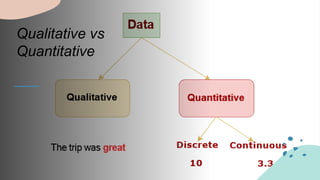
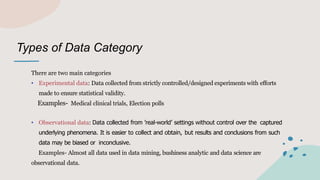
The document outlines the steps for conducting a data science project, emphasizing the importance of identifying a problem, collecting, and preparing data, exploring it, and communicating results. It defines data as a set of facts with two main types: qualitative and quantitative, and discusses various data formats and categories, including experimental and observational data. The document highlights the significance of data collection for decision-making and improving services based on customer feedback.