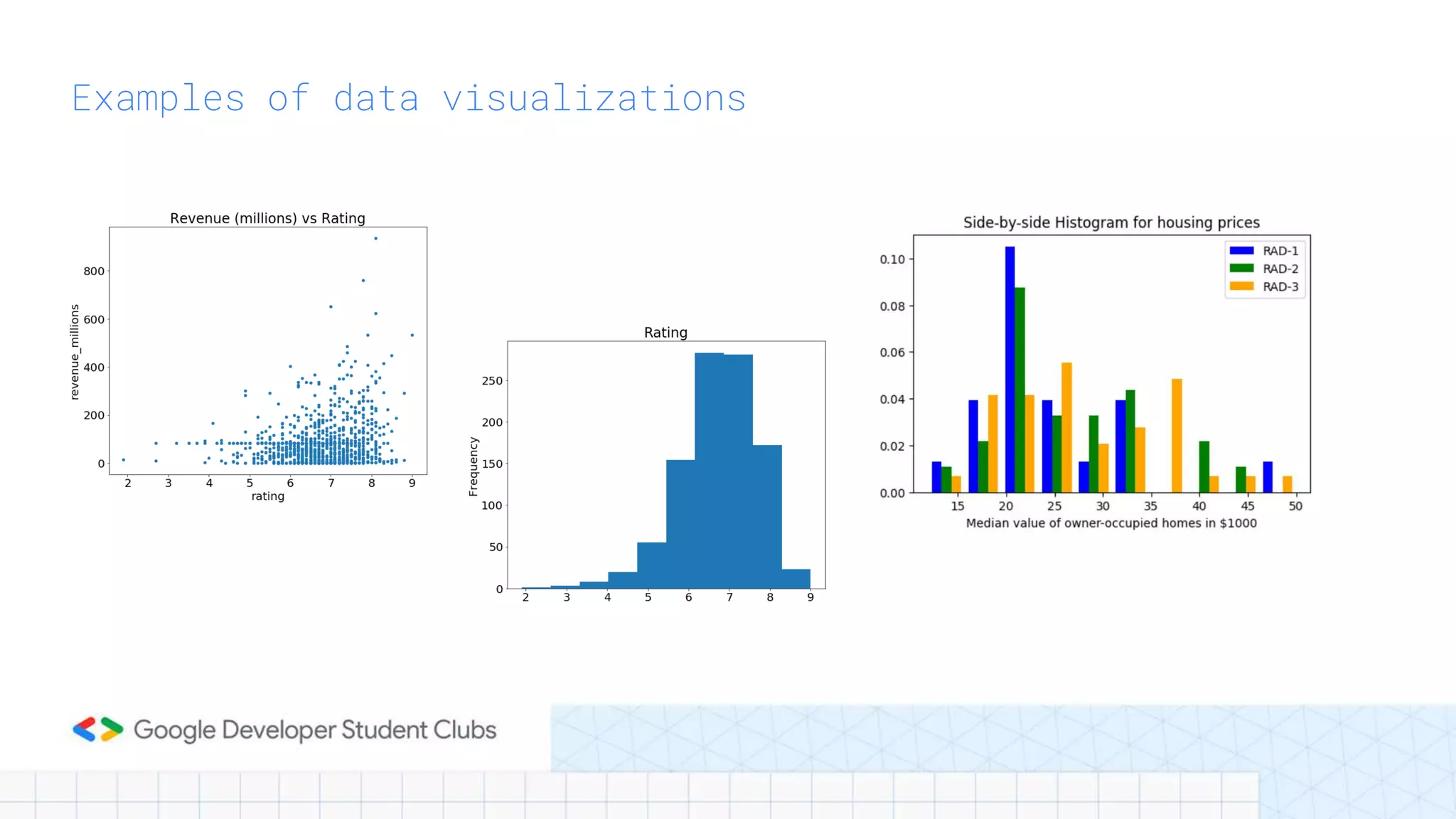
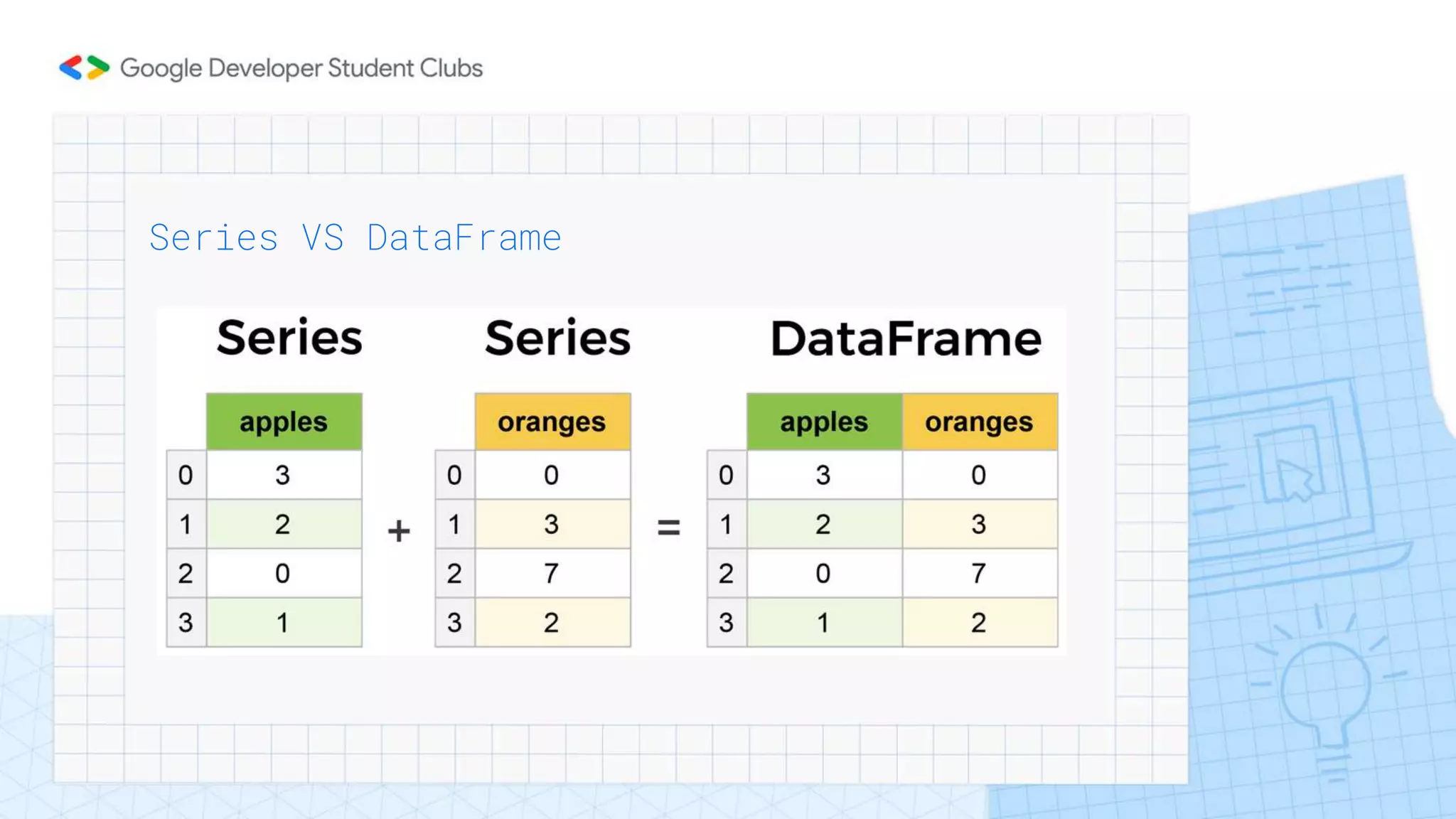
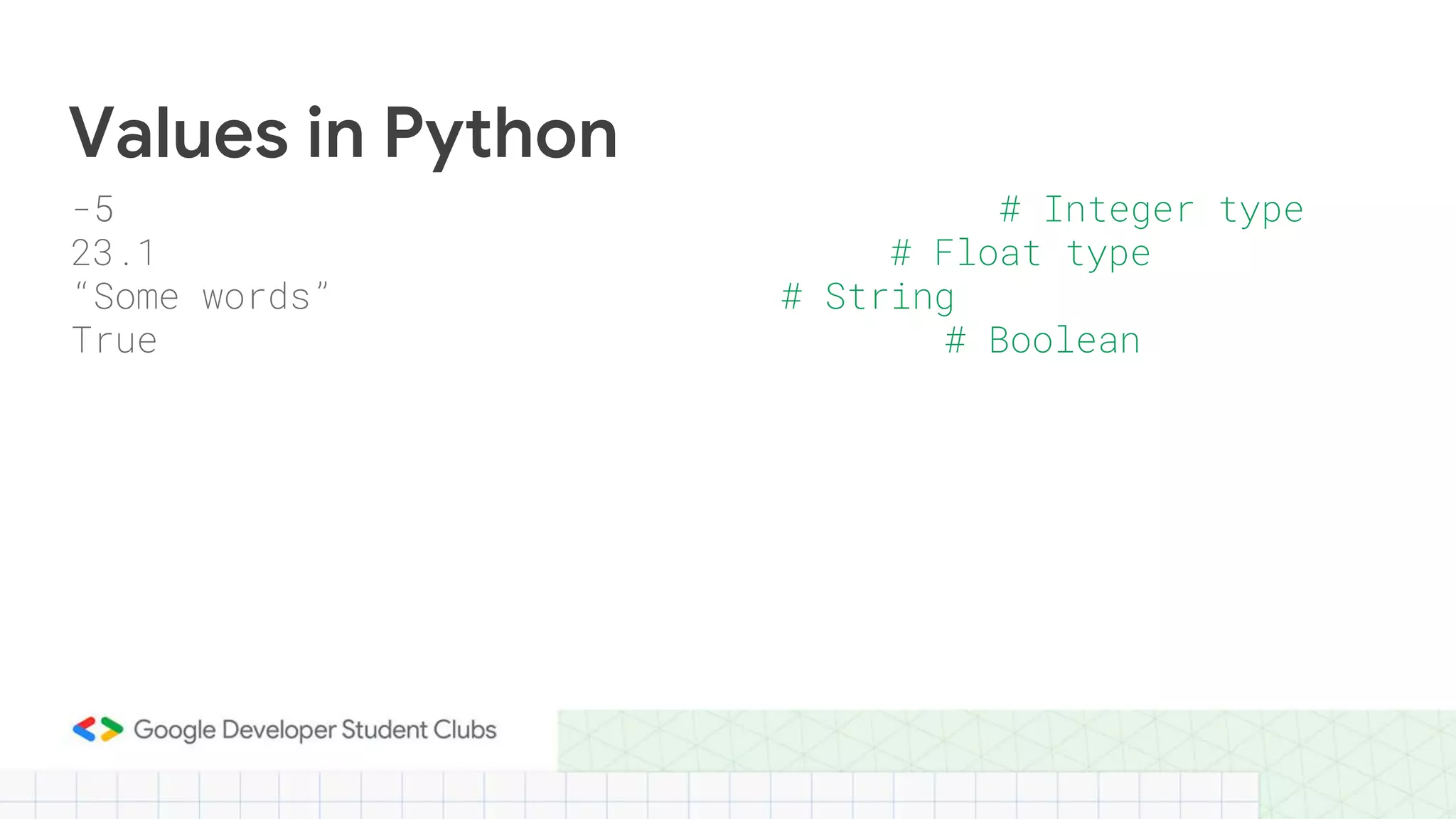
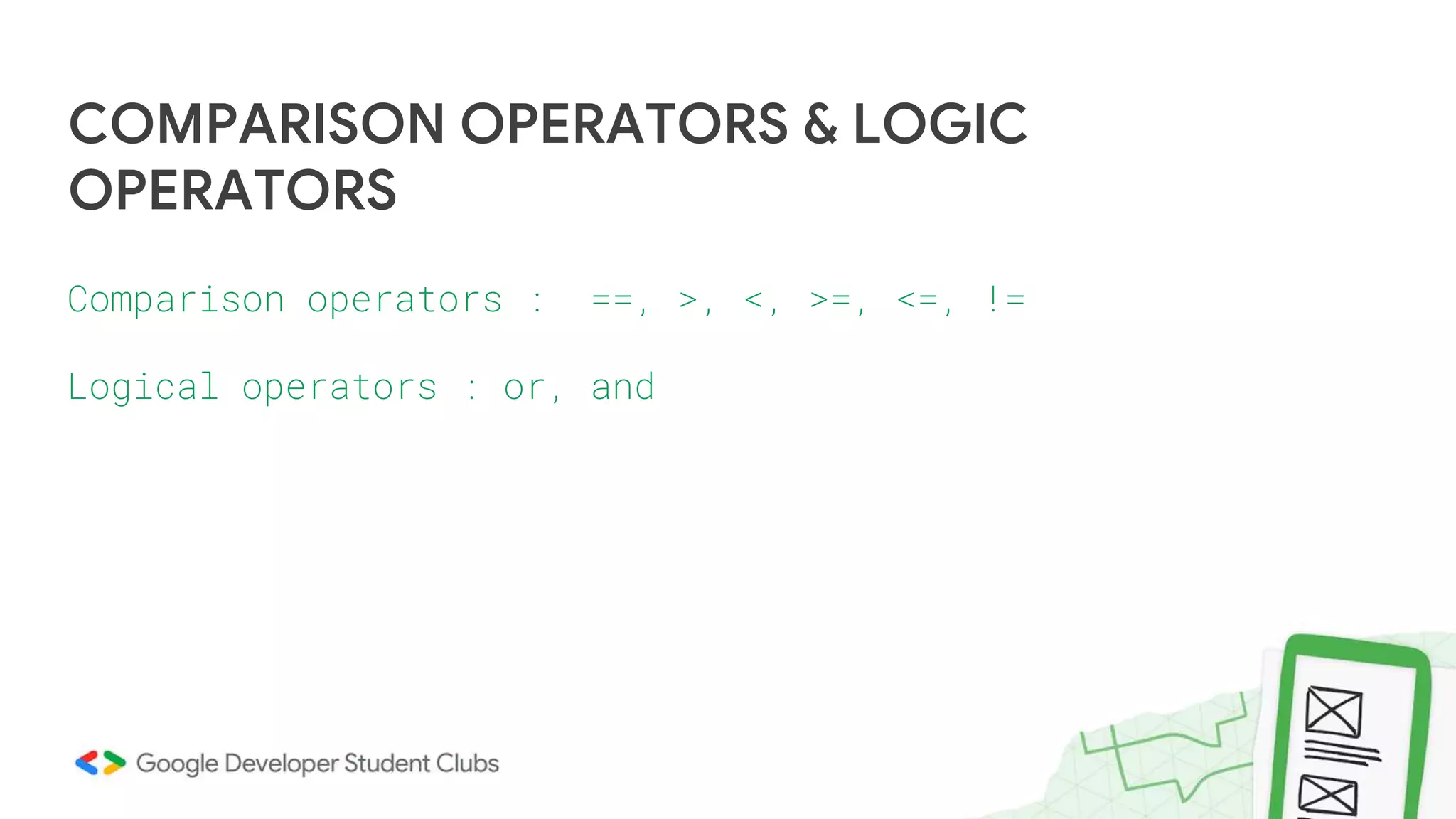
This document provides an introduction to Python and the Pandas library. It begins with an overview of Python, describing its history, key features like readability and cross-platform compatibility. It then covers Python basics like variables, data types, operators, conditional and loop statements. Object-oriented concepts are explained like classes, methods and functions. Key data structures are defined, including lists, tuples, dictionaries and sets. The document concludes with an introduction to Pandas, describing its use for data analysis, cleaning, transformation and visualization.




![public class Main {
public static void main(String[]
args) {
System.out.println(“Hello
World”);
}
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
printf(“Hello world”);
return 0;
}
JAVA C
>>> print(“Hello world!”)
PYTHON
Hello world!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python101-221203131403-73a89254/75/PYTHON-101-pptx-6-2048.jpg)







![In Python, lists are ordered collections of items that
allow for easy use of a set of data
List values are placed in between square brackets [ ] ,
separated by commas.
My_list = [1, 12, 7, 3, 3]
Lists](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python101-221203131403-73a89254/75/PYTHON-101-pptx-16-2048.jpg)
![Python Lists: Data types
In Python, lists are a versatile data type that can
contain multiple different data types within the same
square brackets. The possible data types within a list
include numbers, strings, other objects, and even other
Lists.
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 10]
names = ['Jenny', 'Sam', 'Alexis']
mixed = ['Jenny', 1, 2]
list_of_lists = [['a', 1], ['b', 2]]
Learn more about lists in the notebook](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python101-221203131403-73a89254/75/PYTHON-101-pptx-17-2048.jpg)