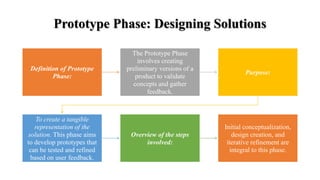
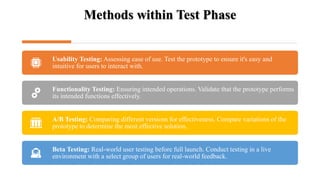
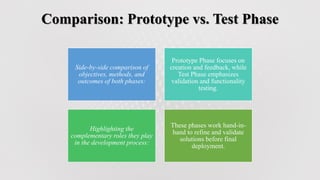
The document discusses the prototype and test phases in solution design. The prototype phase focuses on creating initial versions of a solution to gather feedback, using methods like wireframing, rapid prototyping, and user testing. The test phase then validates the effectiveness and functionality of the prototype, ensuring it meets user needs through usability testing, functionality assessment, and identifying flaws before final deployment. Together these phases provide iterative refinement and user validation critical to the development process.