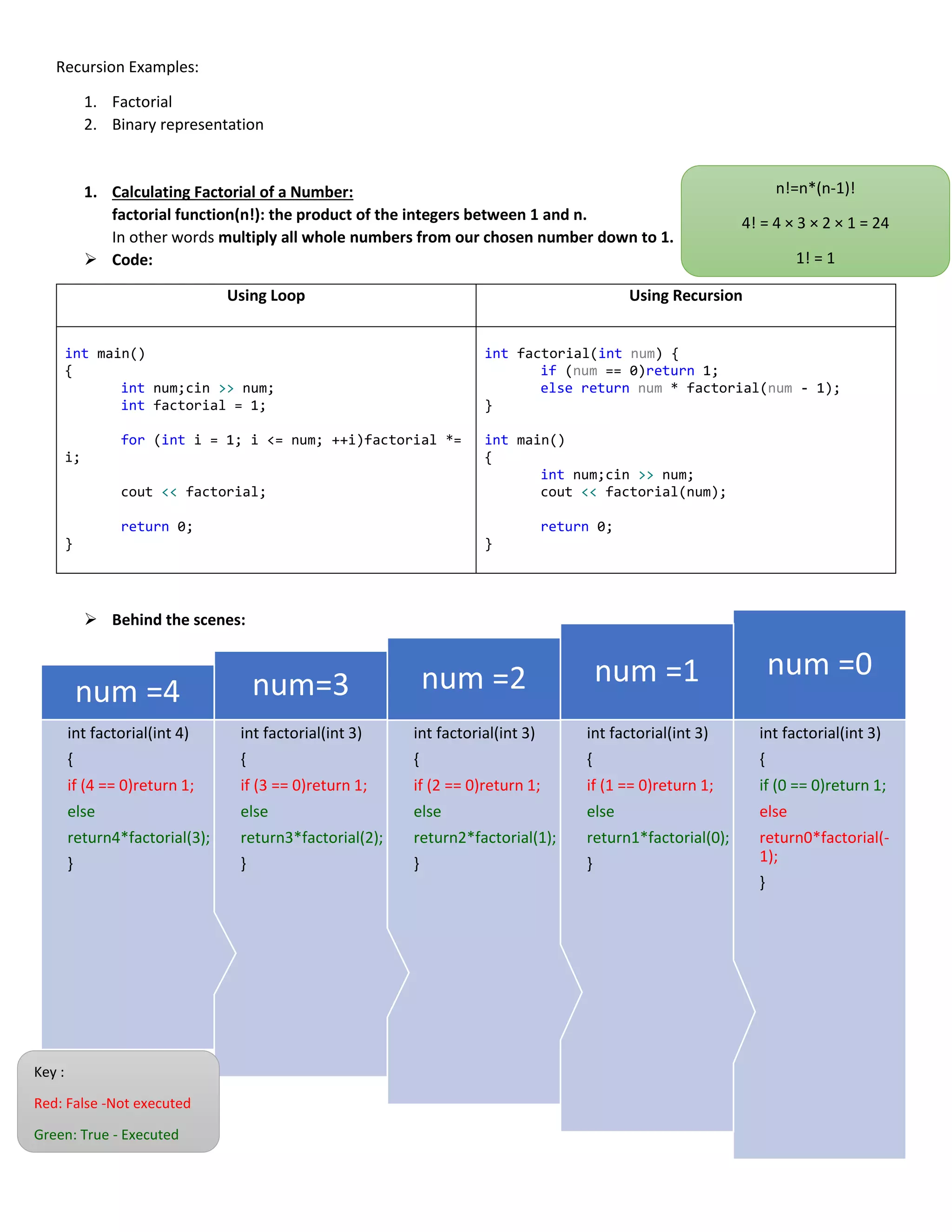
This document provides examples of using recursion to calculate factorial numbers and convert numbers to their binary representations. It explains that recursion involves defining a problem in terms of simpler versions of itself, with a base case that can be solved directly. For factorial, the base case is 0! = 1, and larger numbers are calculated as n! = n * (n-1)!. For binary conversion, the base case is when the number equals 1 (output 1), and larger numbers are converted by recursively processing the number divided by 2 and outputting the remainder.
![ Important Note:
when a function calls itself, a new copy of that function is run. The local variables in the second version are
independent of the local variables in the first, and they cannot affect one another directly.
➢ Steps:
1. Identify the basic cases (those in which the subprogram can solve the problem directly without recurring to
recursive calls) and determine how they are solved.
For example, in the case of factorial, the only basic case used in the function is n=0. Similarly, we could have
considered a more general basic case (e.g., n ≤ 1). In both cases, the function should return 1.
2. Determine how to resolve the non-basic cases in terms of the basic cases, which we assume we can already
solve.
In the case of a factorial, we know that the factorial of a number n greater than zero is n*factorial(n-1).
3. Make sure that the parameters of the call move closer to the basic cases at each recursive call. This should
guarantee a finite sequence of recursive calls that always terminates.
In the case of a factorial, n-1 is closer to 0 than n. Therefore, we can guarantee that this function terminates.
2. Writing Binary Representation of a Number:
➢ Code
Using Loop Using Recursion
int binary[32];
int main()
{
int num;cin >> num;
int i = 0;
for (; 0 < num; ++i) {
binary[i] = num % 2;
num /= 2;
}
for (int j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
cout << binary[j];
}
return 0;
}
void binary(int num)
{
if (num == 1) cout << 1;
else {
binary(num / 2);
cout << num % 2;
}
}
int main()
{
int num; cin >> num;
binary(num);
return 0;
}
1
3*2=6
1*2=2
1*1=1
4*6=24
4!= 4*3!
3!=3*2!
2!=2*1!
1!=1*0!
0!=1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recursionexamples-210923205317/85/Recursion-examples-2-320.jpg)