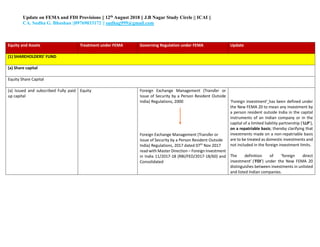
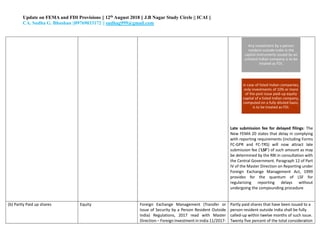
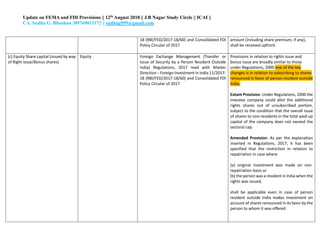
The document provides an update on provisions related to foreign exchange management (FEMA) and foreign direct investment (FDI) in India. Key changes include clarifying that investments made on a non-repatriable basis are treated as domestic rather than foreign investments. For FDI, investments in unlisted companies are treated as FDI, while for listed companies only investments of 10% or more equity are considered FDI. Other updates relate to share issuance timelines, valuation methods, employee stock ownership plans, and external commercial borrowing regulations.