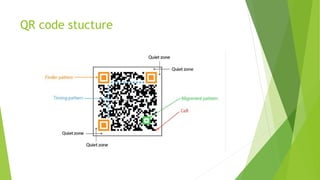
A QR code, or quick response code, is a 2D barcode developed in 1994 that allows users to access information using a smartphone or scanner. It can store various data types including text, URLs, and payment information, gaining further popularity during the COVID-19 pandemic for facilitating contactless transactions. The integration of QR codes in libraries has enhanced resource access and management, although challenges in user knowledge persist in some areas.