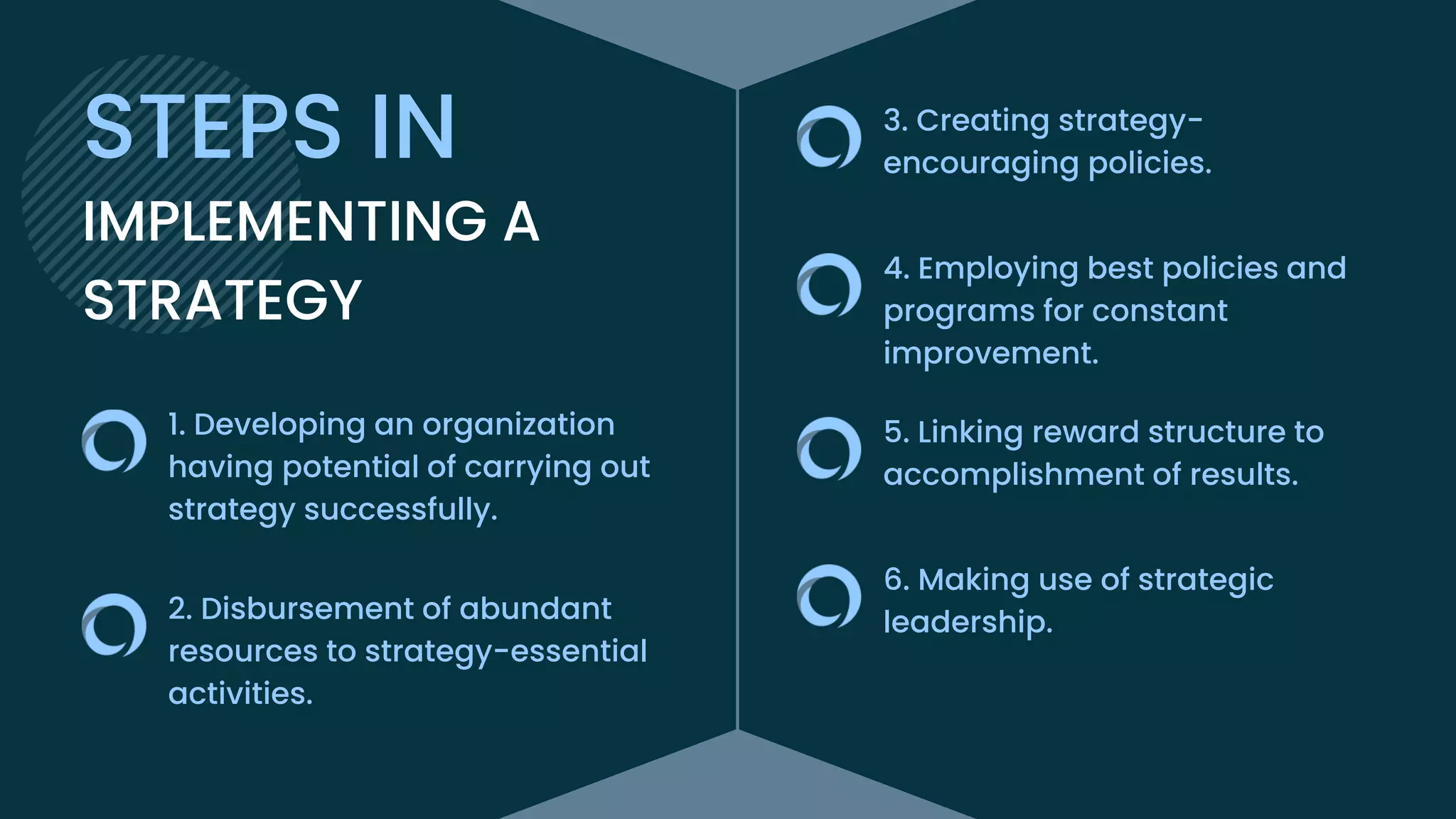
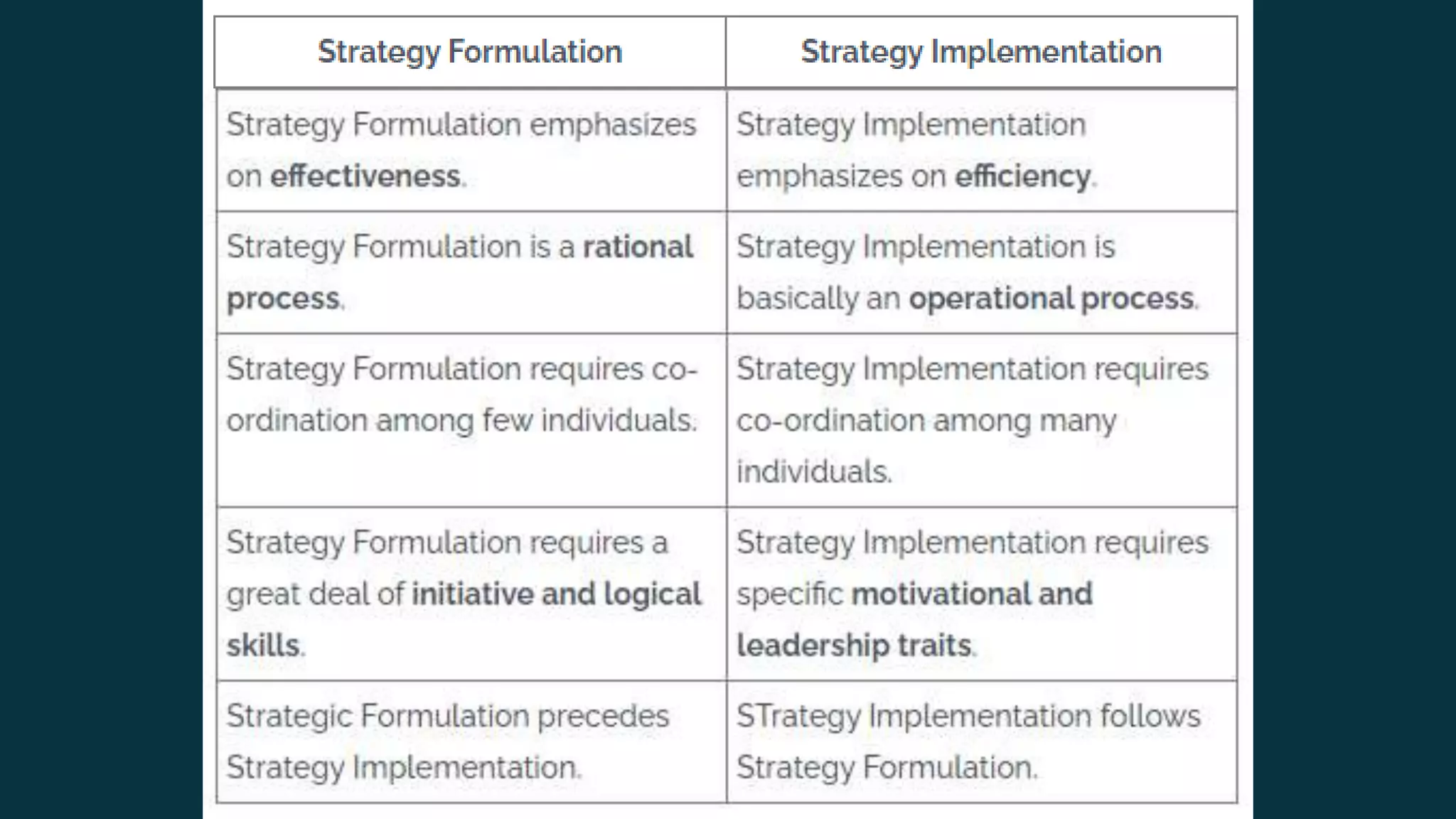
This document discusses the processes of strategic formulation and implementation. It describes the six main steps of strategic formulation as setting organizational objectives, evaluating the organizational environment, setting quantitative targets, aligning with divisional plans, performing analysis, and choosing a strategy. It then explains that strategic implementation involves translating the chosen strategy into organizational actions through developing an effective organizational structure, control systems, culture, and aligning resources and incentives. Finally, it notes that strategic formulation and implementation must be closely linked to ensure strategies are properly executed and bring competitive advantage.