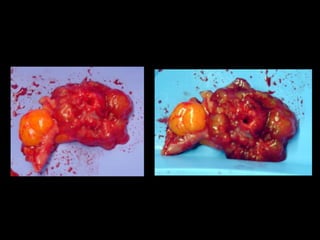
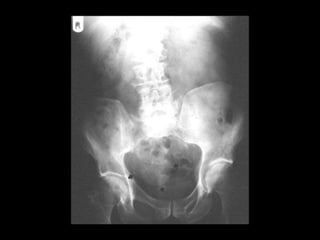
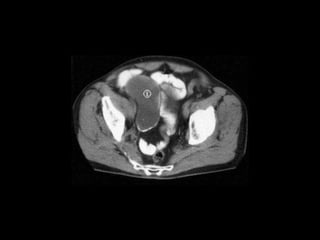
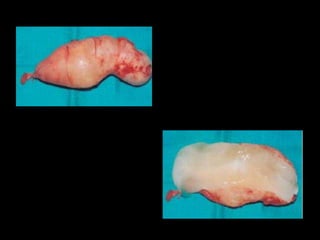
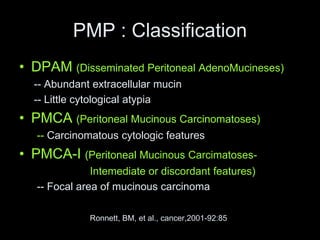
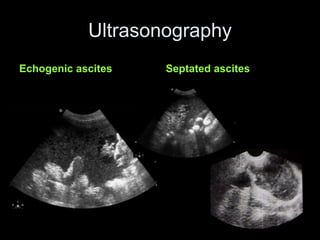
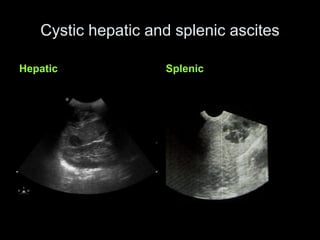
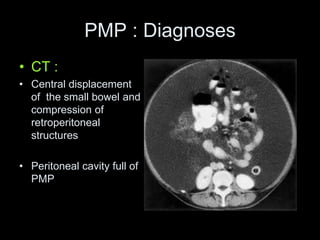
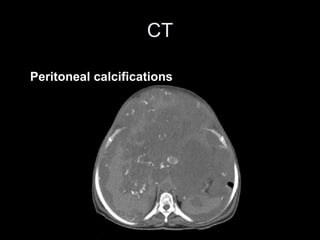
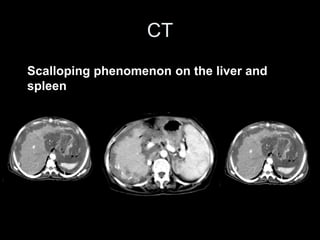
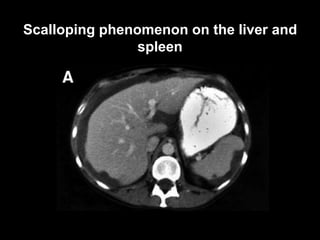
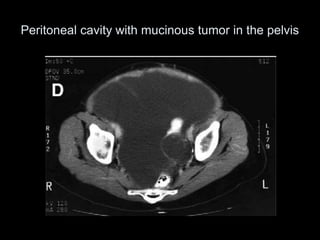
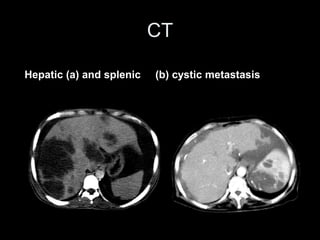
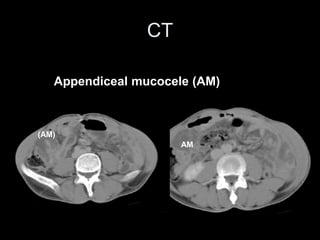
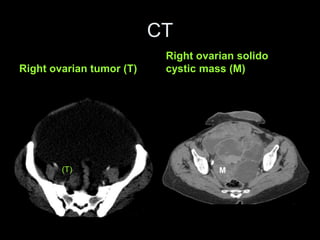
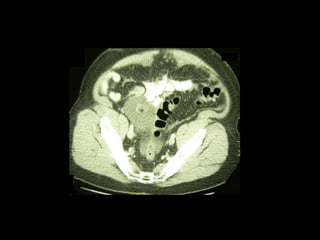
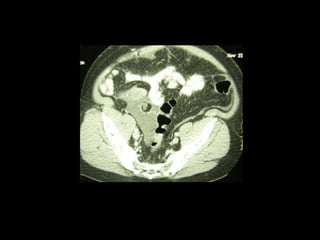
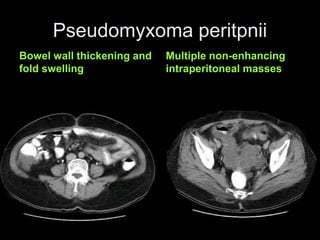
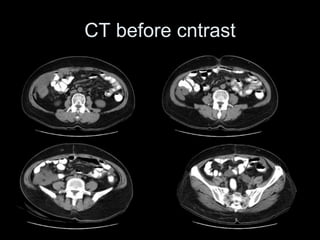
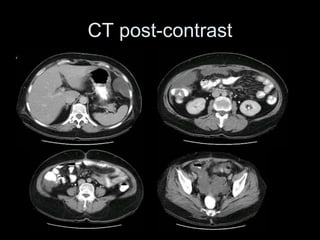
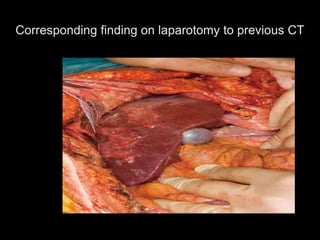
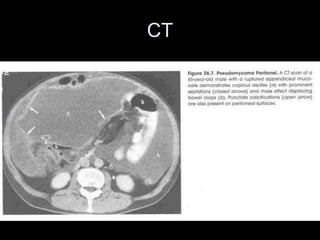
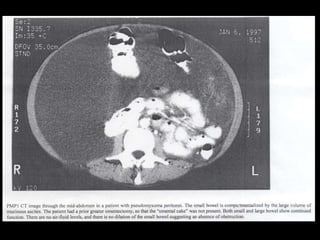
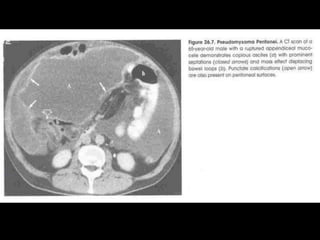
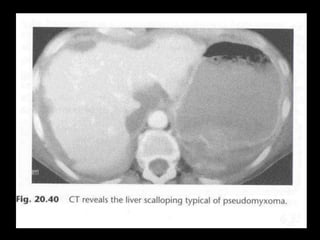
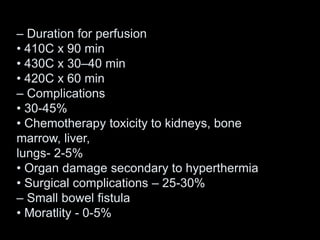
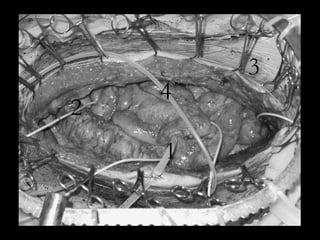
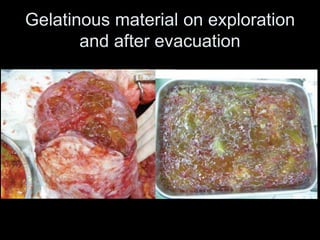
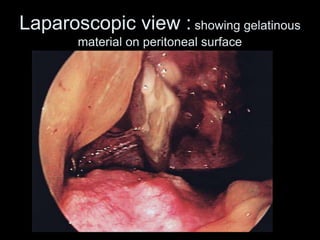
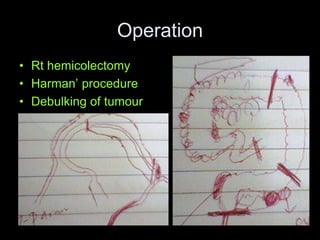
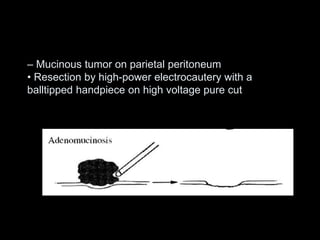
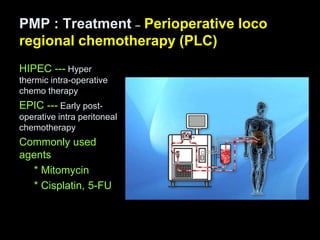
Pseudomyxoma peritonei (PMP) is a rare condition characterized by gelatinous ascites resulting from the rupture of appendiceal mucinous tumors, leading to significant abdominal complications. The incidence is approximately 2 cases per million per year, with a predominance in females, and diagnosis often relies on imaging techniques like ultrasound and CT scans. Effective treatment involves cytoreductive surgery combined with hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) to manage disease progression and improve outcomes.