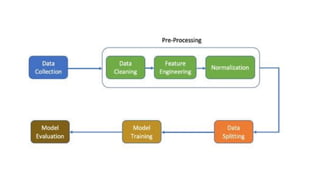
This project aims to develop an intelligent system for earthquake prediction using machine learning models. The system will be trained on a dataset containing records of 782 past earthquakes from 2001 to 2023, including attributes like magnitude, date, location, and intensity. It will evaluate different algorithms on a test set to identify the best-performing model for predicting future earthquakes. The model could help save lives and reduce damage by providing more accurate earthquake forecasts.