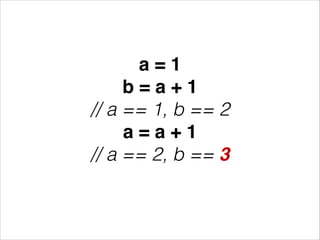
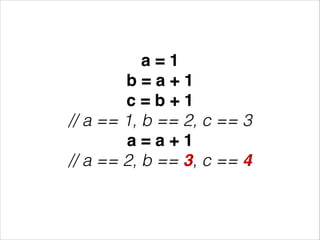
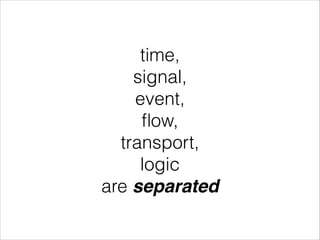
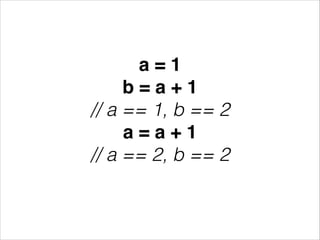This document discusses functional reactive programming (FRP) as a way to handle ever-changing data. It explains that in FRP, values can change over time and logic does not explicitly account for time, but instead recomputes based on value changes. This allows modeling of signals, events, flows, transports, and logic separately. It provides examples using Erlang and Elm frameworks that partially or fully implement FRP concepts. Finally, it suggests FRP could be useful for problems involving interaction, streaming data, robotics, continuous analytics, and machine-to-machine communication where logic needs to reapply on constant value changes.