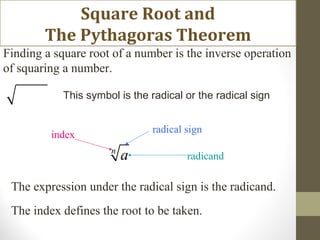
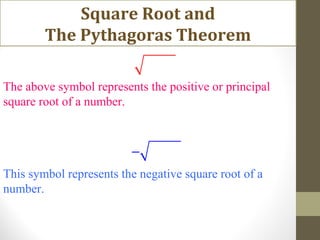
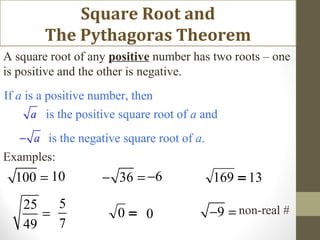
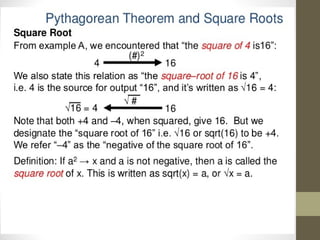
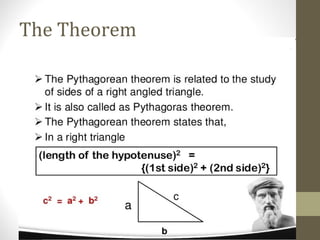
The document discusses square roots and the Pythagorean theorem. It defines square roots, their notation, and provides examples of calculating positive and negative square roots. It then gives a brief history of Pythagoras, noting that he was a Greek mathematician born in 570 BCE who studied in Egypt and made many contributions to mathematics, including proving what is now known as the Pythagorean theorem. The theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.