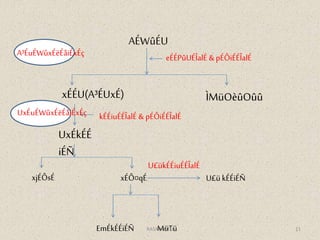
1. Rasadhatu is the first dhatu formed from digested food and circulates throughout the body via the heart and blood vessels, nourishing all tissues.
2. It has properties of snehana (unctuousness), supports the body and mind, and carries nutrients from digested food to all tissues.
3. Rasadhatu is responsible for nutritional status, complexion, health, and zeal. Depletion causes dryness and weakness while excess causes heaviness and laxity.