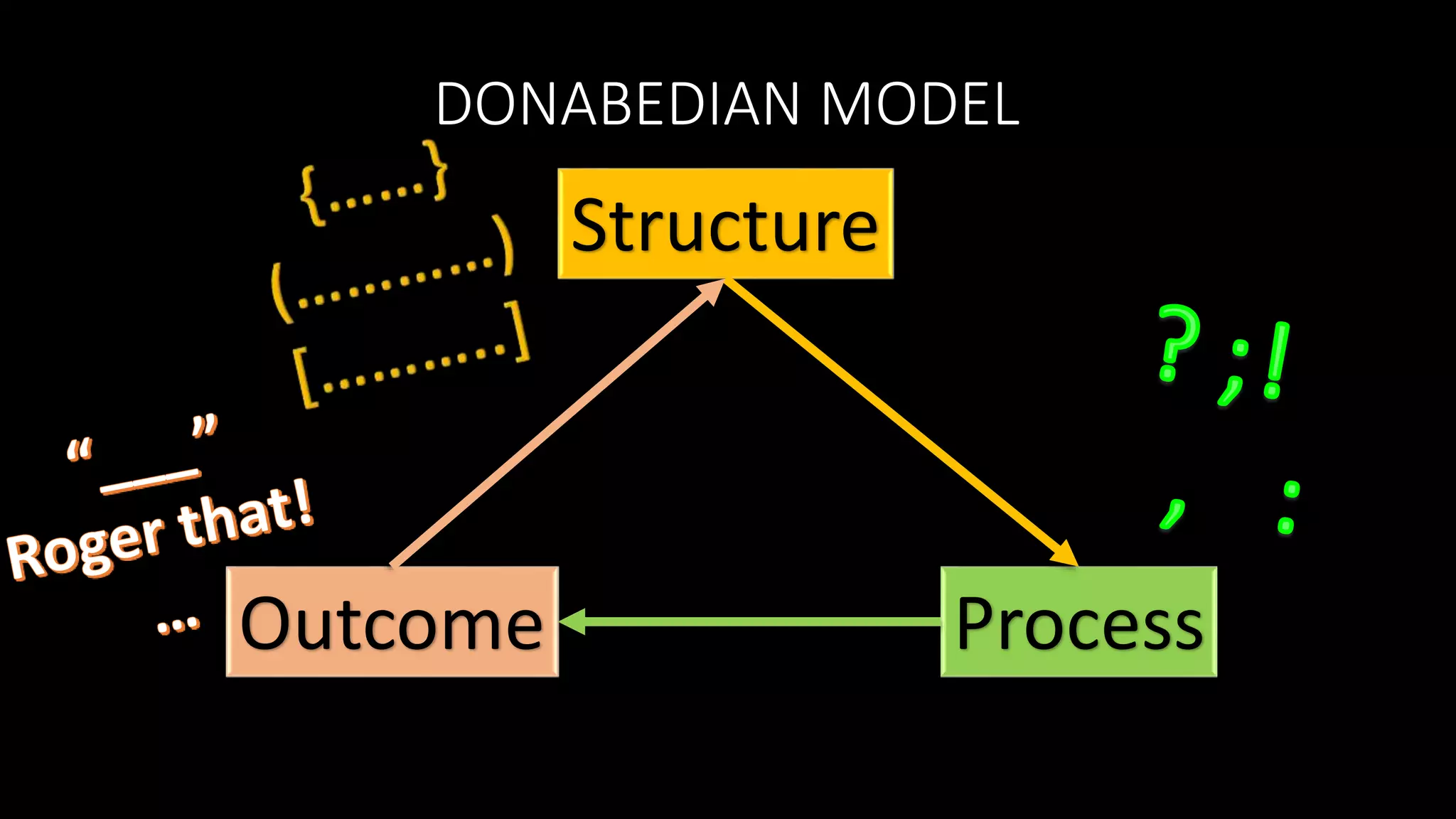
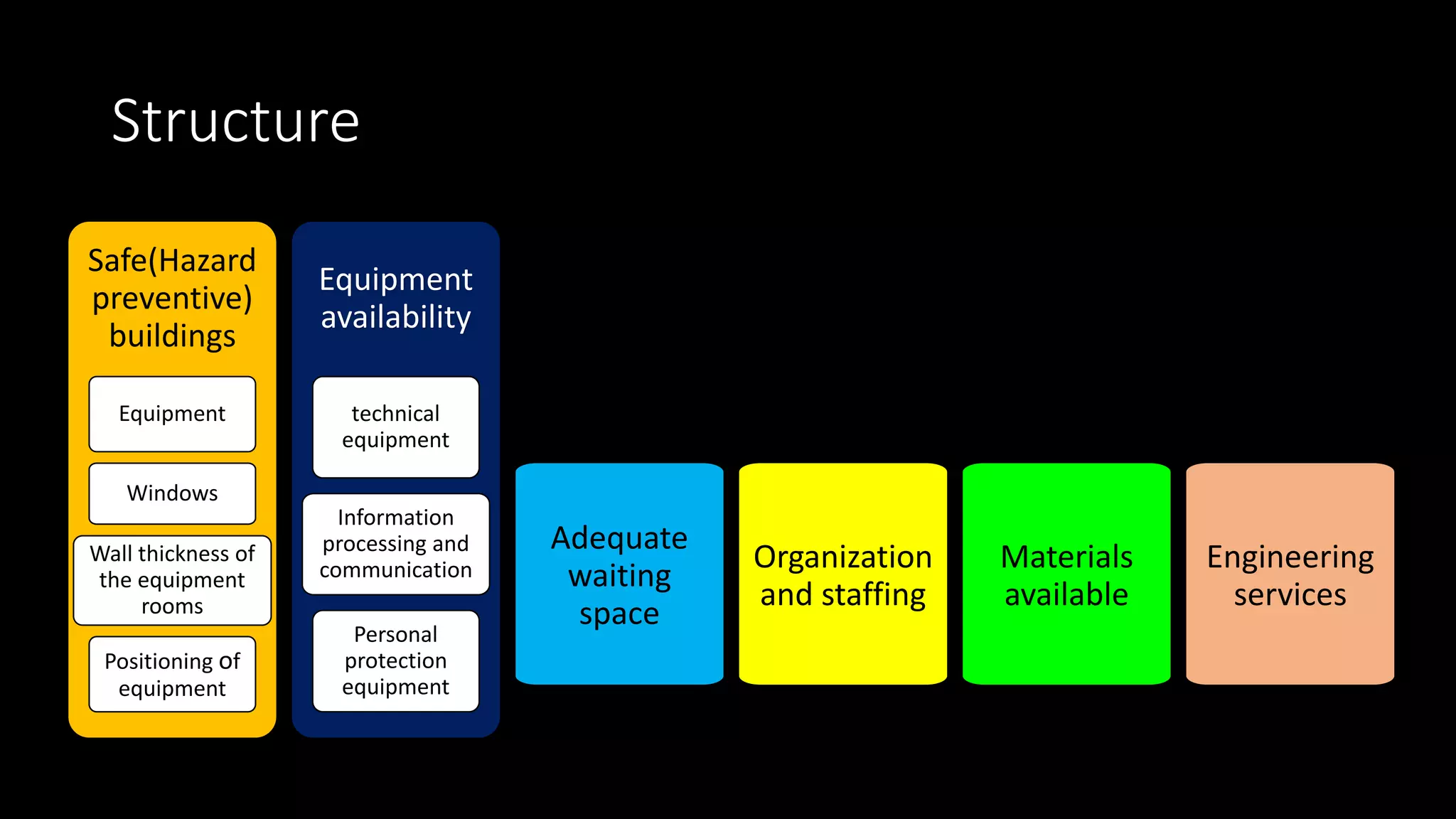
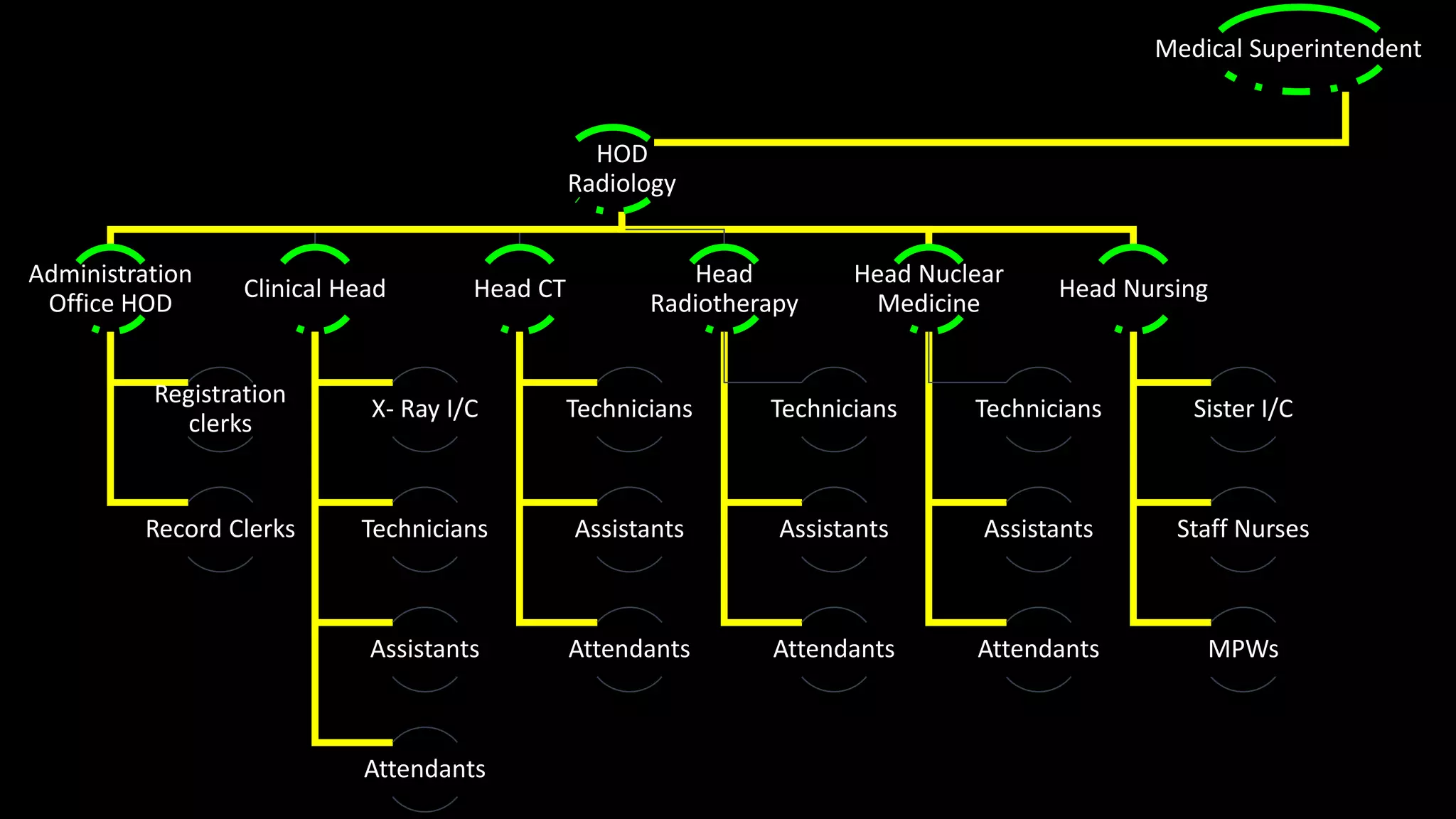
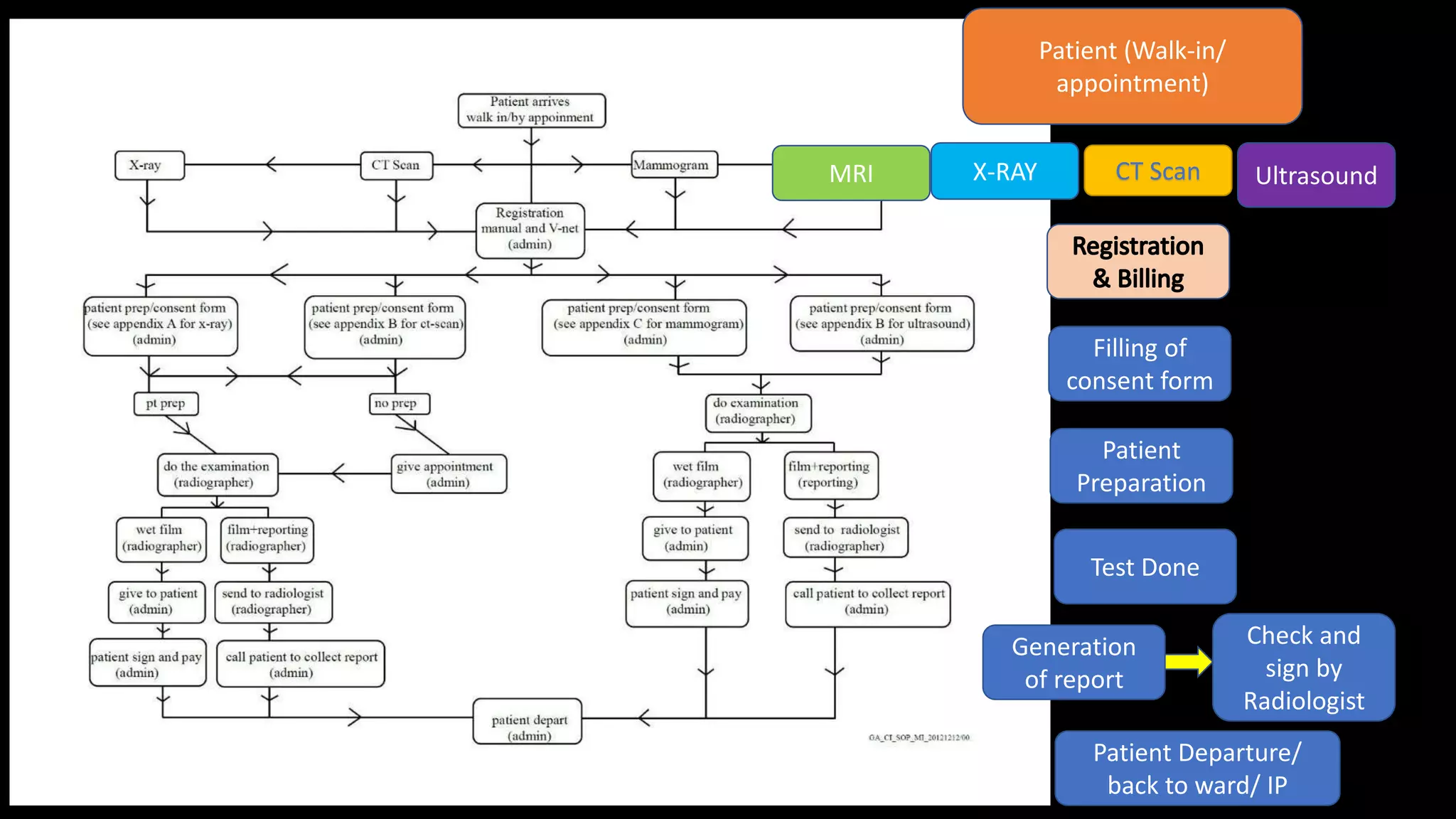
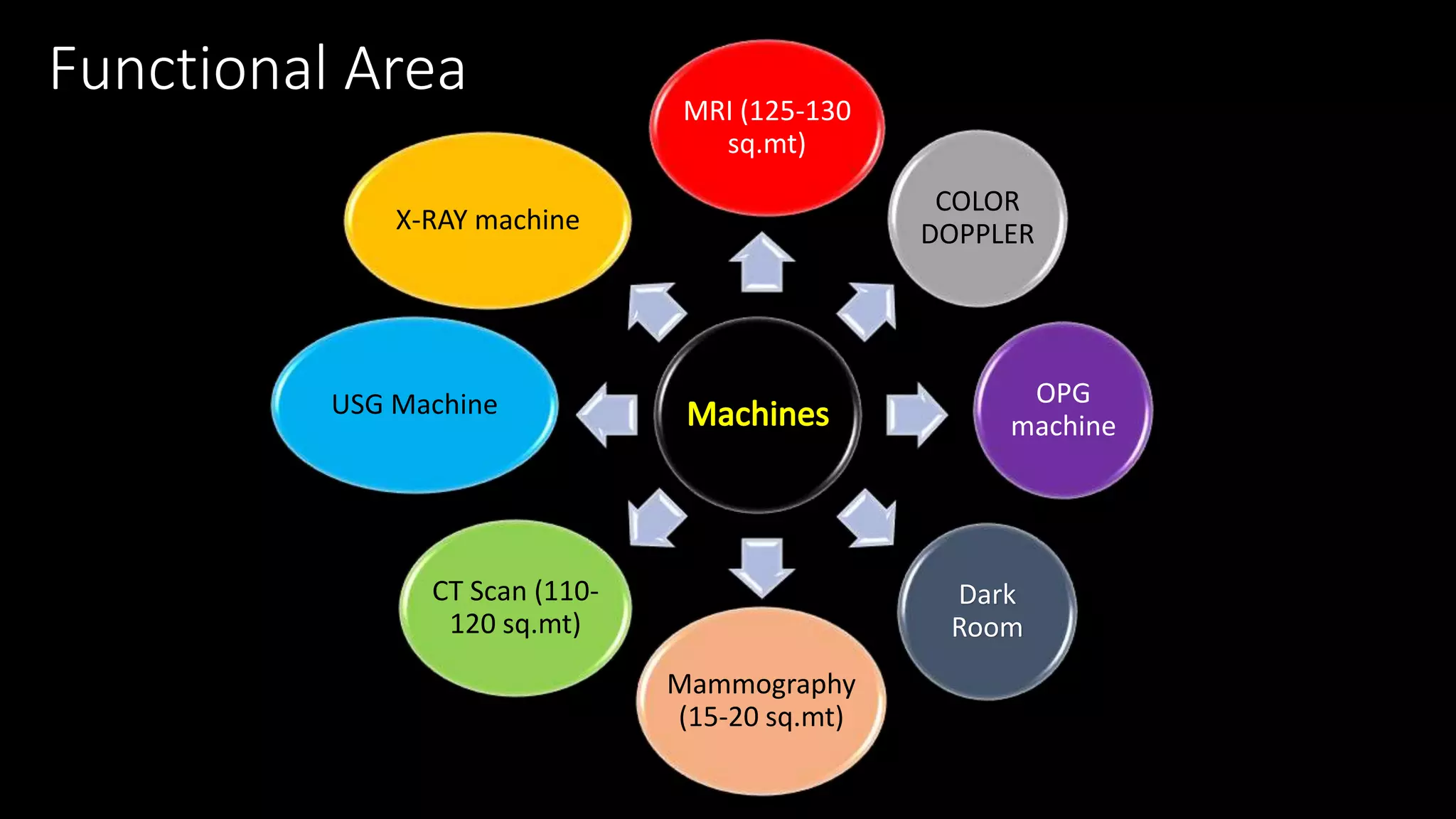
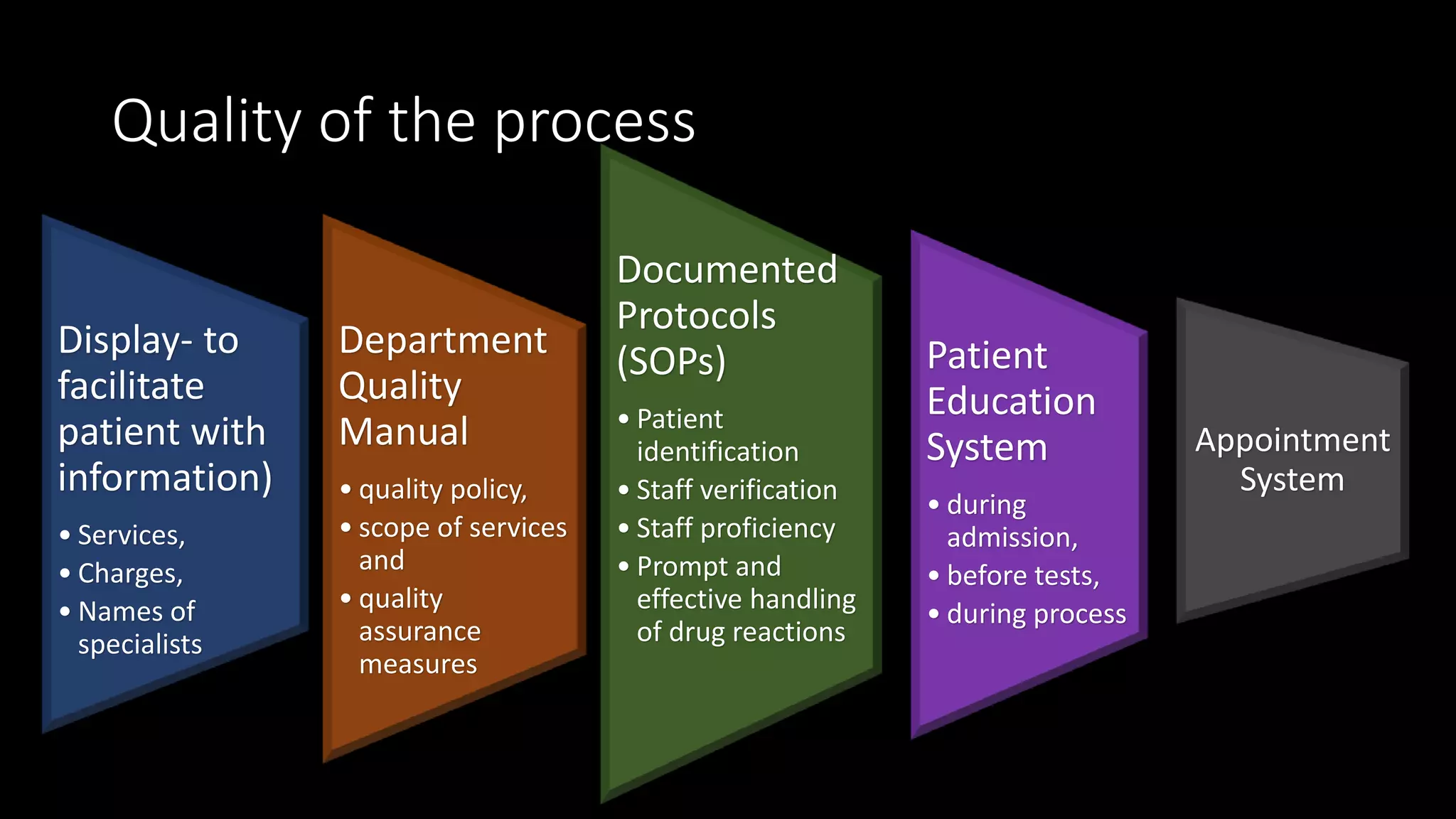
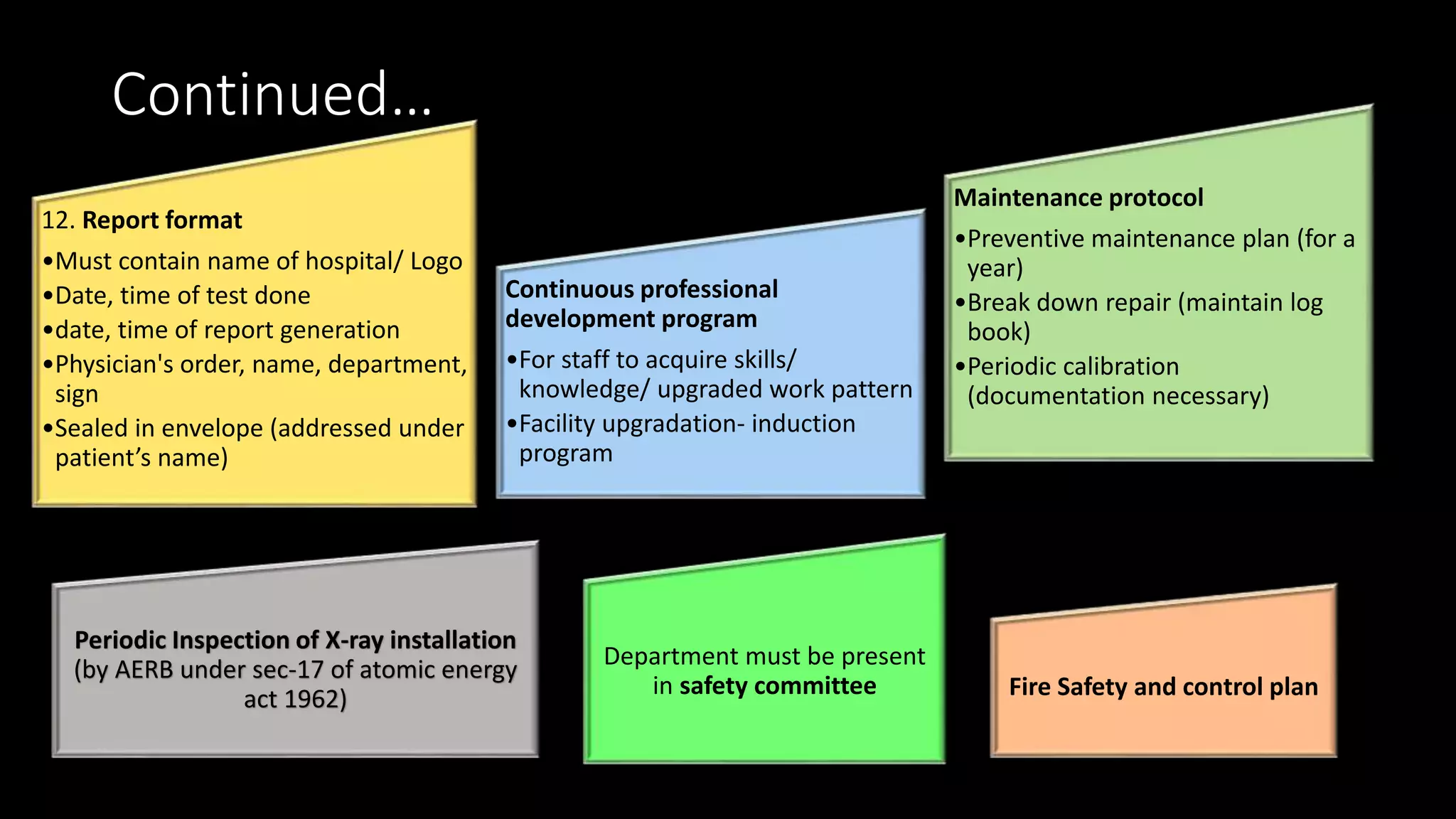
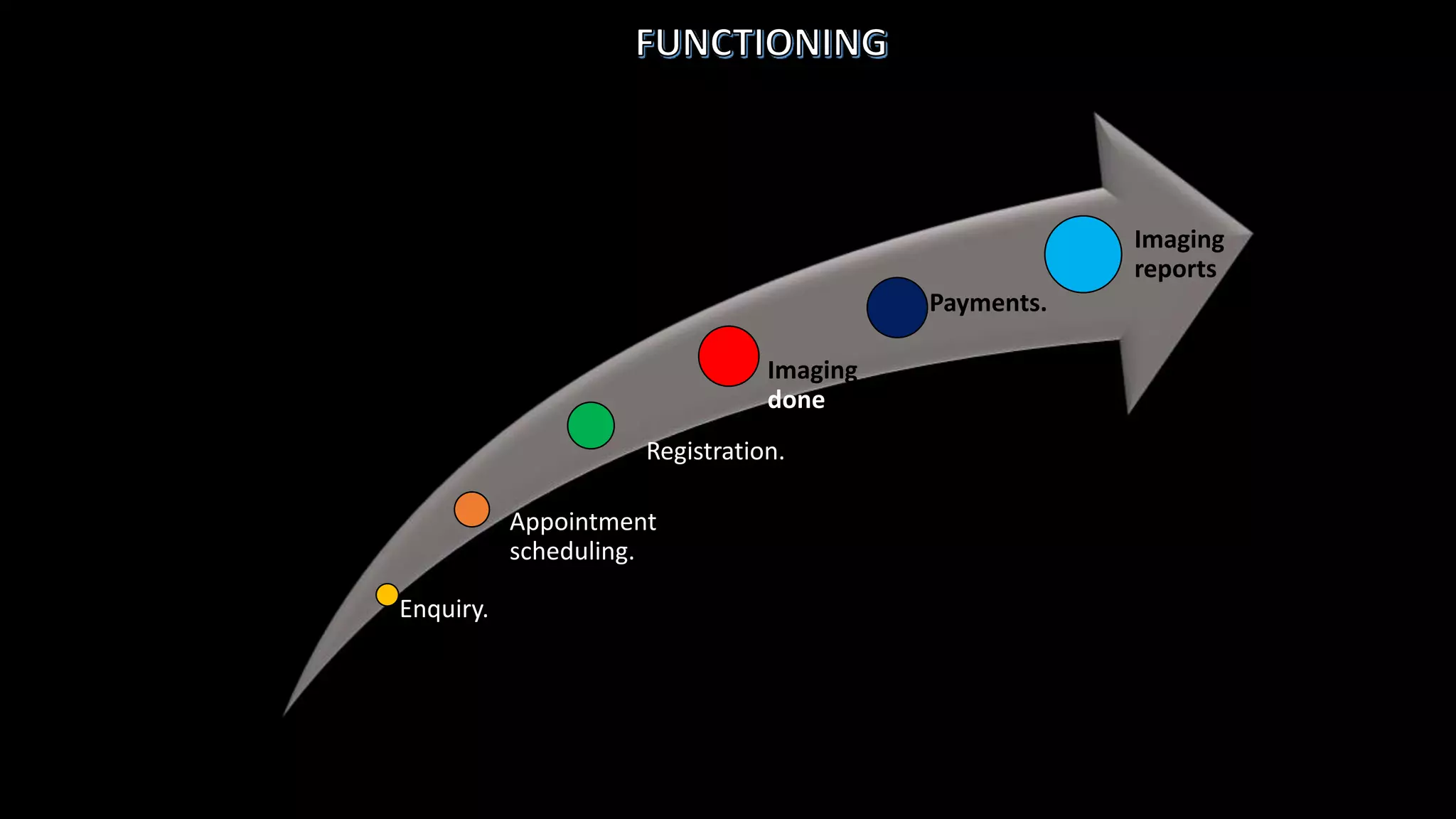
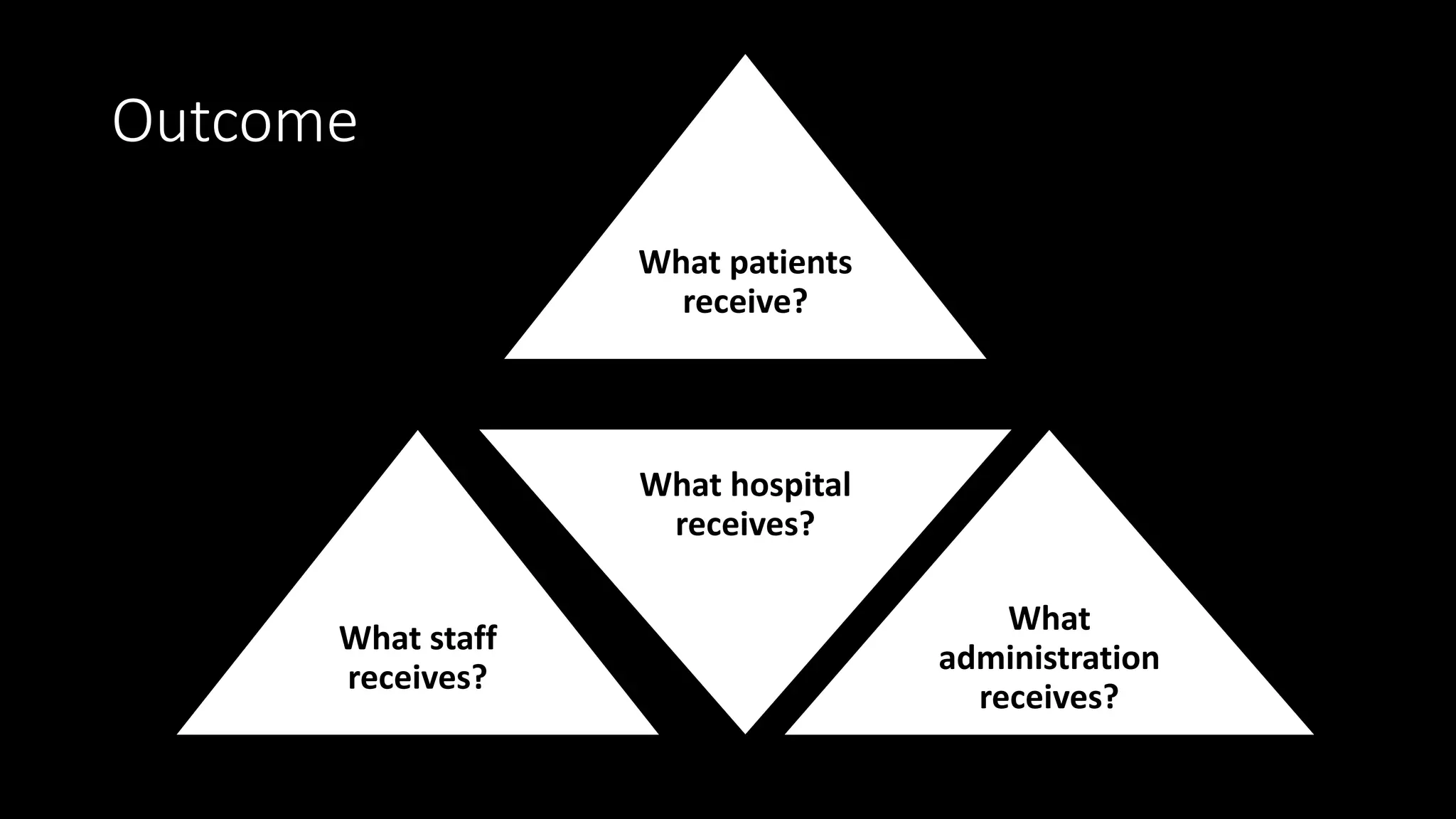
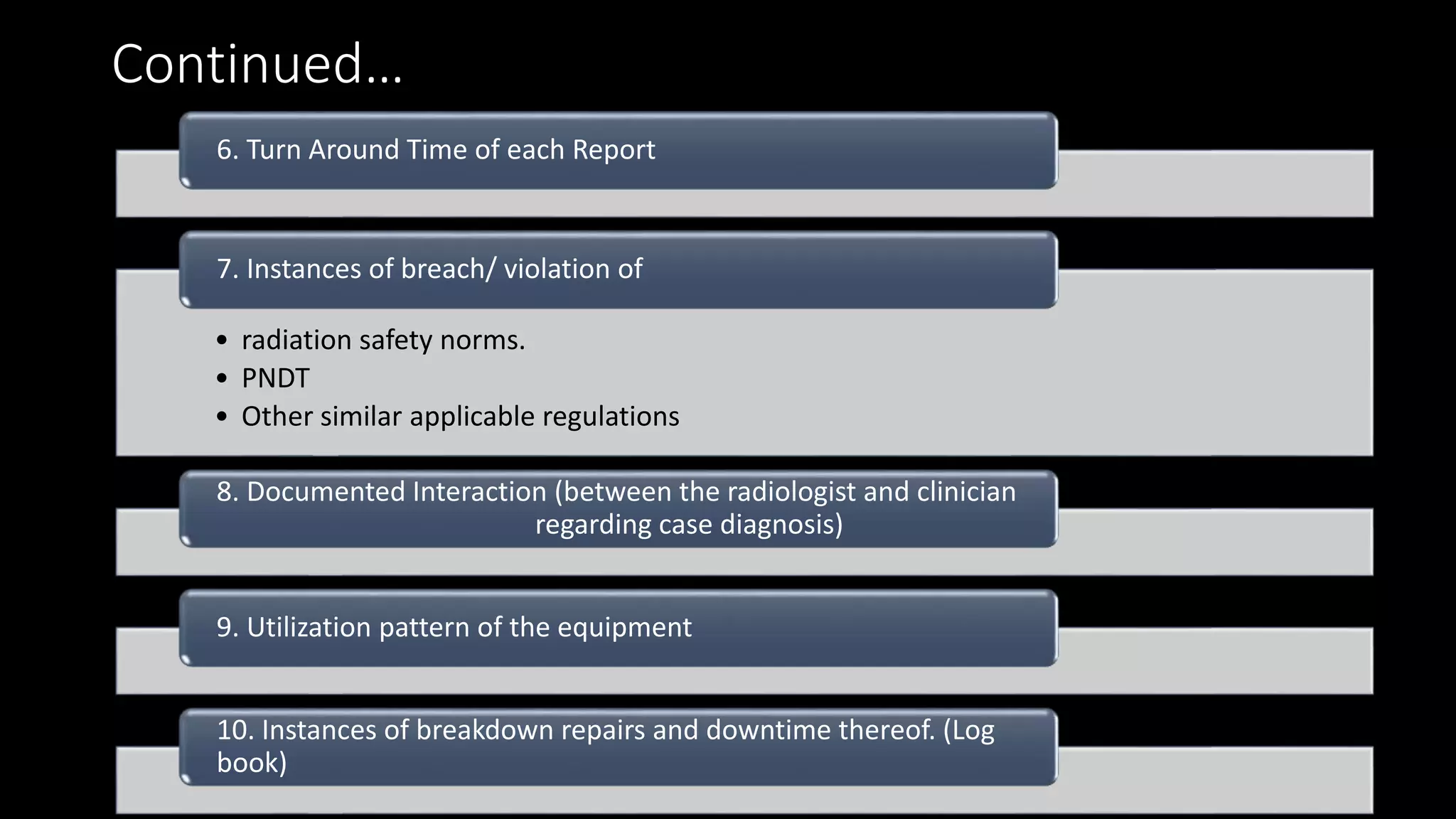
The document outlines the structure, processes, and quality assurance measures for radiology services in a hospital using the Donabedian model. It includes details on equipment specifications, staff roles, patient management, and compliance with legal and safety standards. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of communication, professional development, and monitoring of service quality through various evaluations and audits.