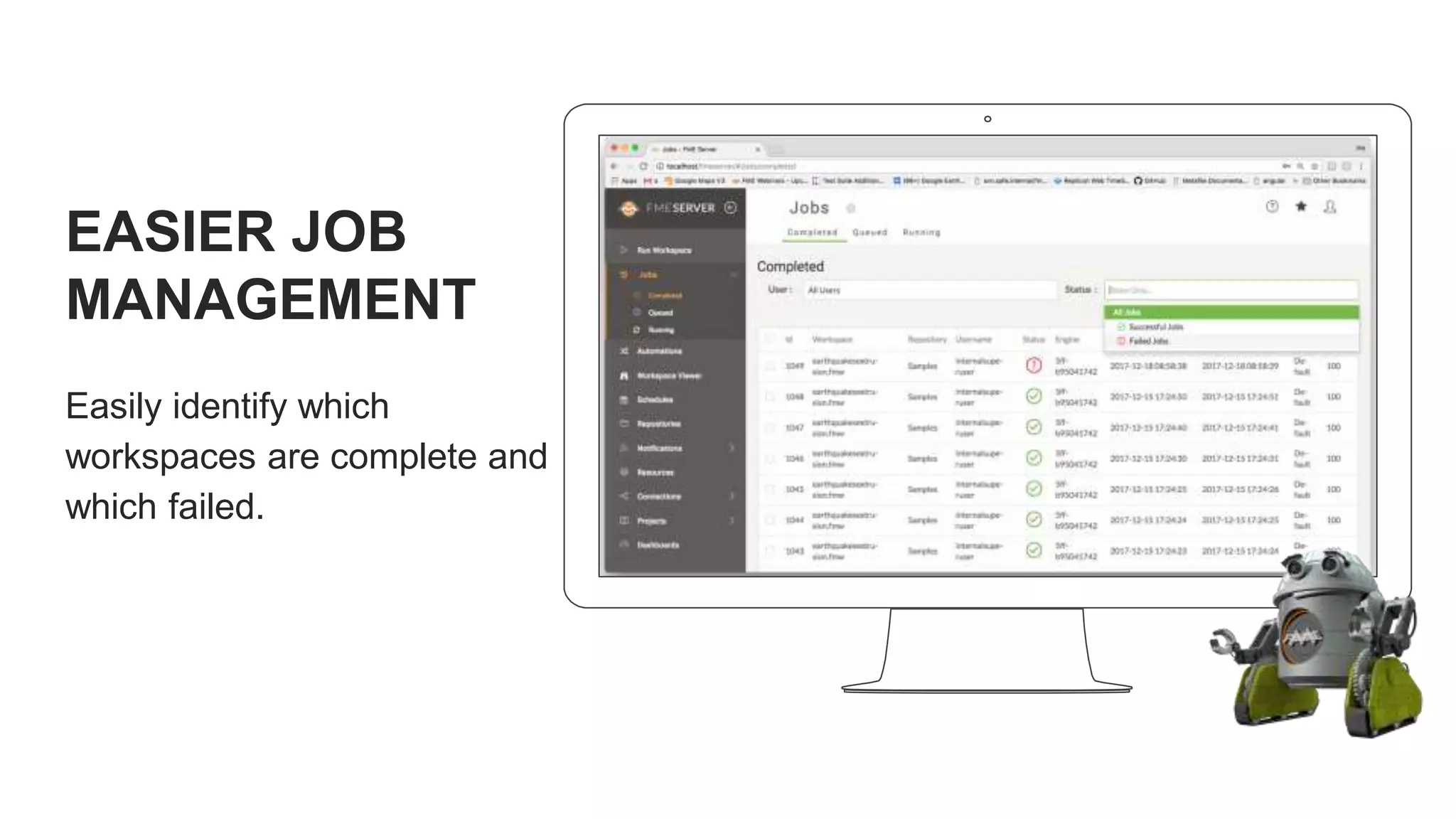
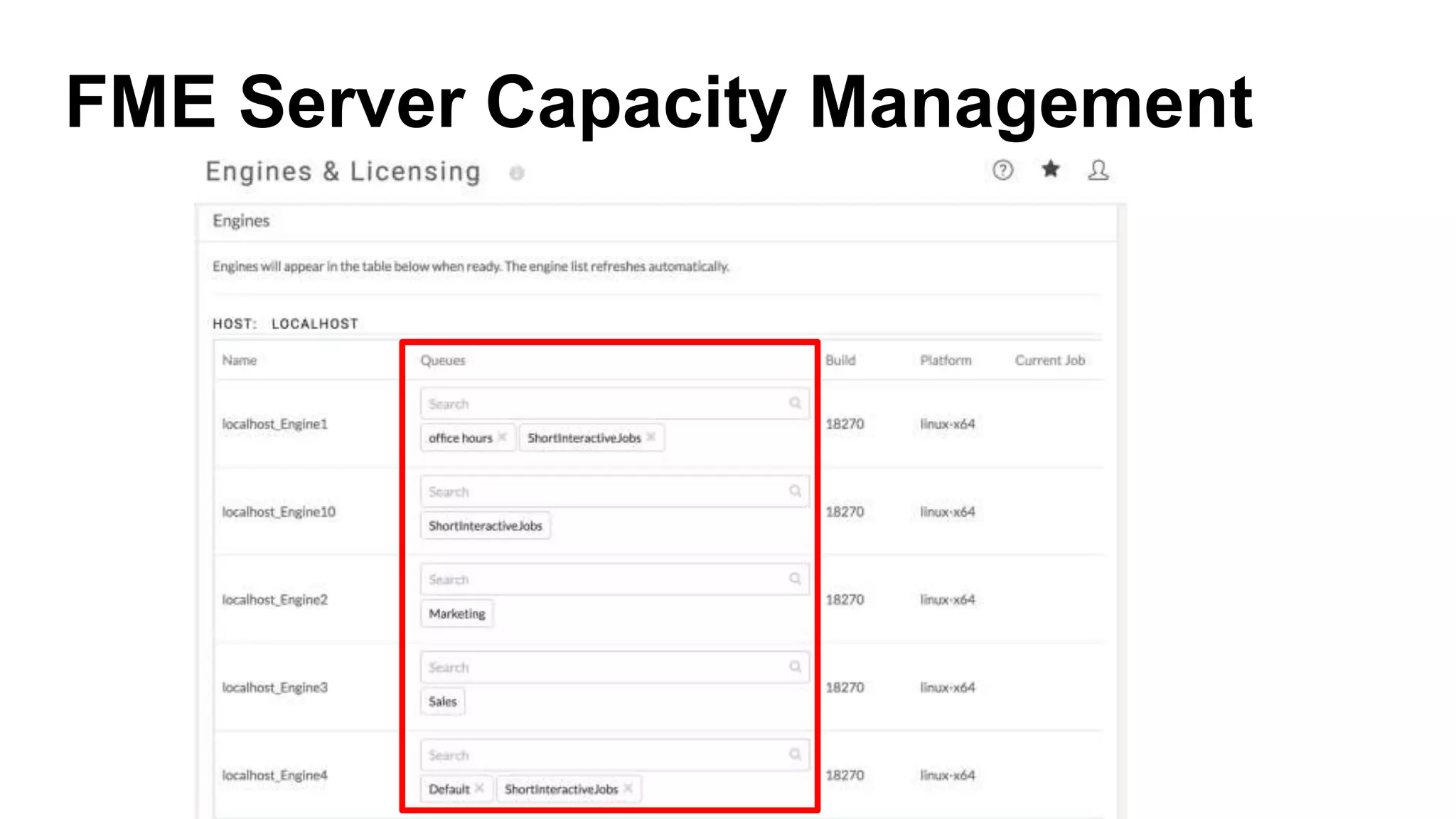
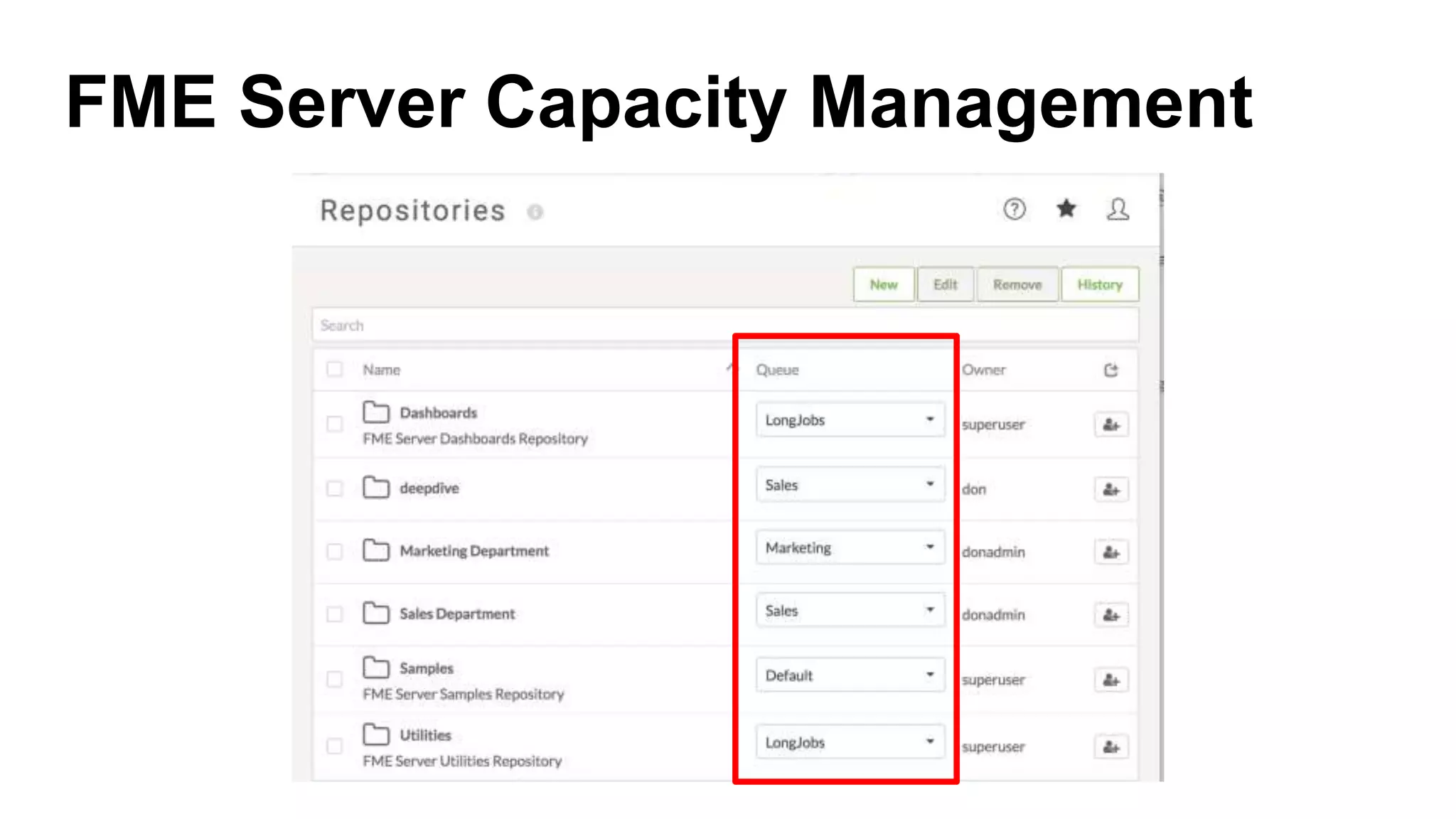
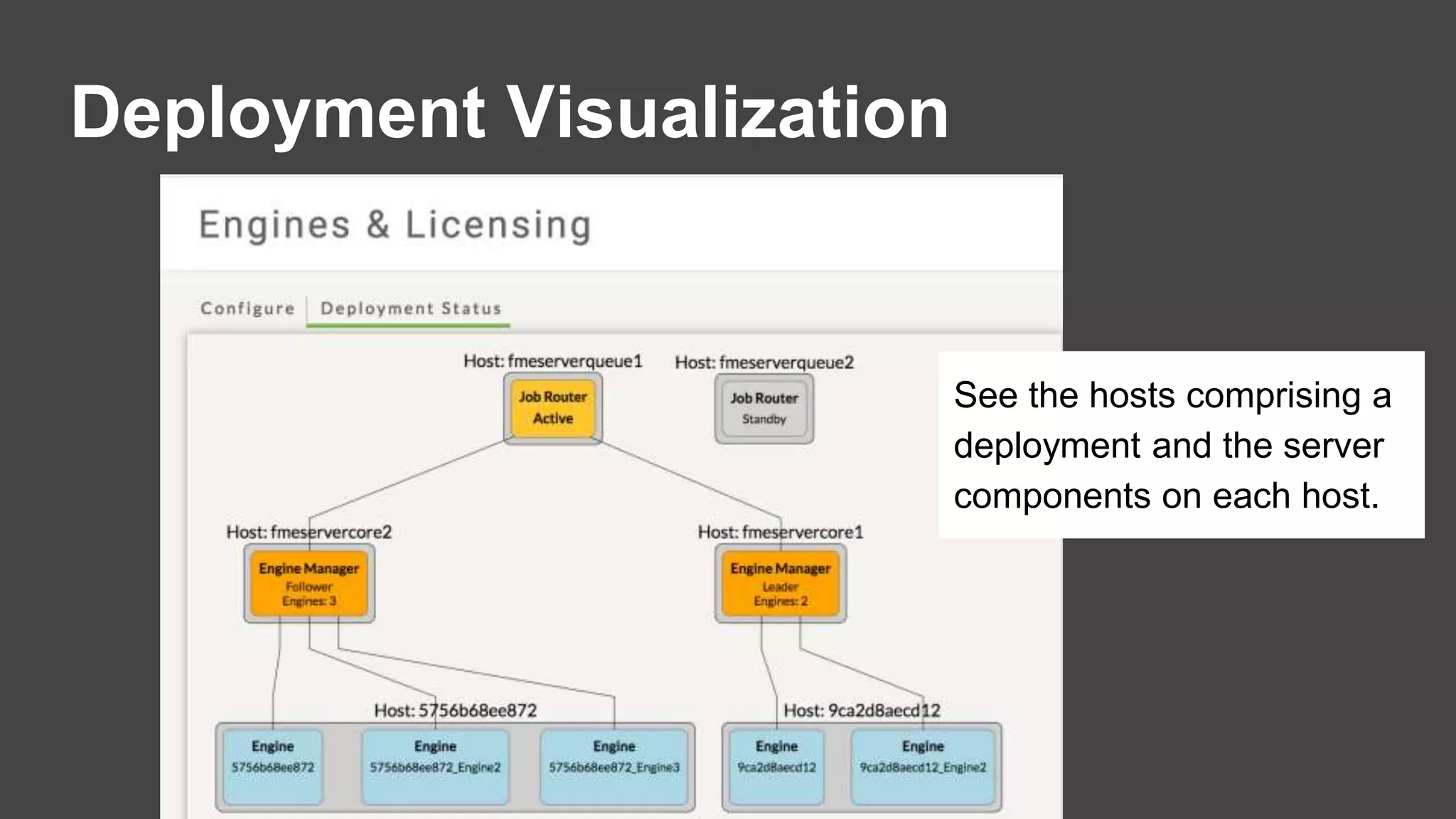
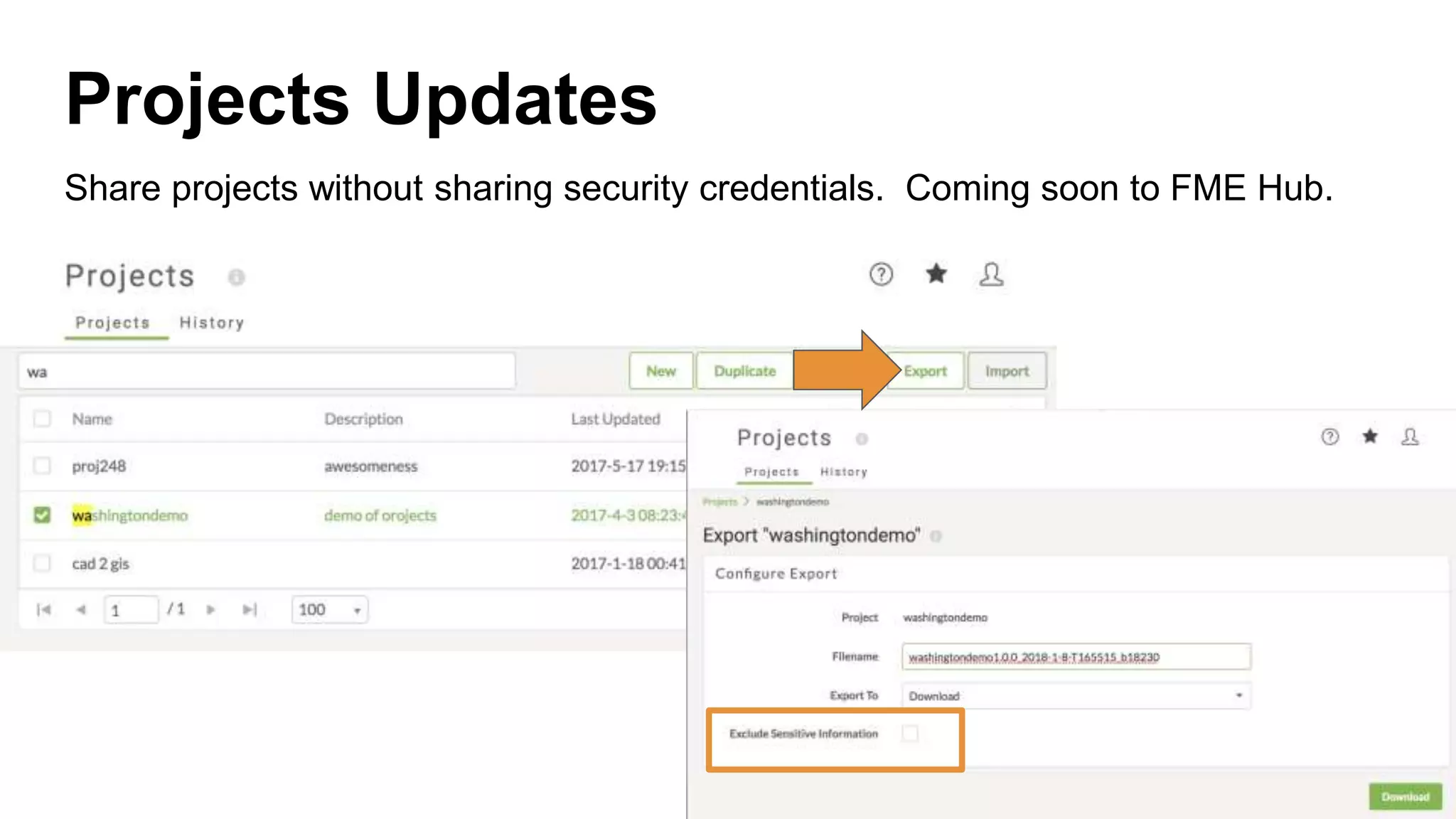
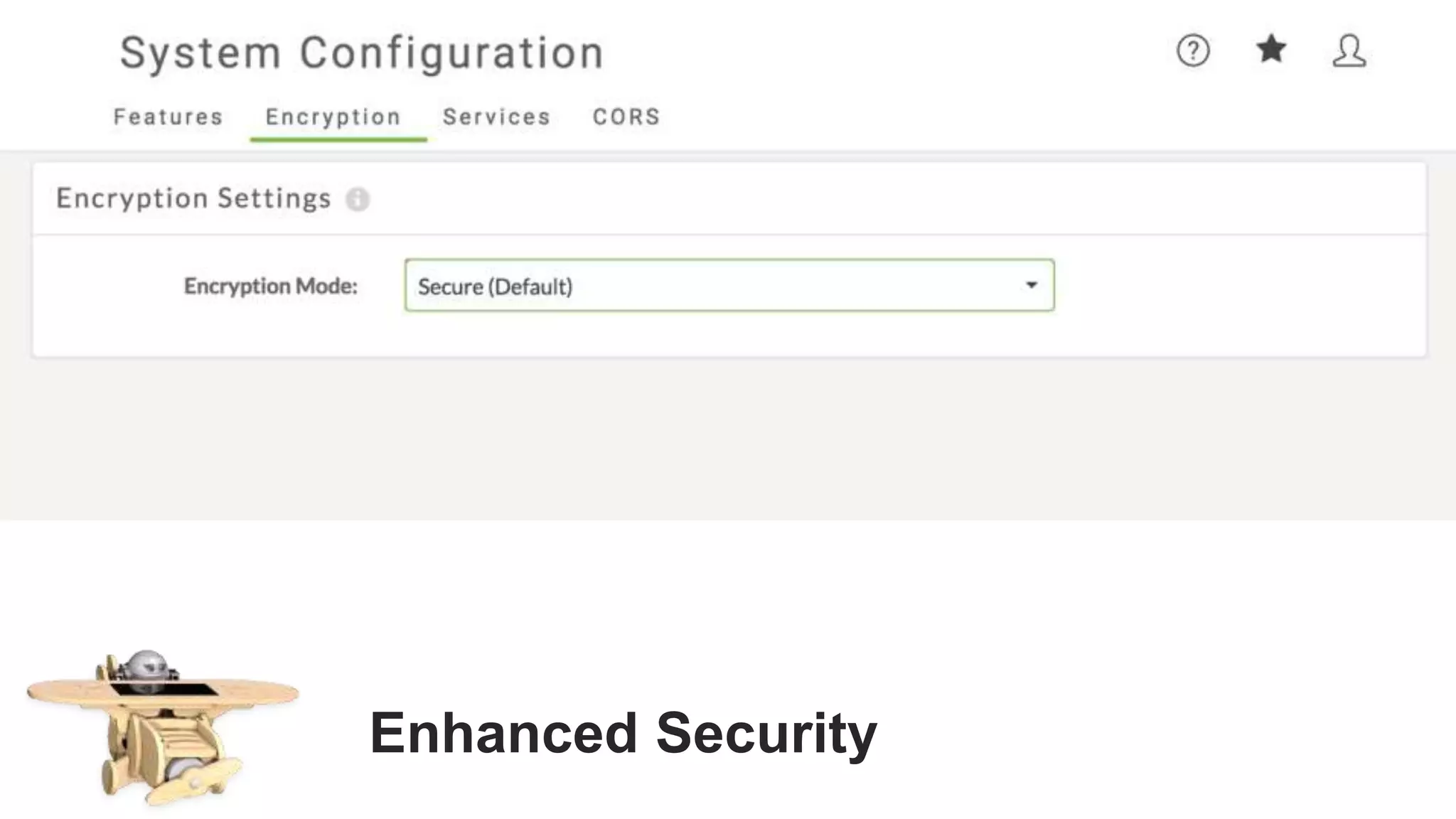
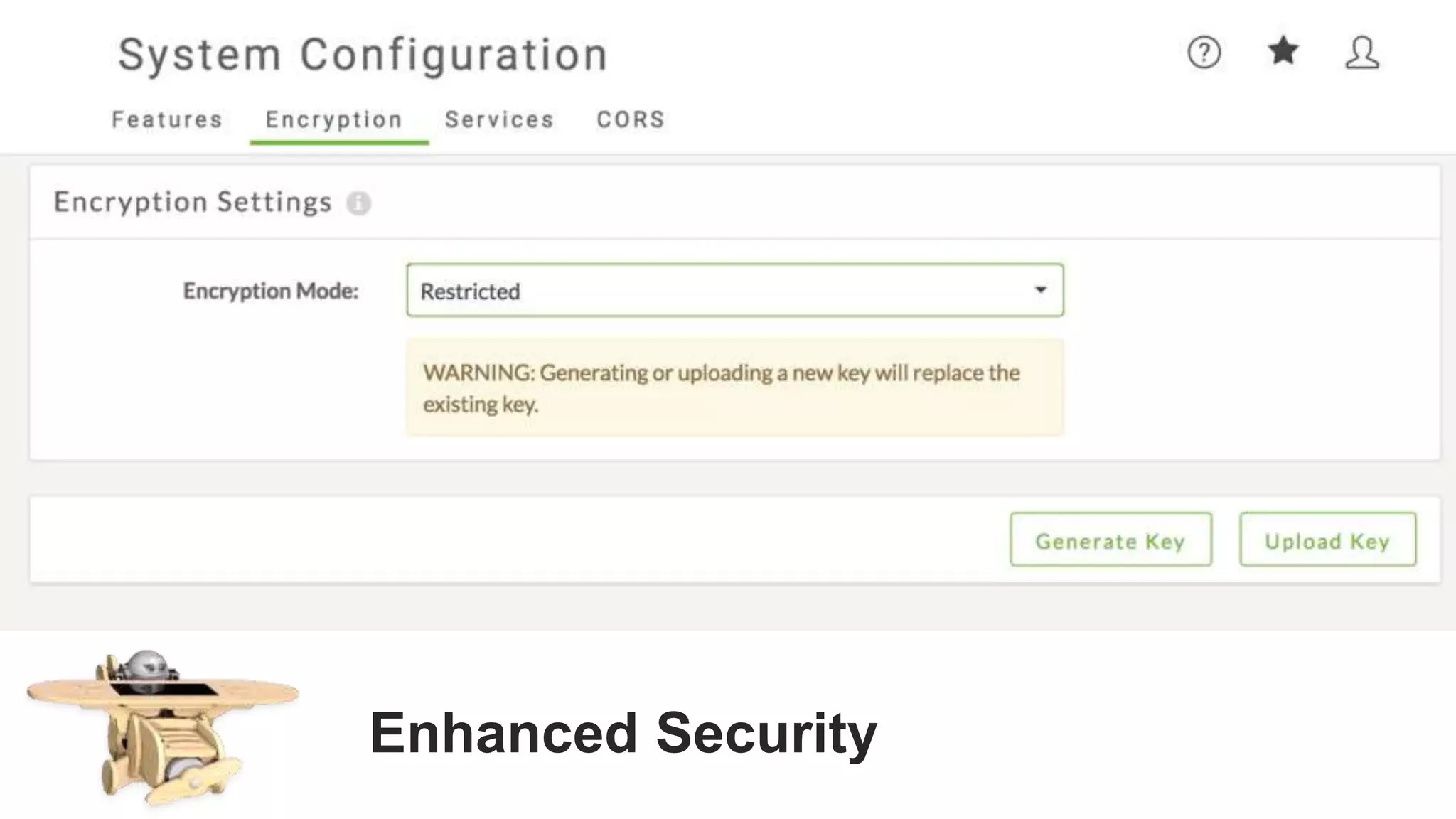
The document outlines the features and agenda for the FME Server 2018, highlighting demos and new functionalities like improved automation, version control, and enhanced security. It emphasizes ease of use with a guided tour and improved job management capabilities. The release also introduces Docker support for easier deployment and sets the stage for future enhancements.