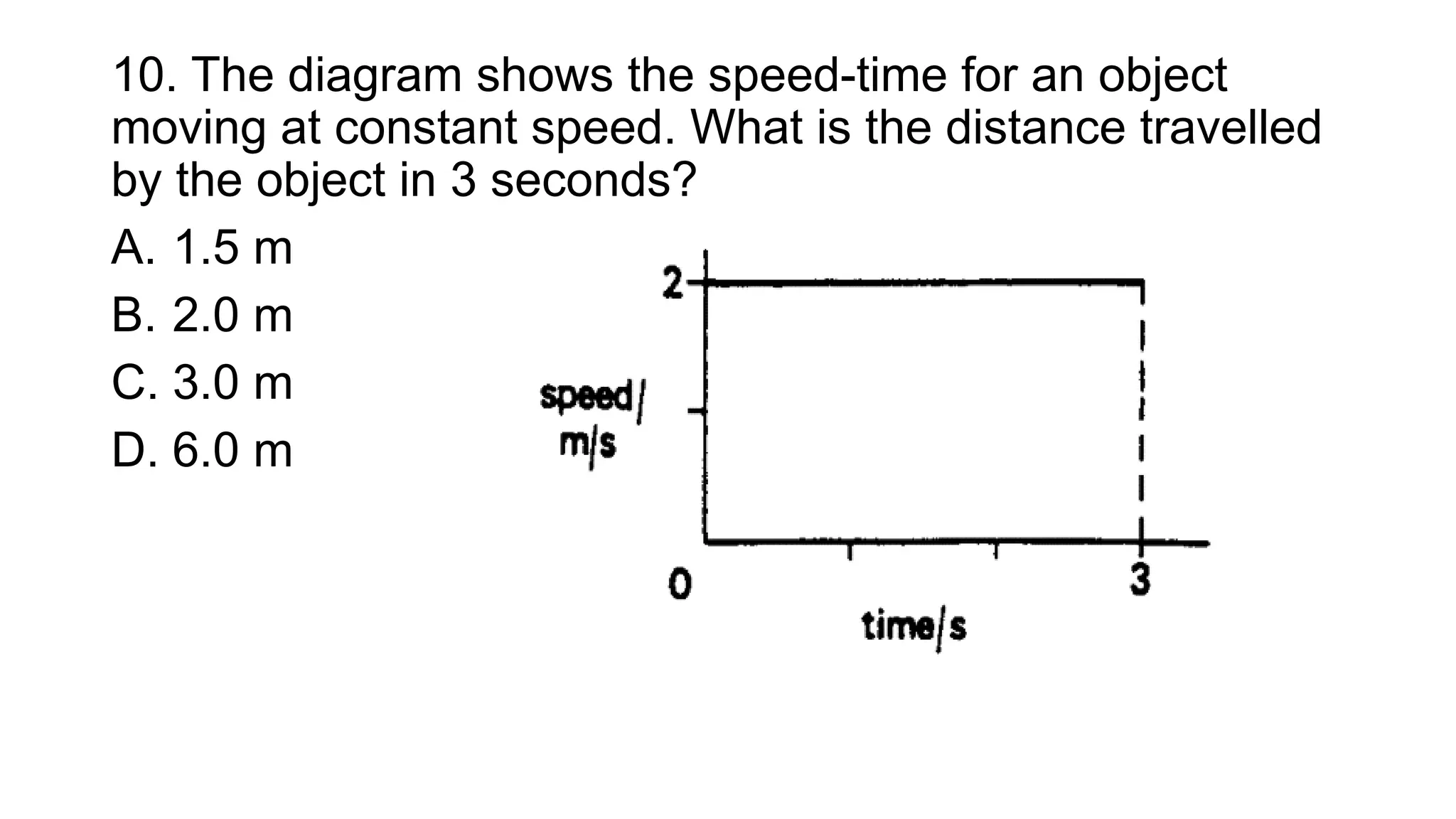
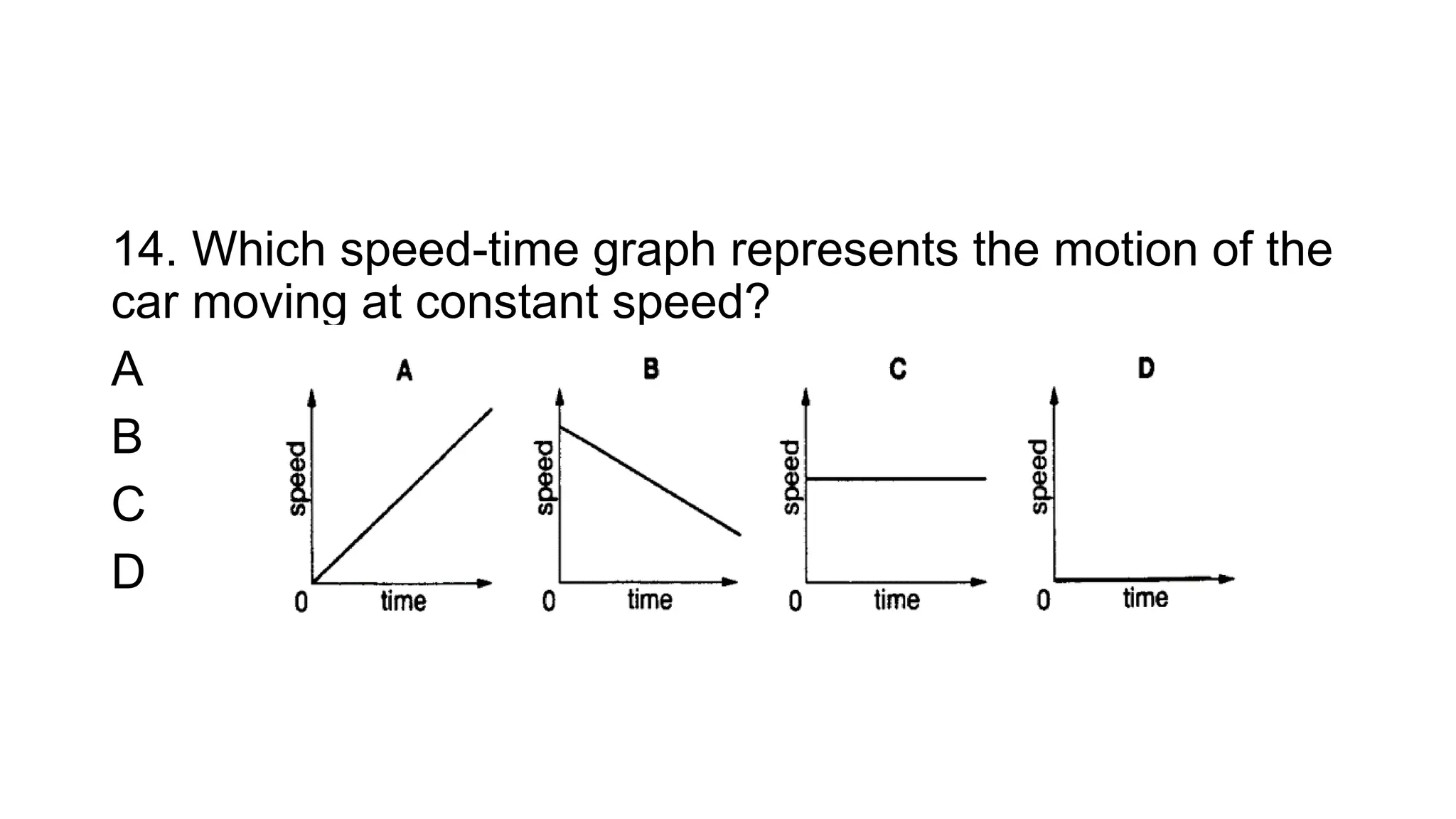
The document is a quiz focusing on concepts of motion, speed, and acceleration, featuring multiple-choice questions related to physics. It includes questions on definitions, formulas, and practical problems to assess understanding of the subject matter. Additionally, it provides an answer key for all the questions to facilitate learning and self-assessment.