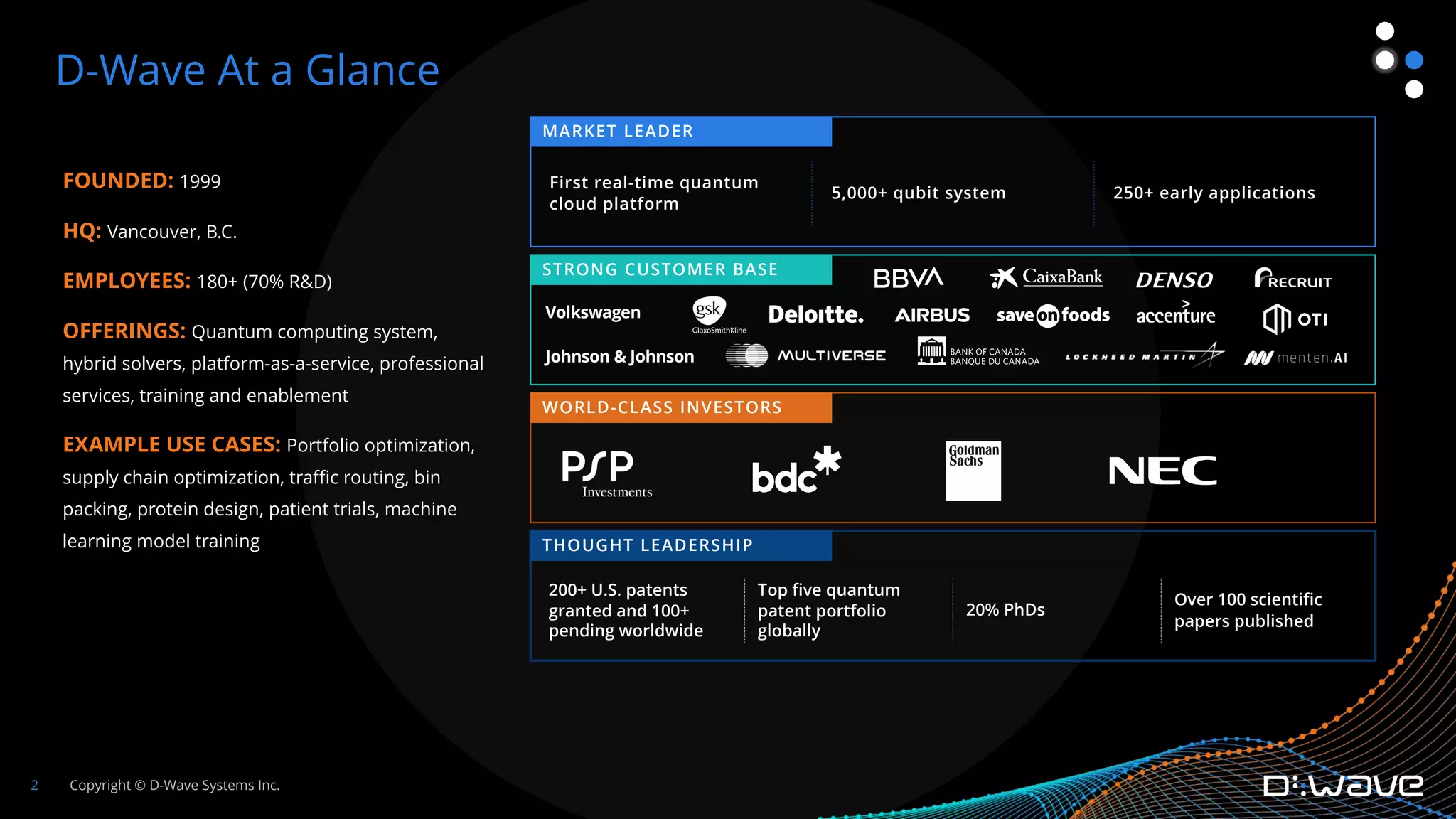
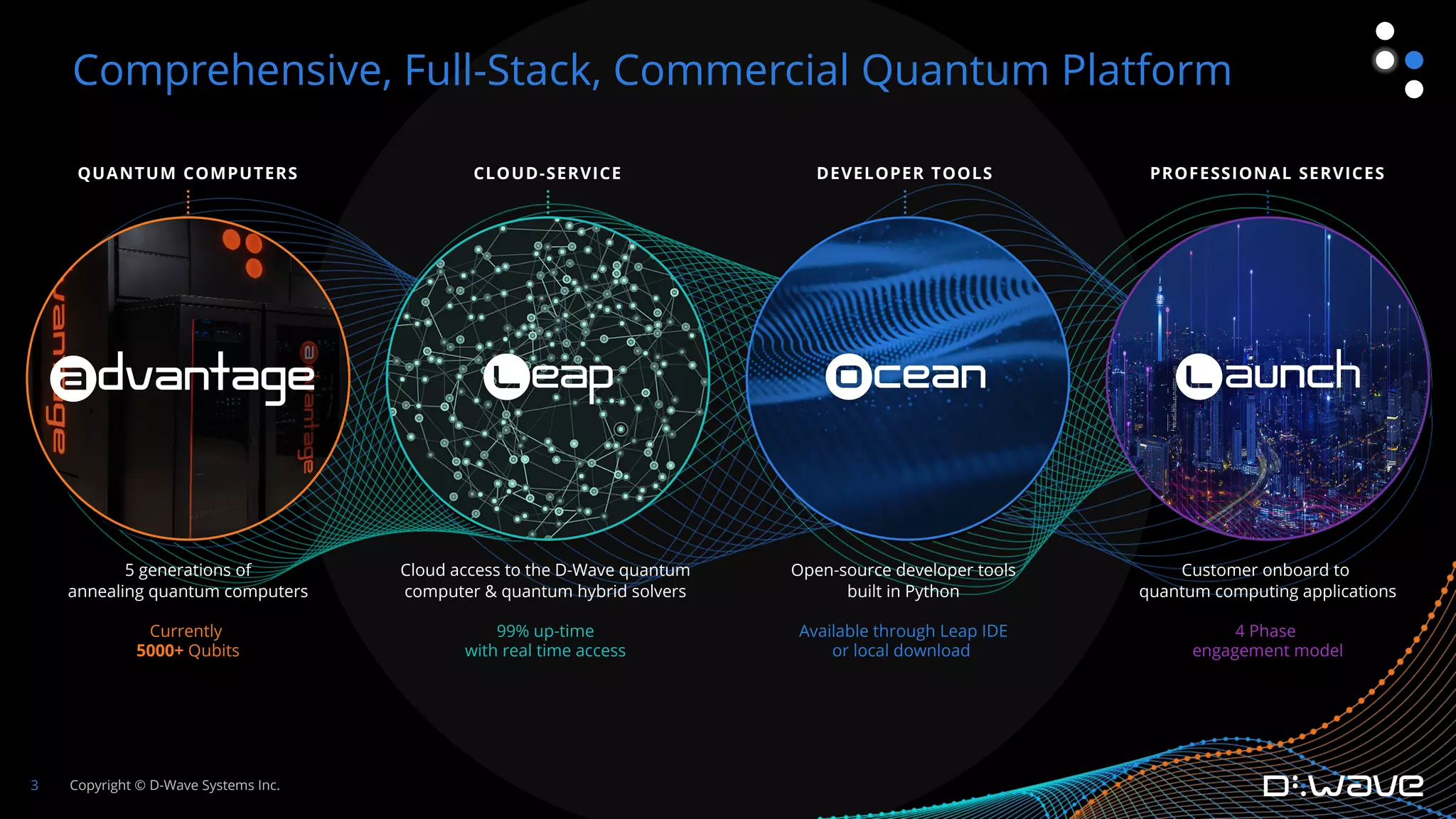
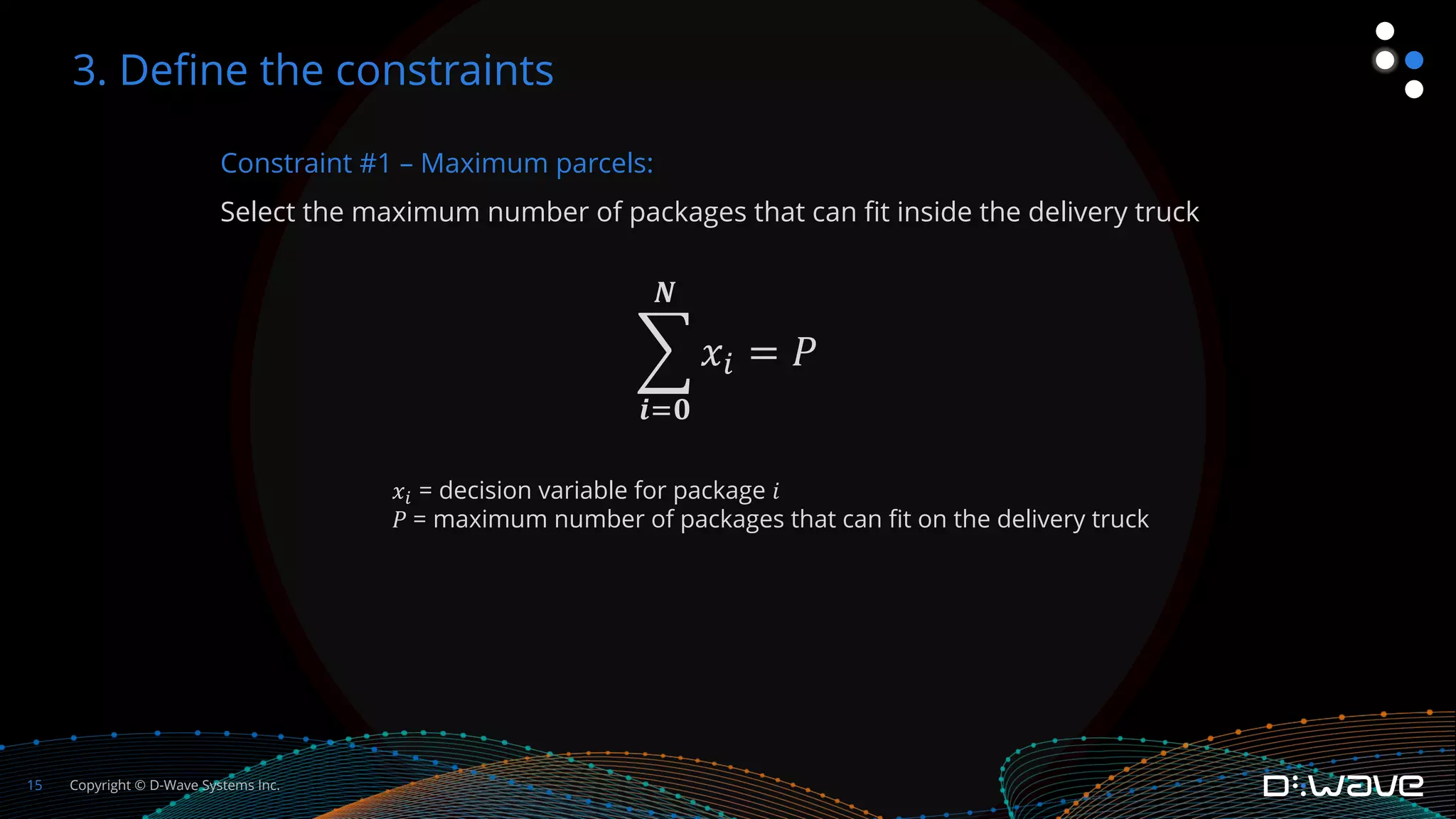
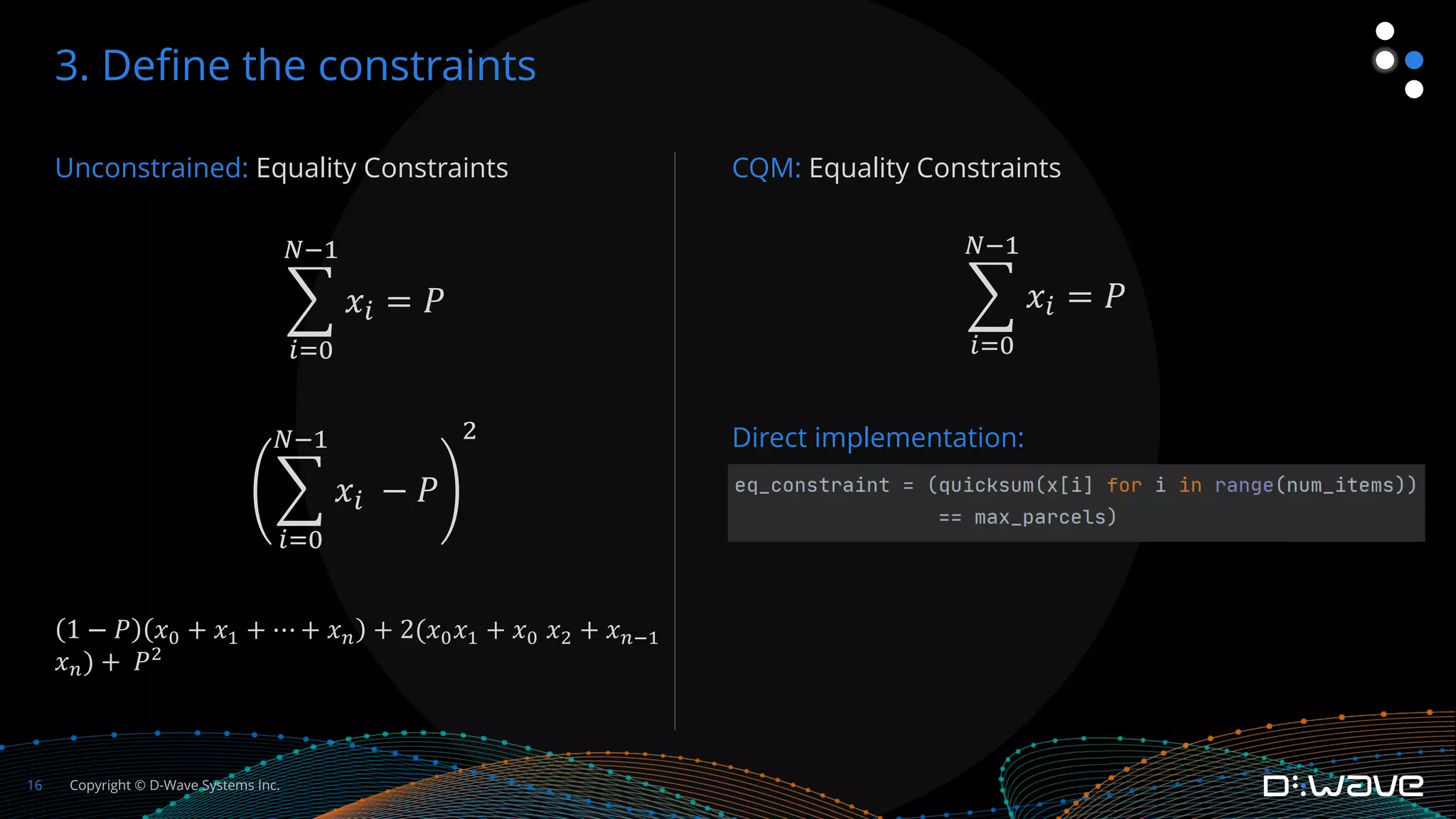
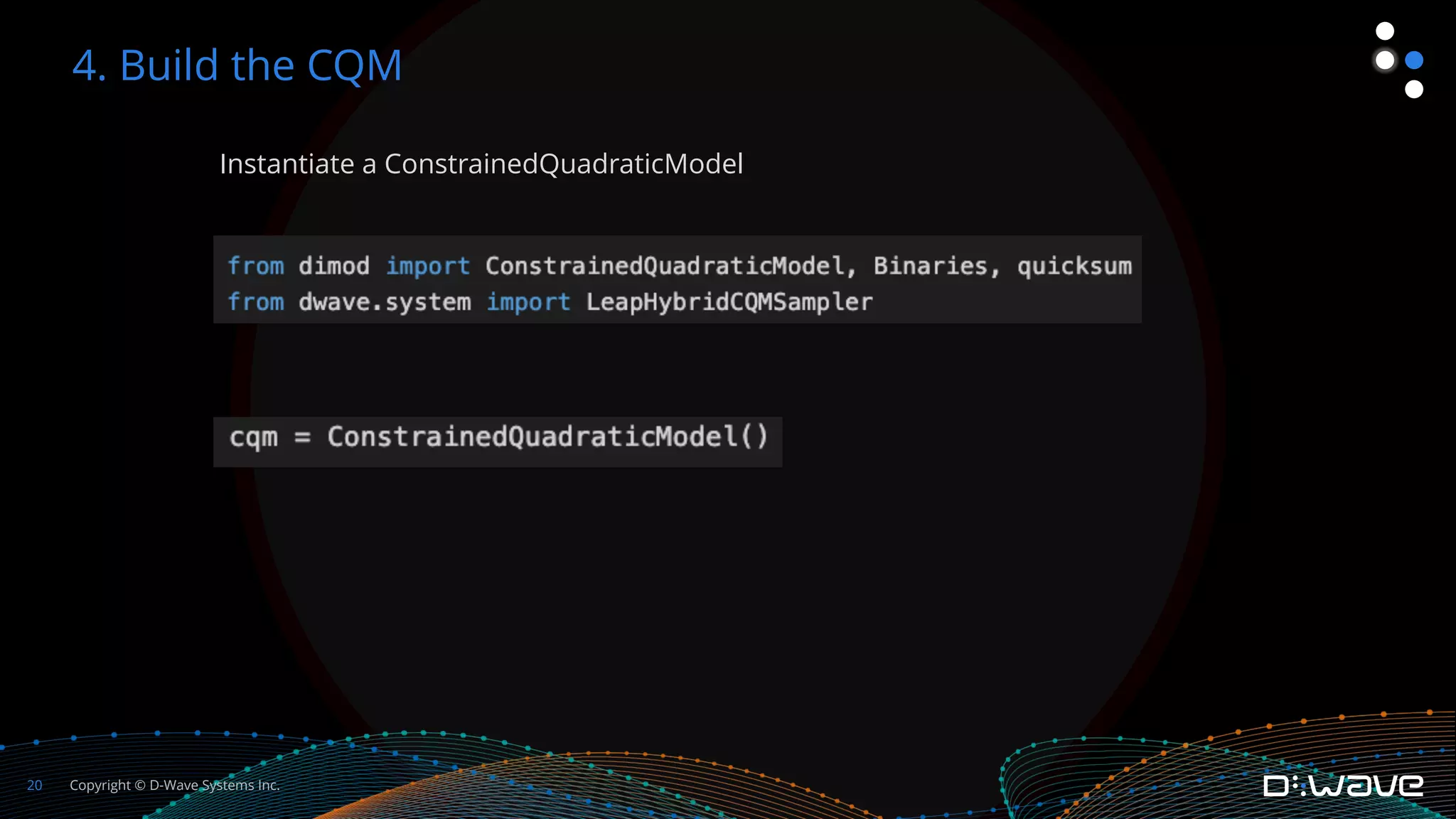
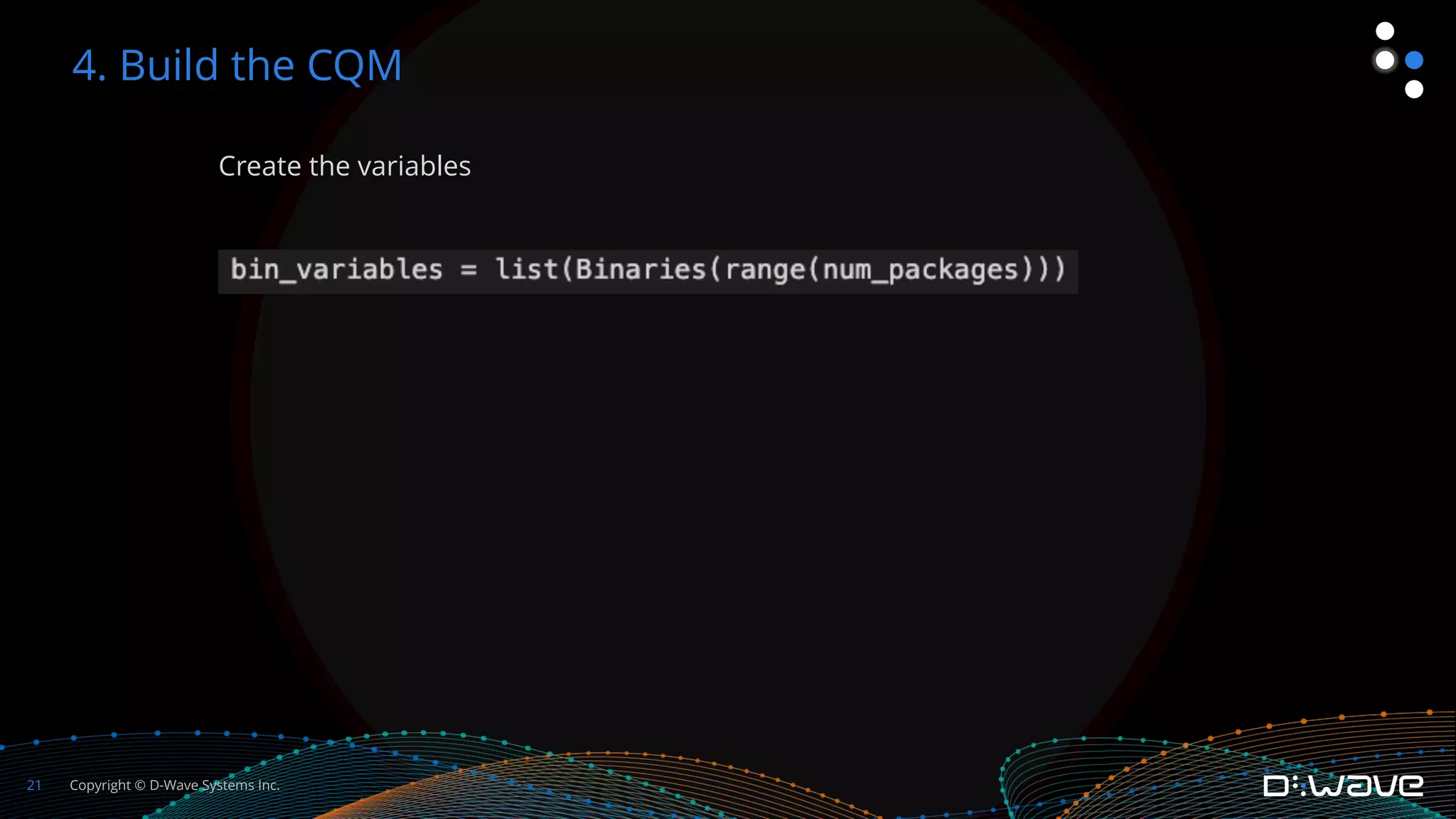
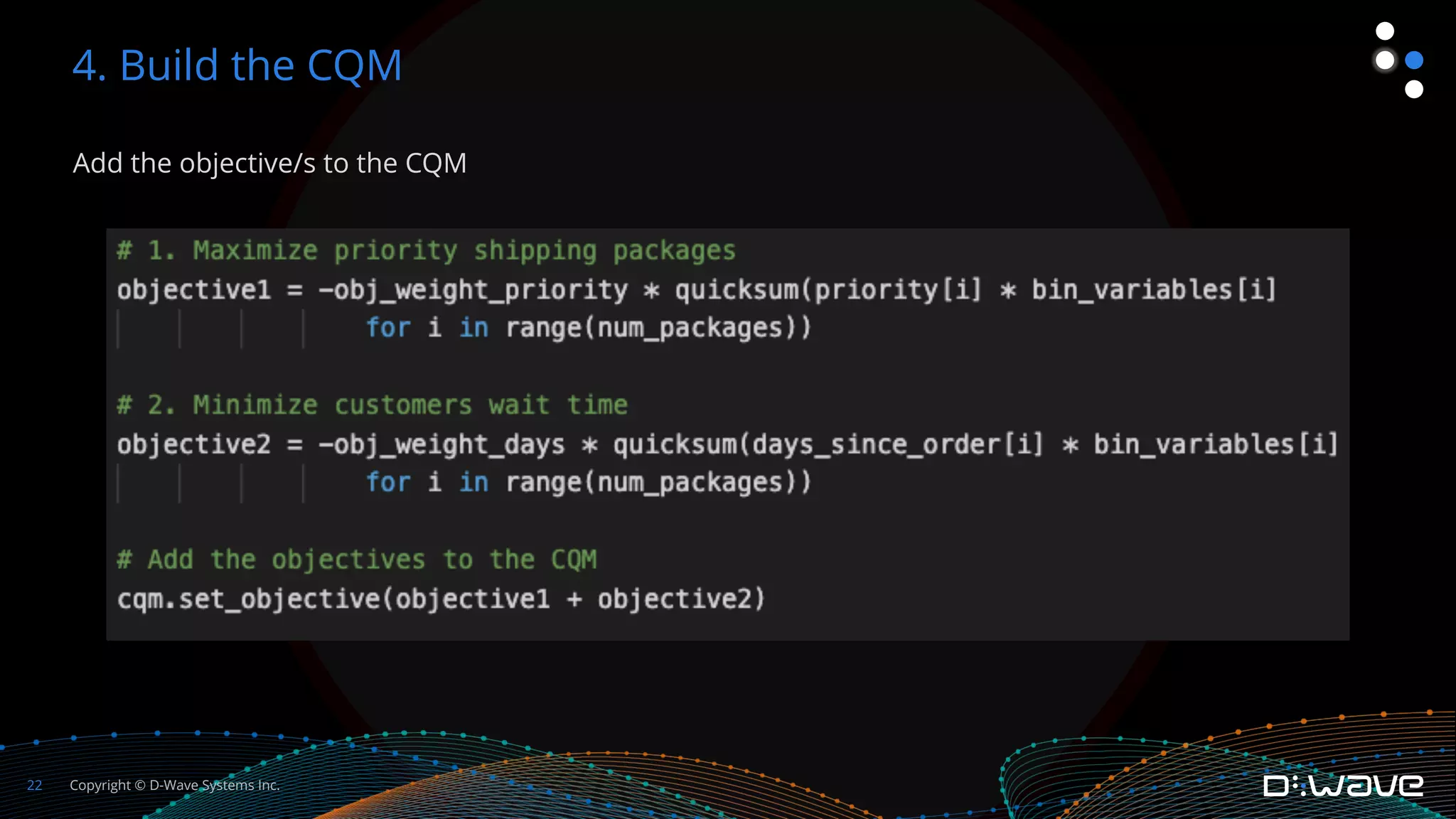
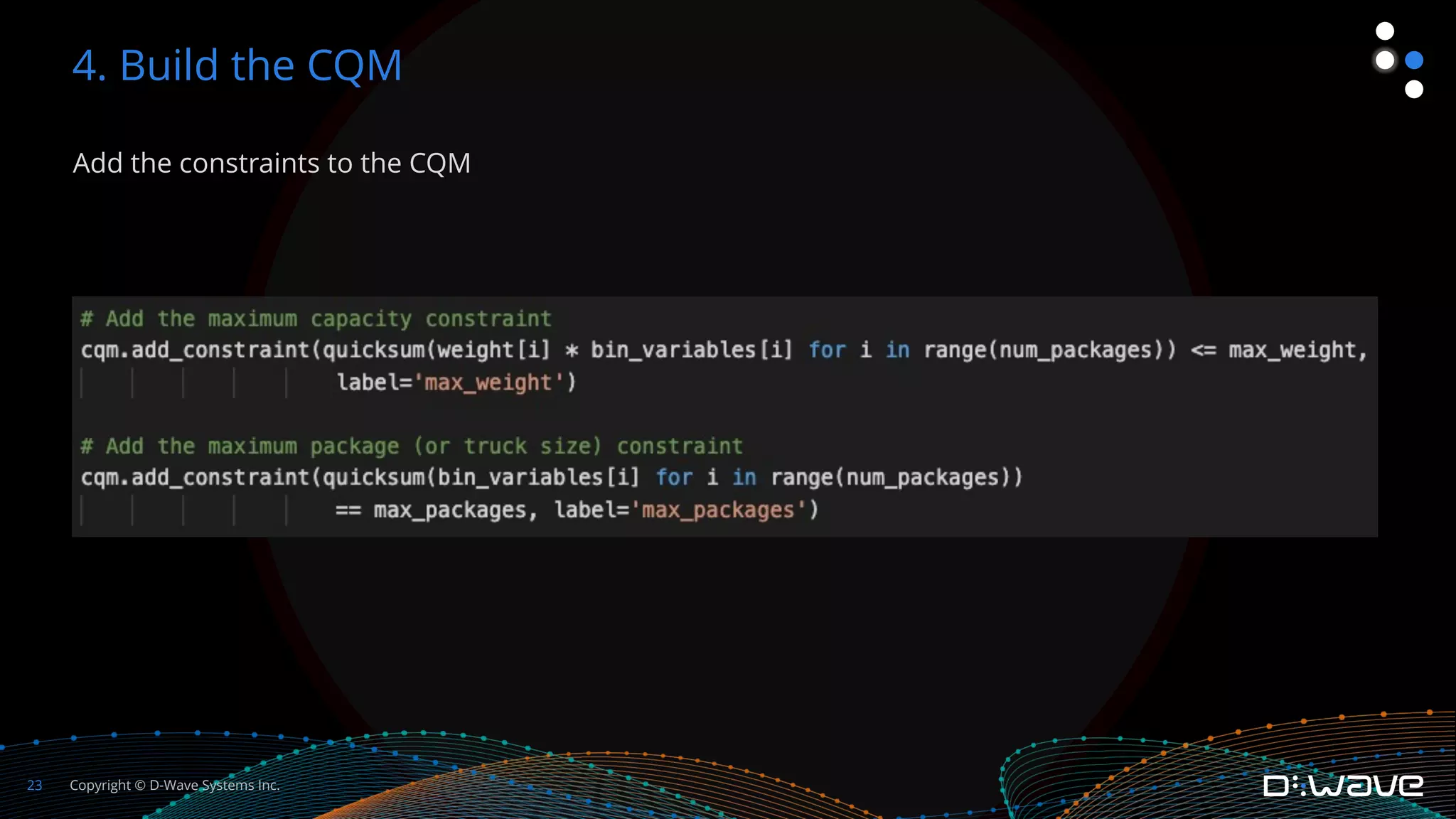
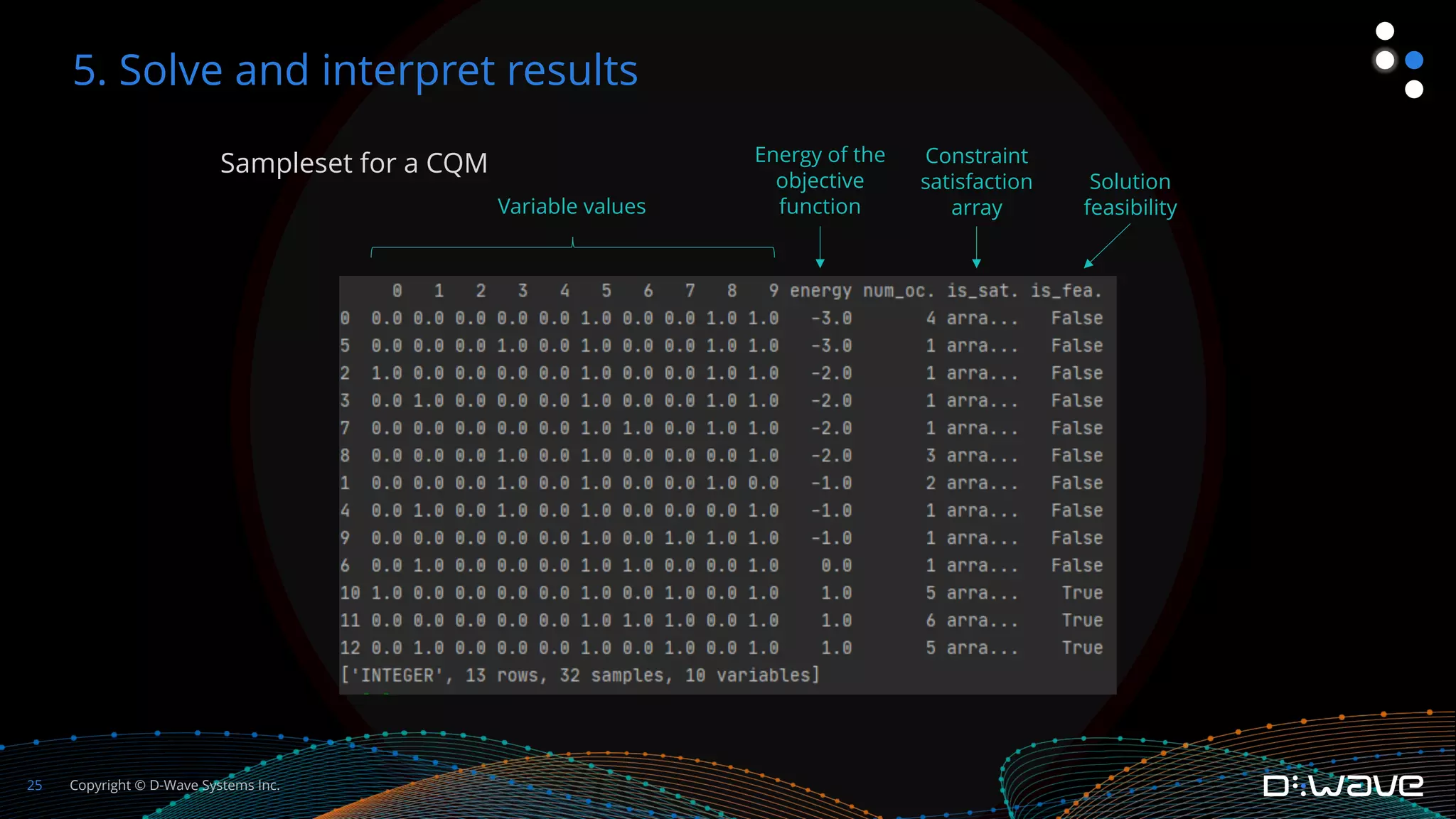
This document provides an overview of D-Wave Systems and quantum programming. It discusses D-Wave's quantum computing products and services, including their quantum computers, hybrid solvers, and developer tools. It then walks through an example of formulating a delivery truck packing problem as a constrained quadratic model (CQM) in order to solve it using D-Wave's quantum annealer. The steps include defining the objectives and constraints in plain language, specifying the variables, converting the objectives and constraints to mathematical statements, and building the full CQM in Ocean software. The document concludes by discussing how to solve the CQM and interpret the results.