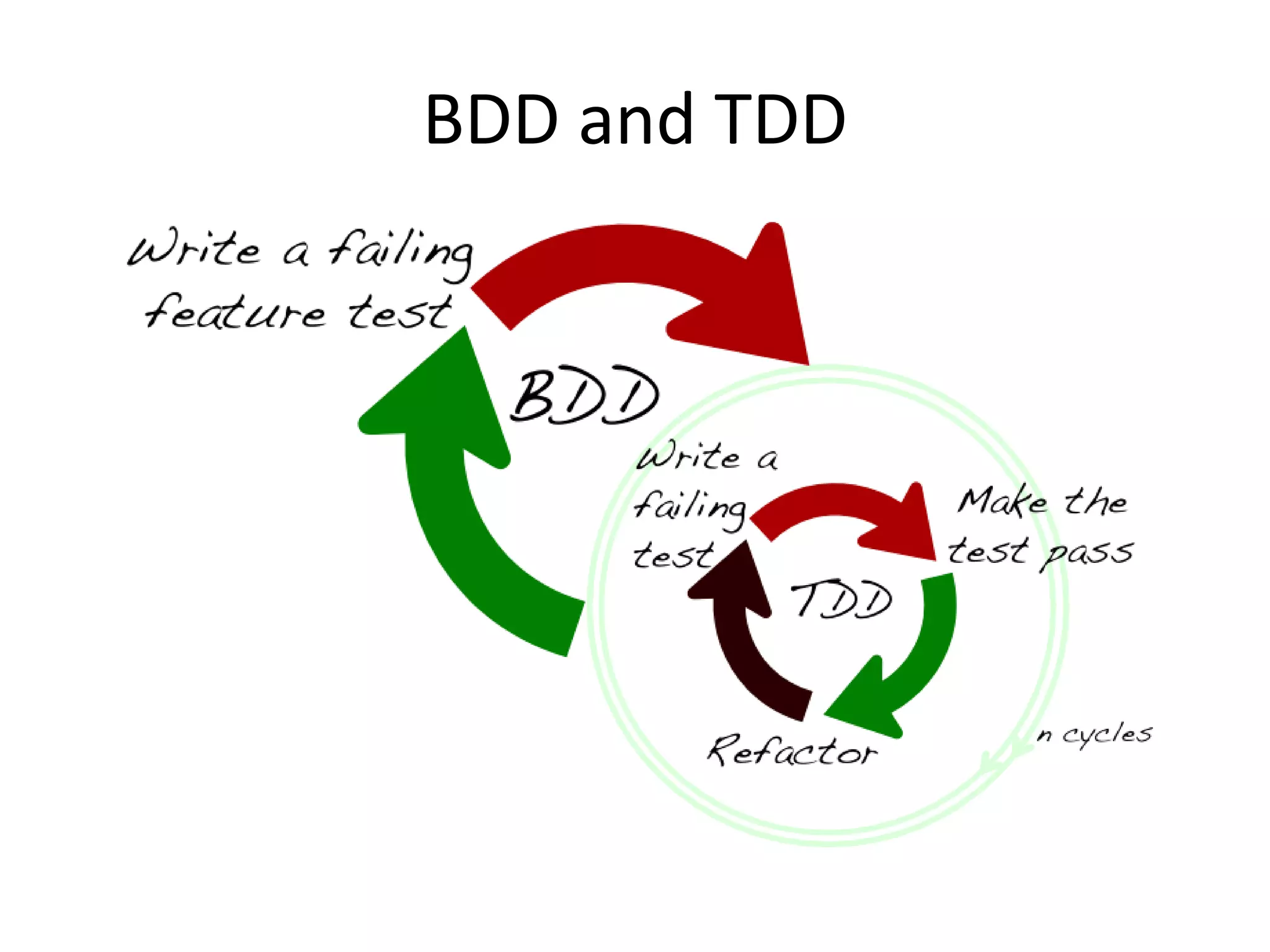
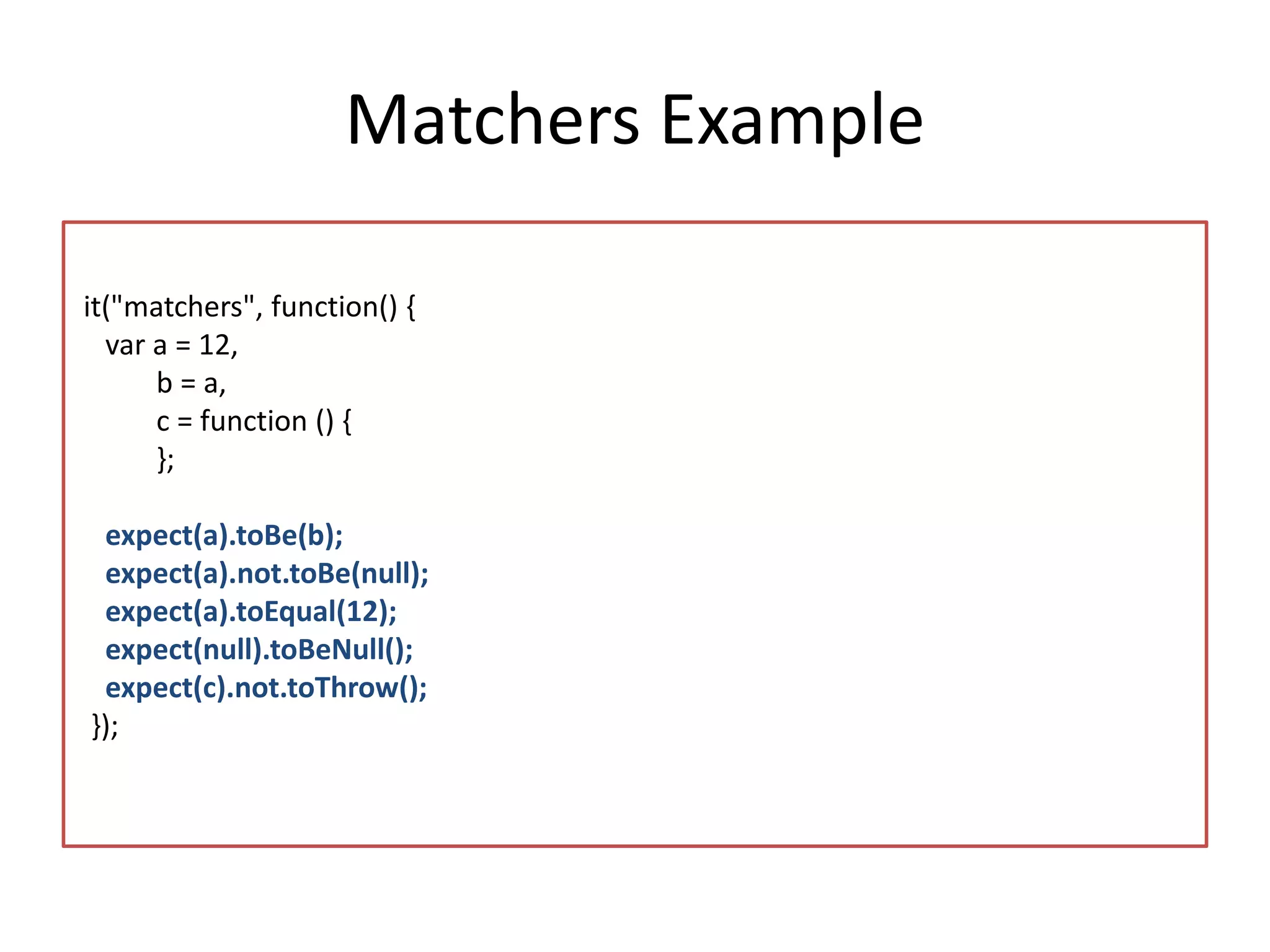
This document discusses front-end unit testing using the Jasmine testing framework. It explains why unit testing is important, introduces behavior-driven development and the Jasmine framework. It also provides an overview of setting up Jasmine, creating test suites and specs, using matchers, and testing asynchronous code. The document demonstrates how to set up the testing environment, write tests with Jasmine, and integrate Jasmine with the Karma test runner.