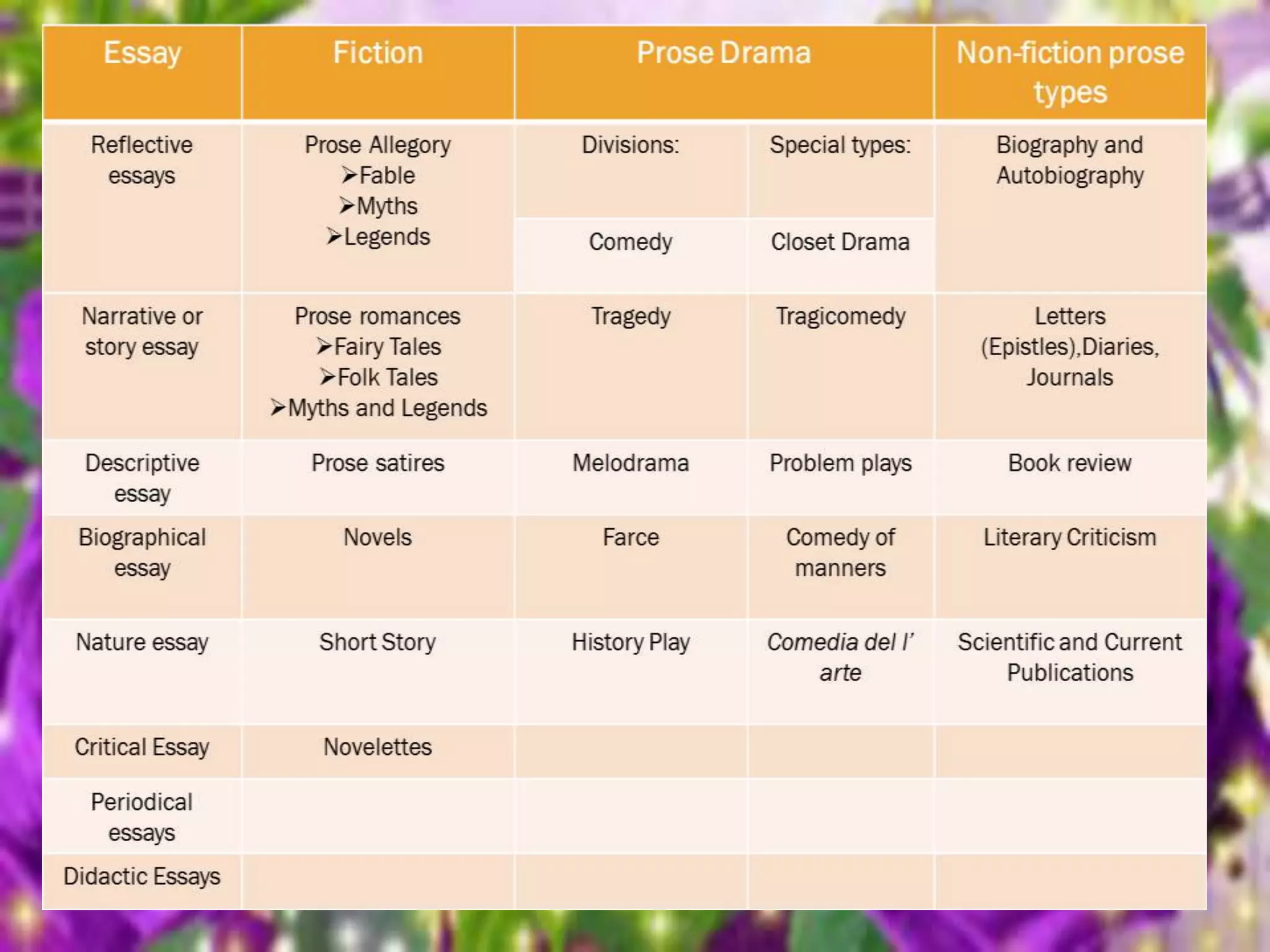
The document discusses various types and forms of prose literature. It describes essays as short compositions dealing with a single subject from a personal perspective, and lists different types of essays including reflective, narrative, descriptive, and critical. It also outlines several types of fiction such as allegory, fables, myths, legends, romances, satires, novels, short stories, novelettes, and drama. Finally, it briefly mentions several non-fiction prose forms like biography, letters, reviews, criticism, and scientific works.