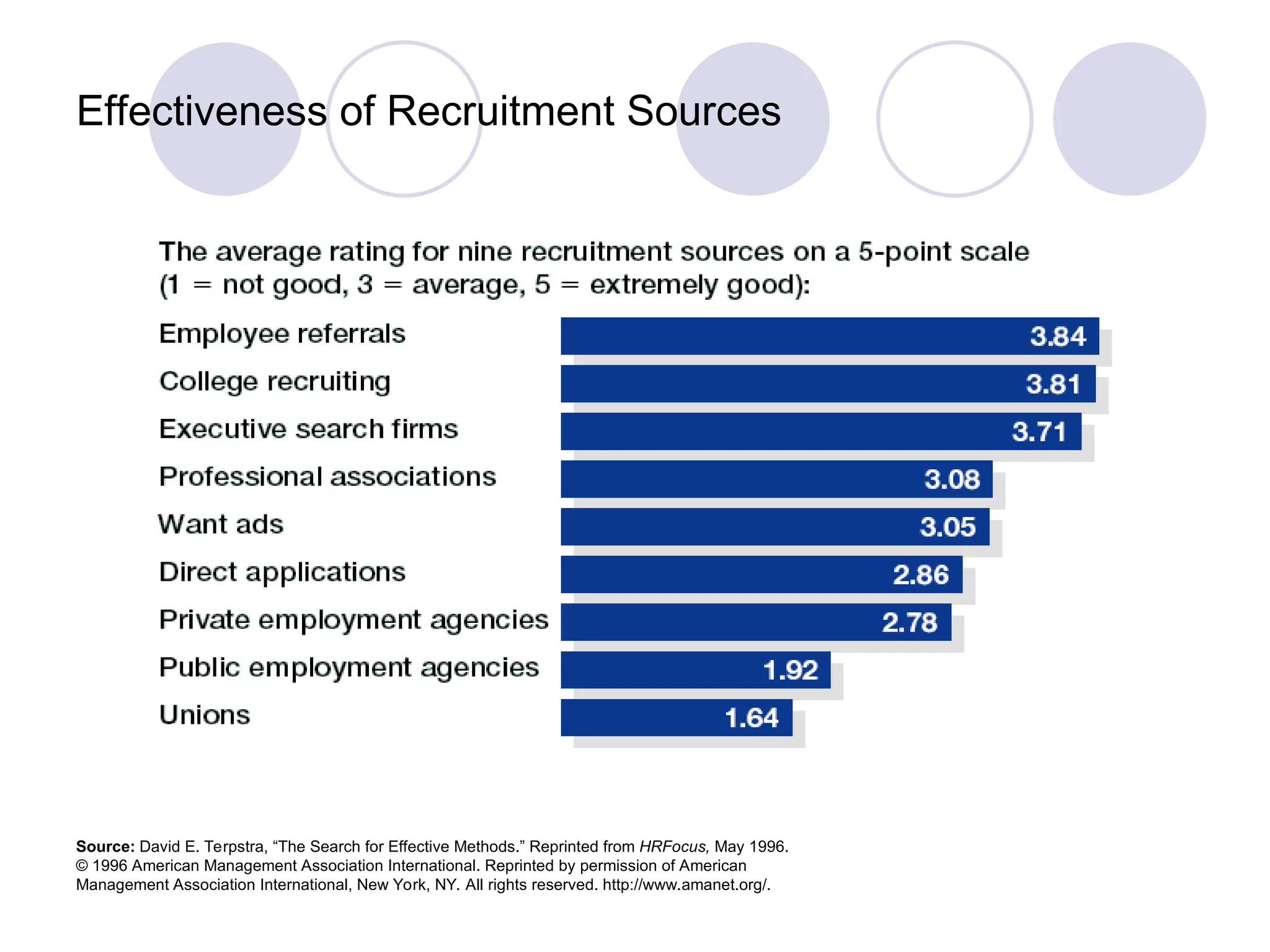
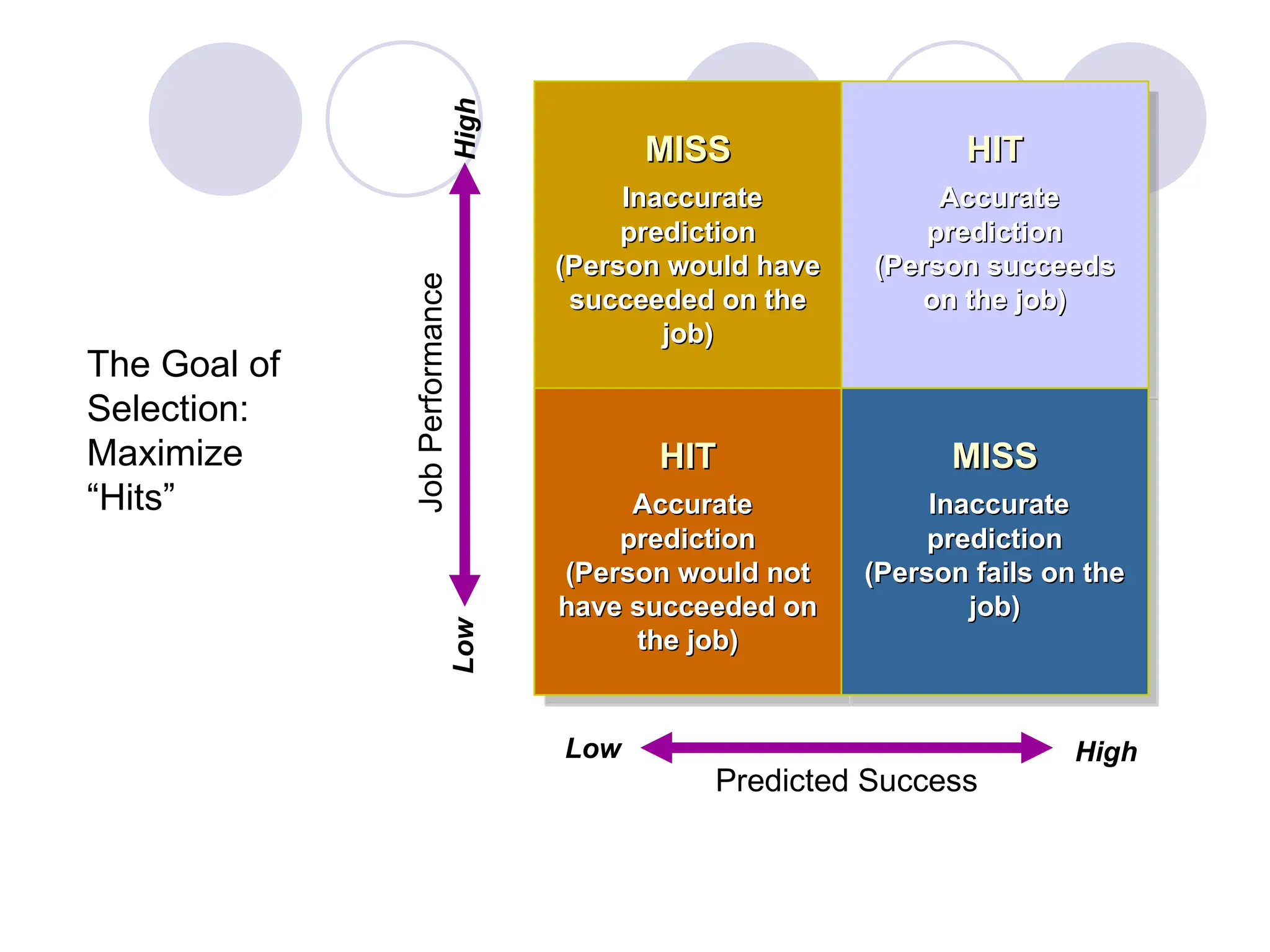
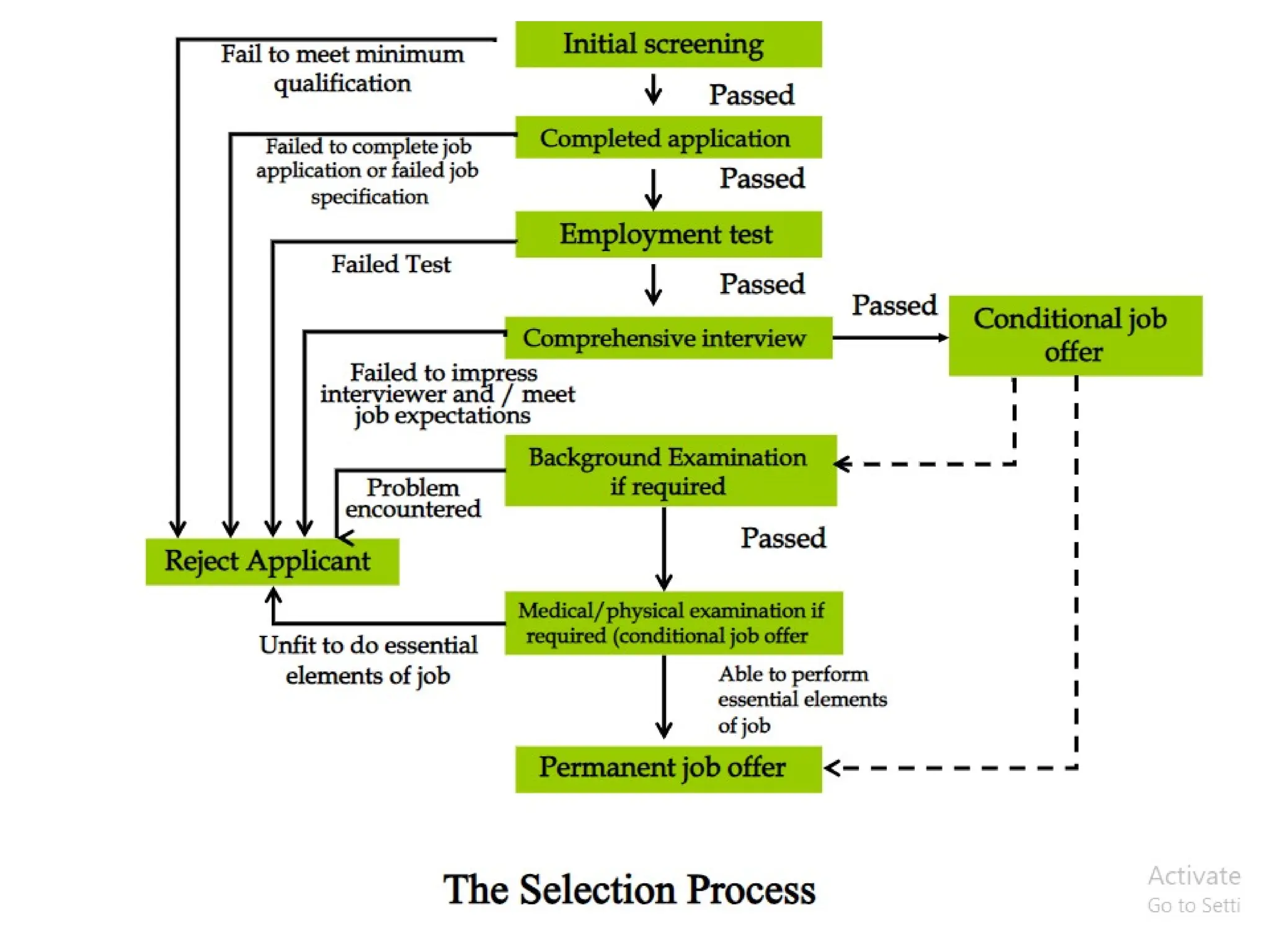
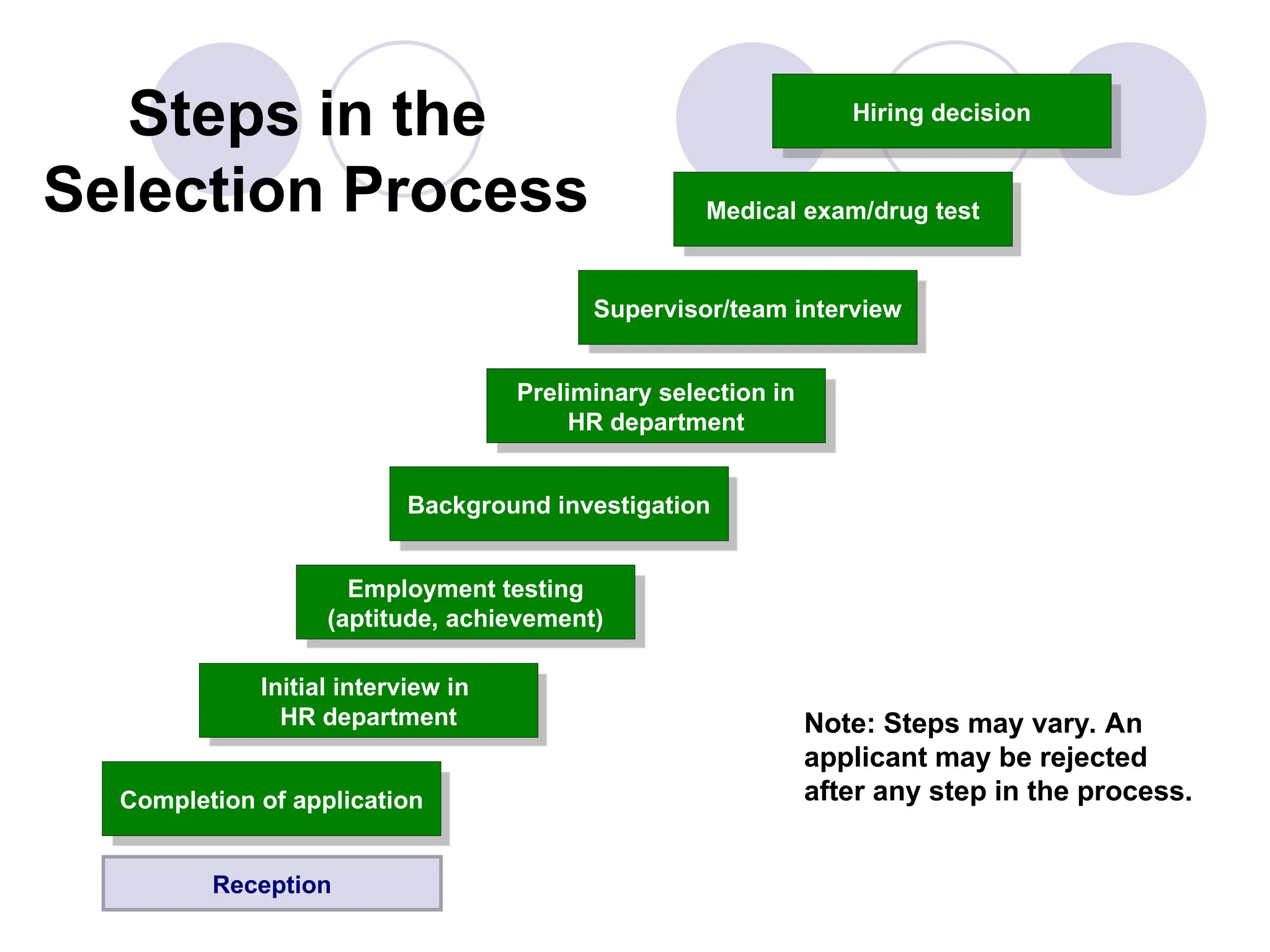
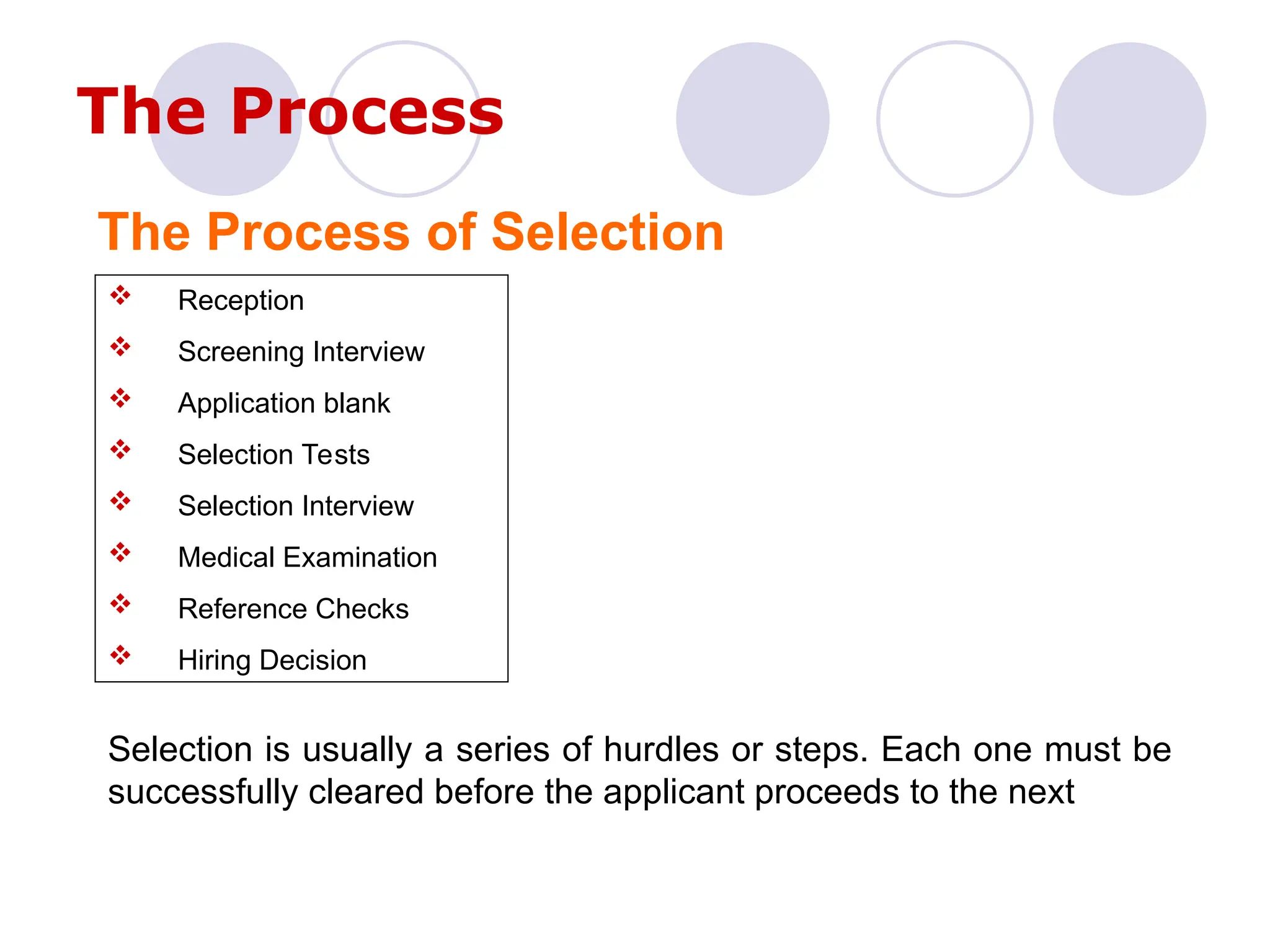
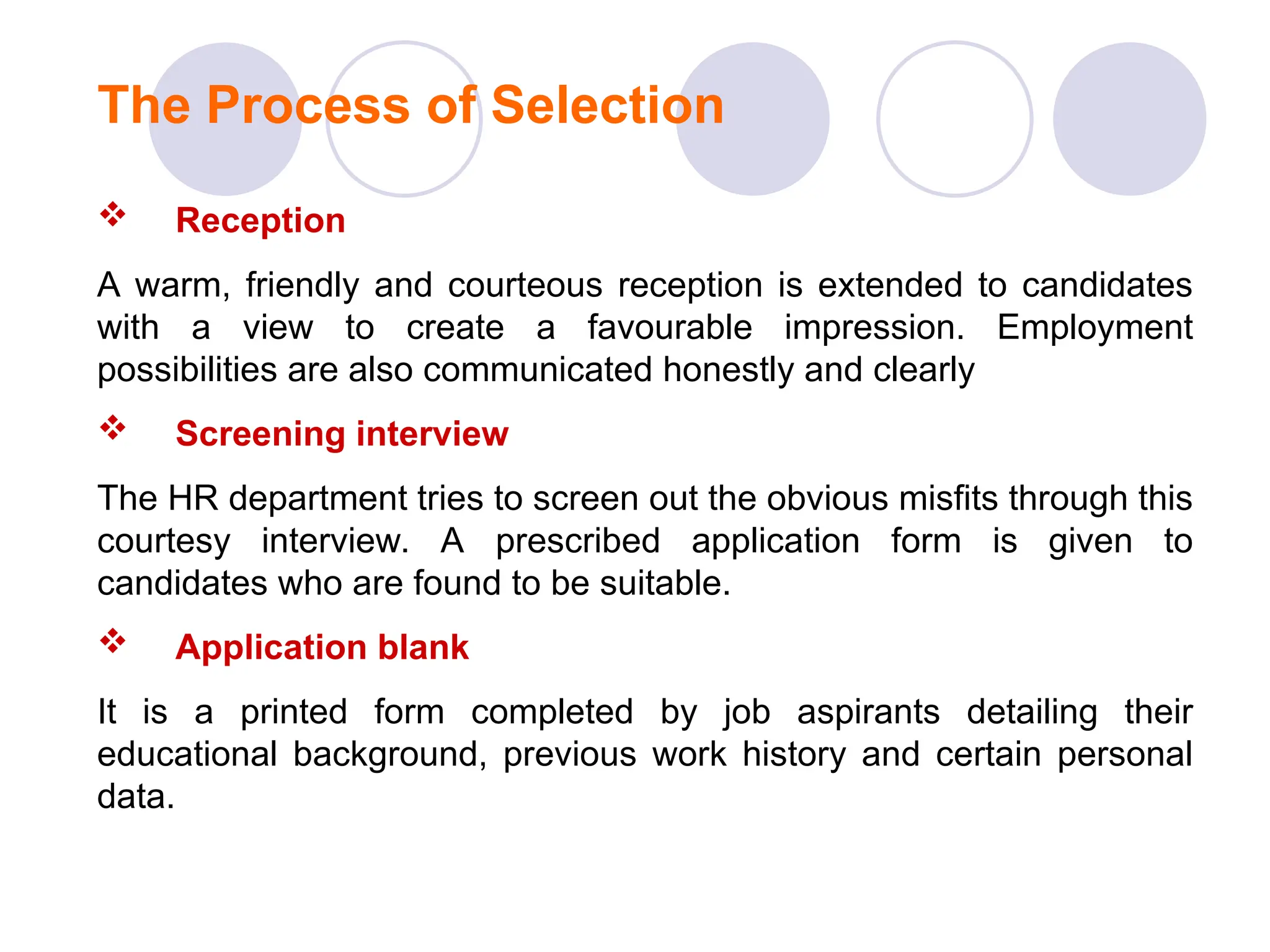
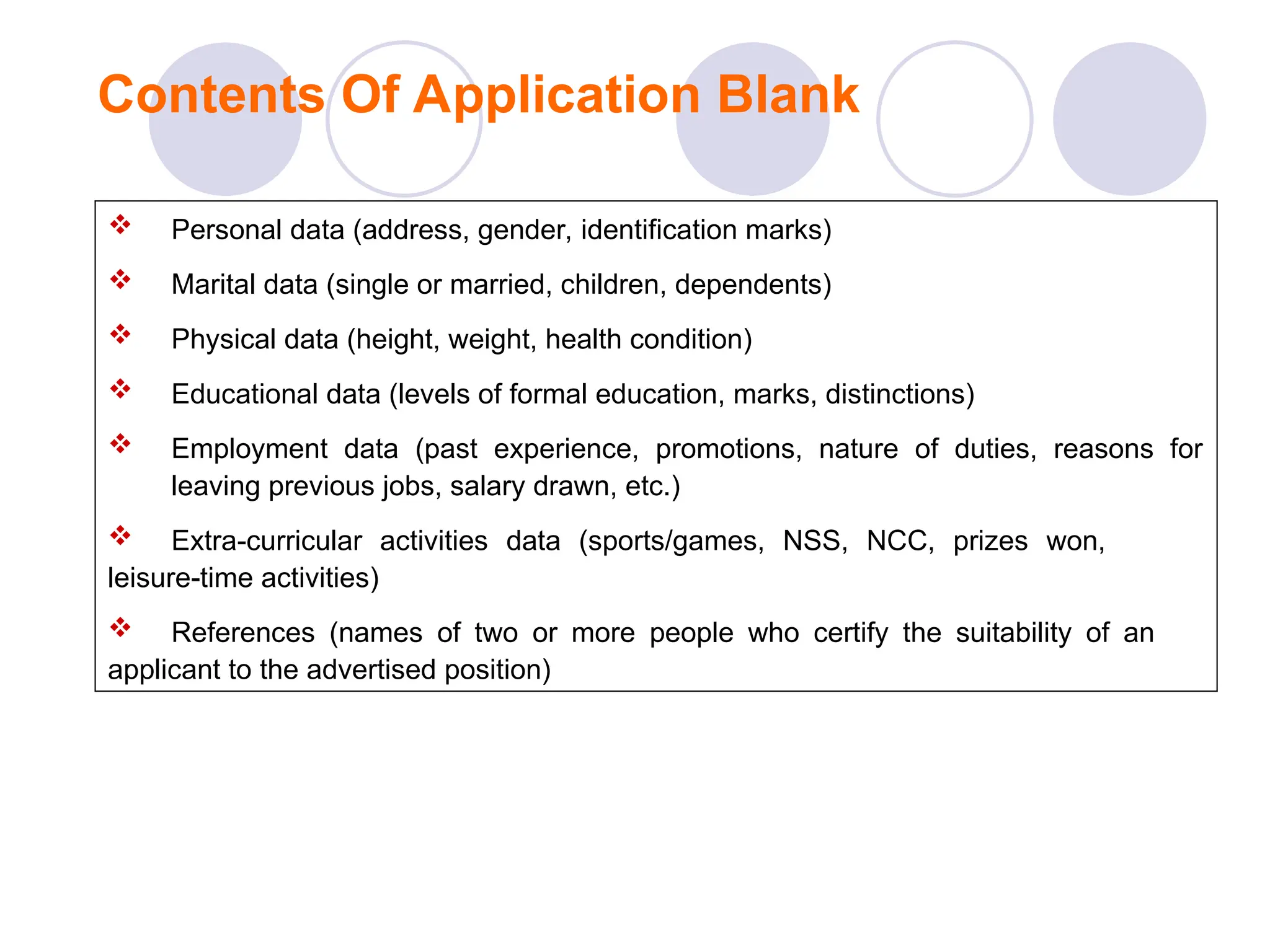
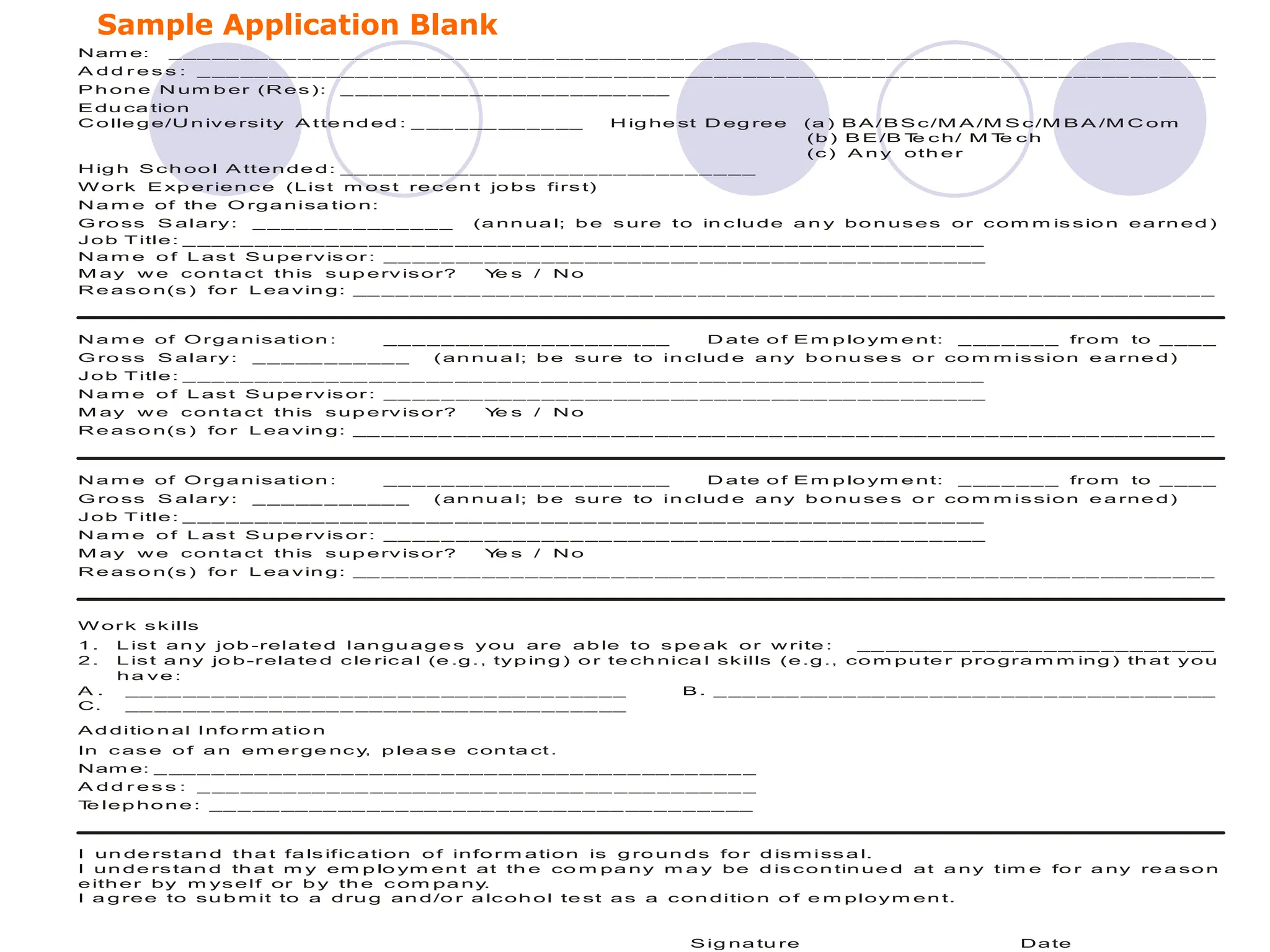
The document outlines the recruitment and selection process, highlighting the significance of attracting capable applicants for employment. It discusses internal and external recruitment sources, the evolving employment patterns impacting recruitment, and the selection process including various tests and interview techniques. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of matching individuals with job roles and organizational culture to maximize successful employment outcomes.