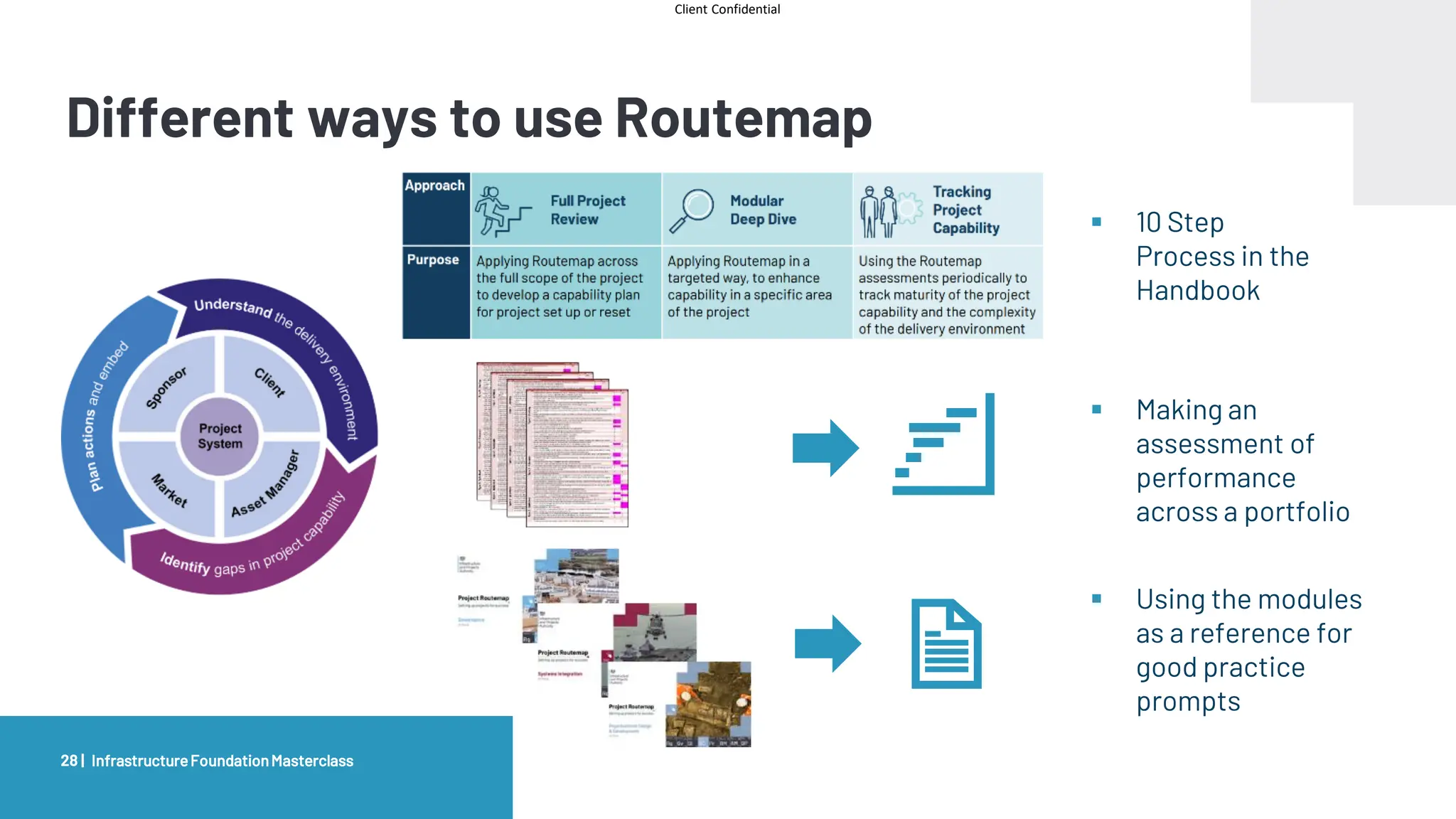
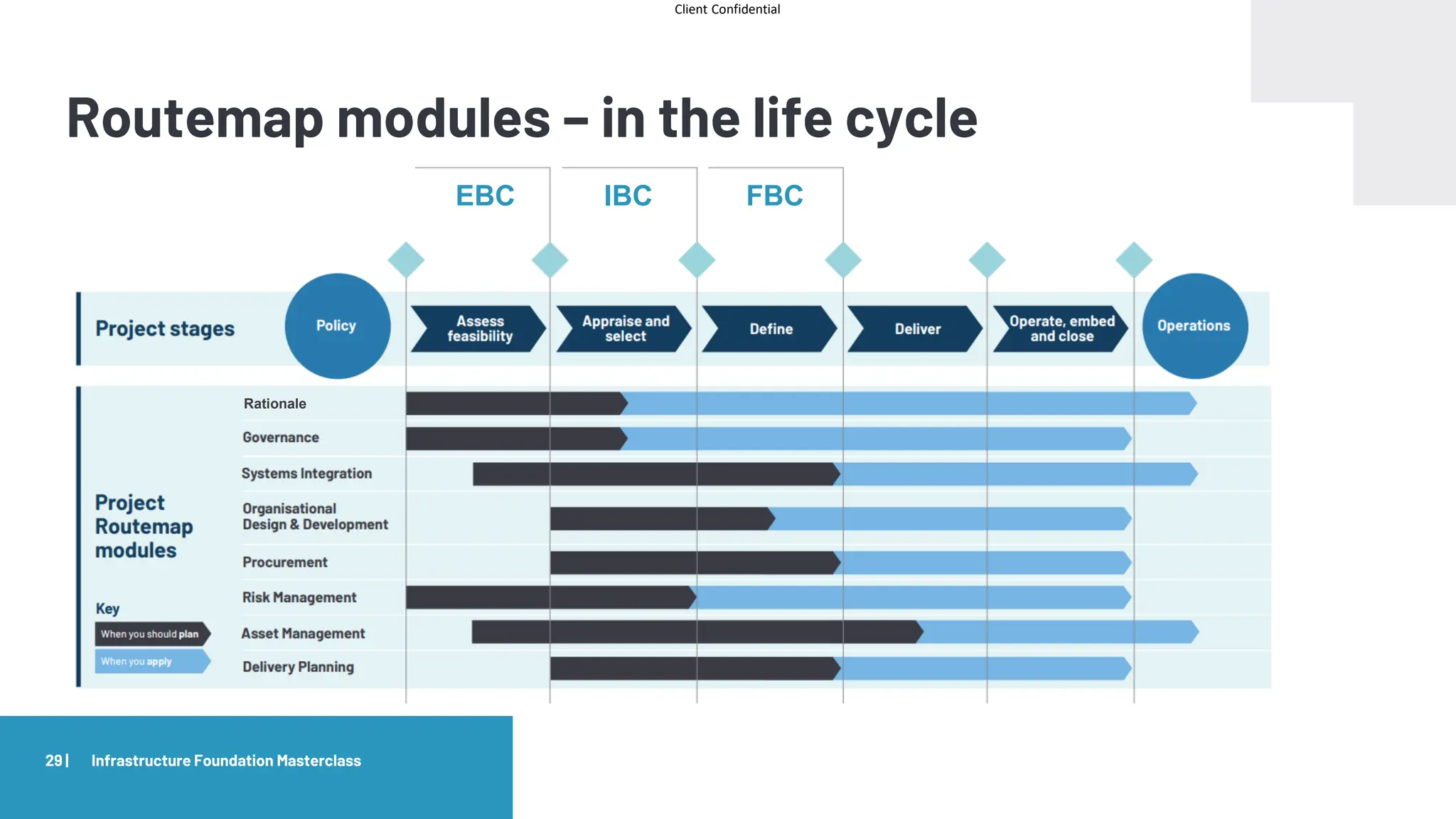
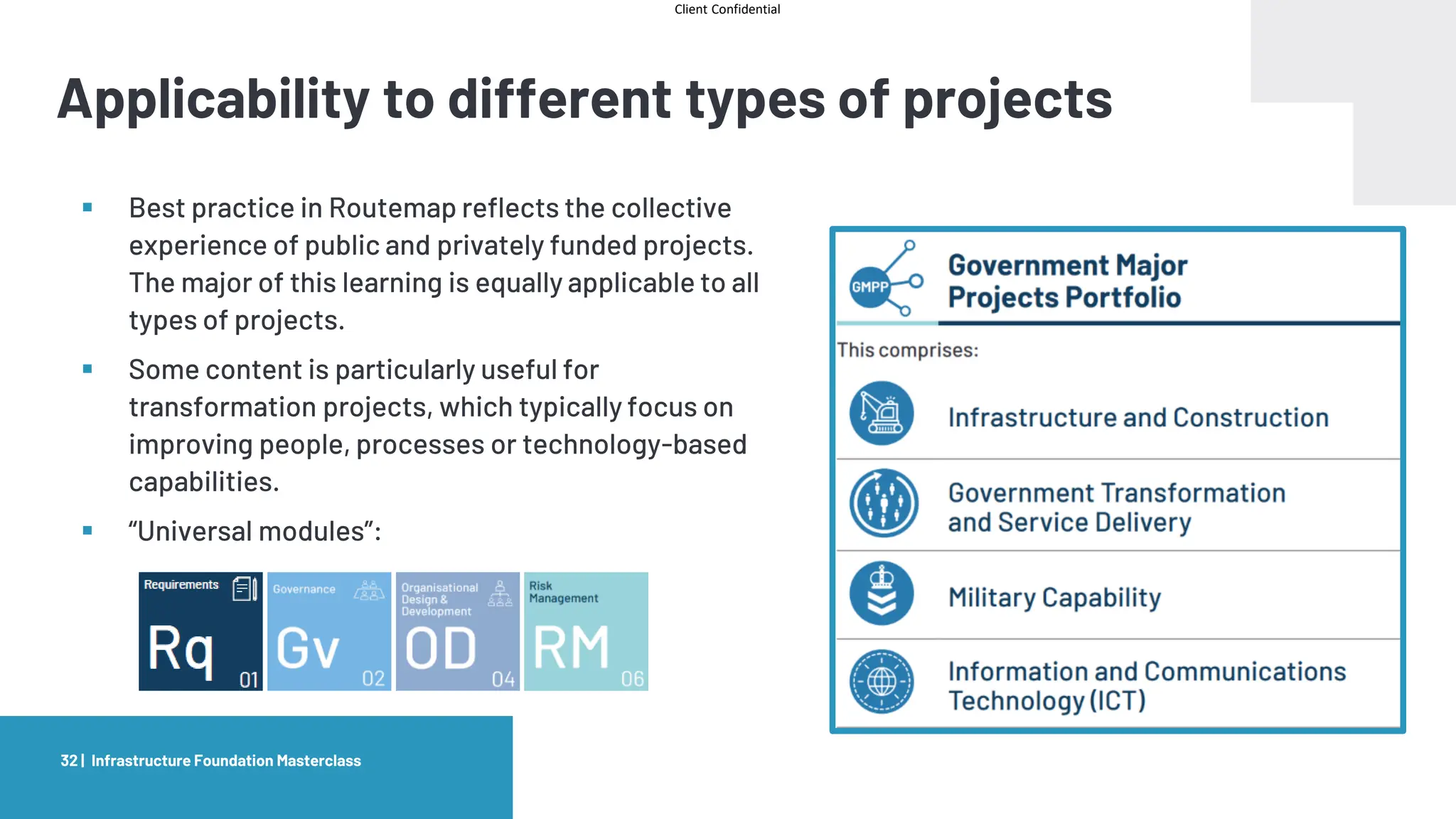
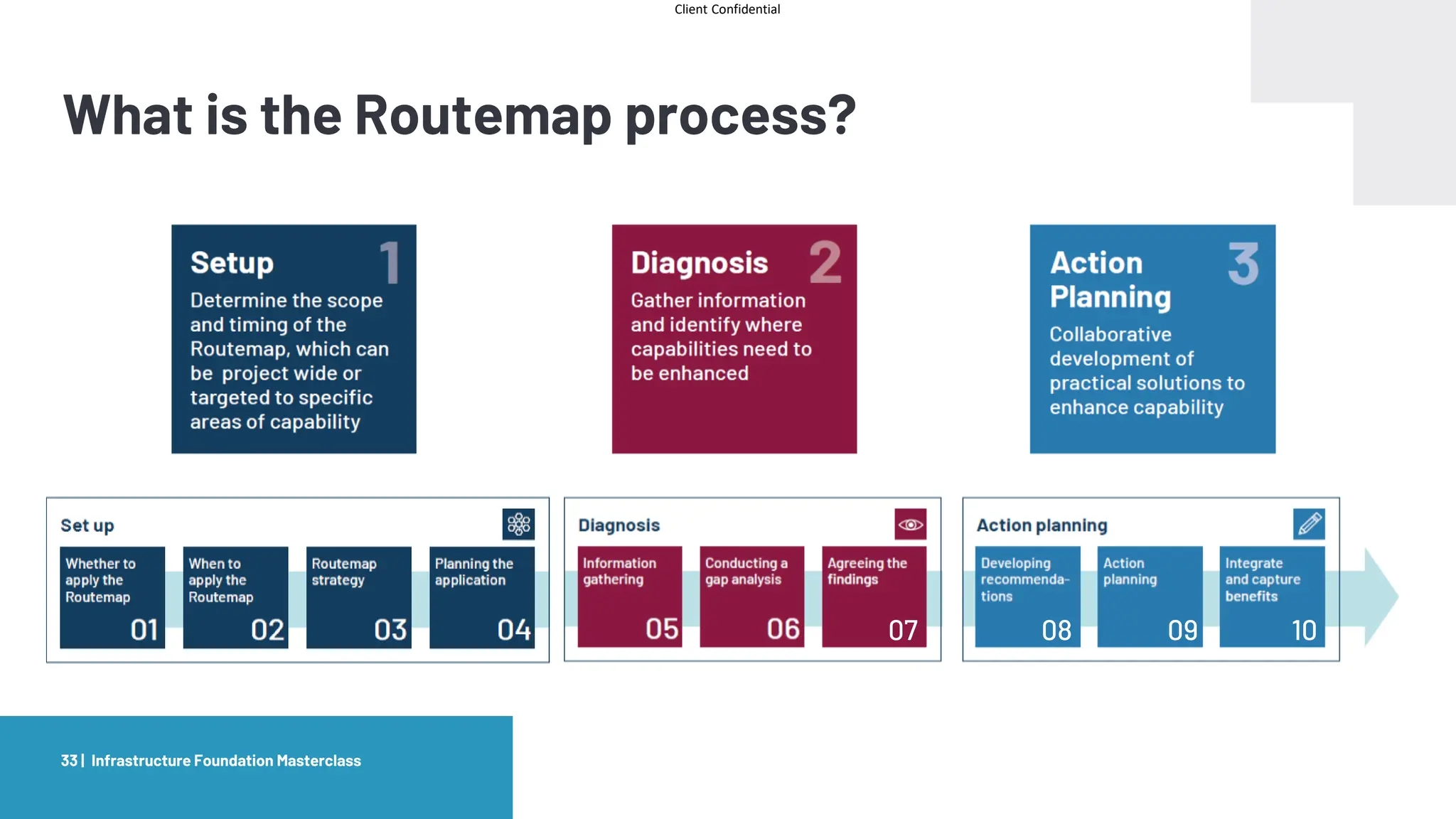
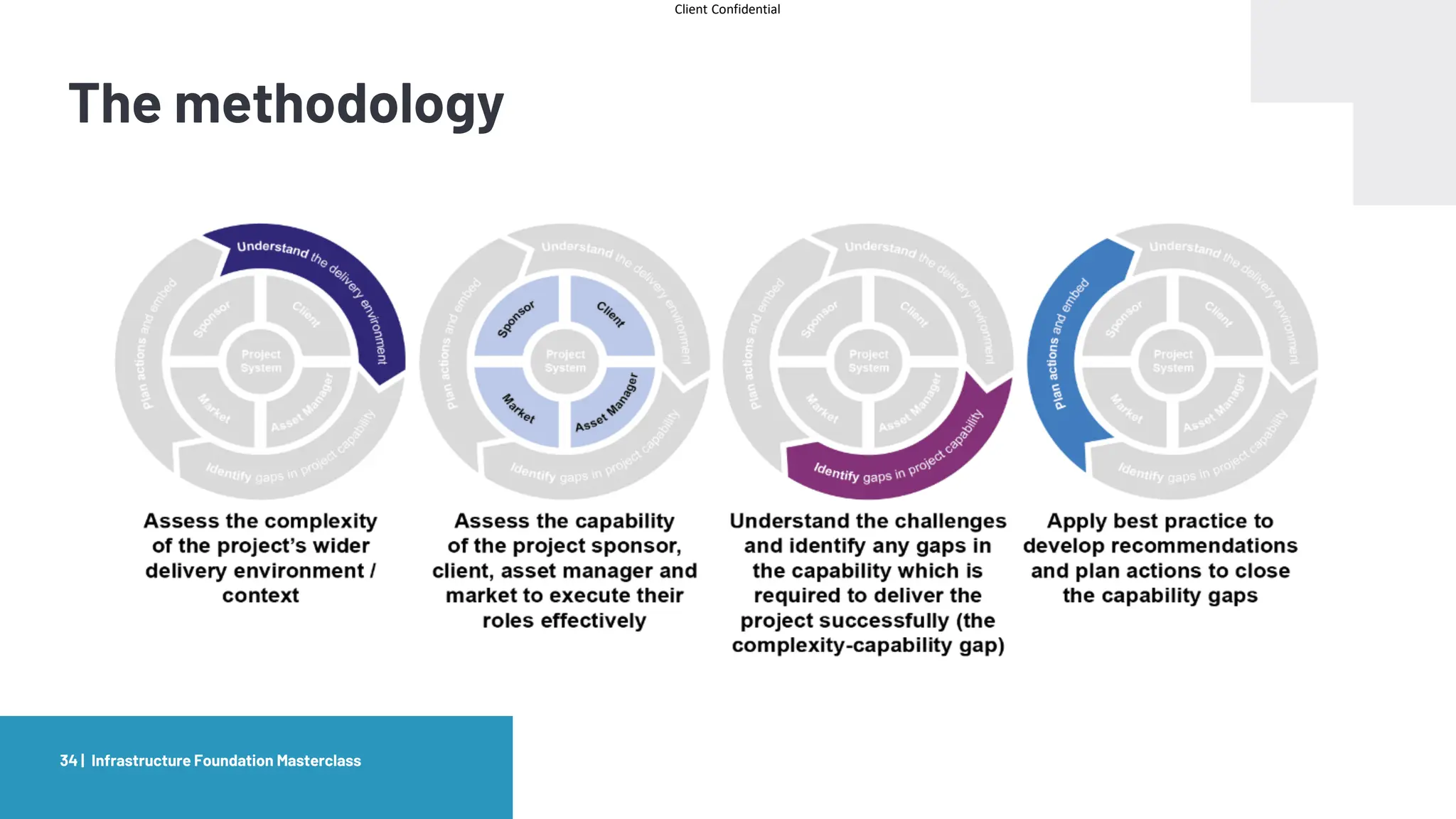
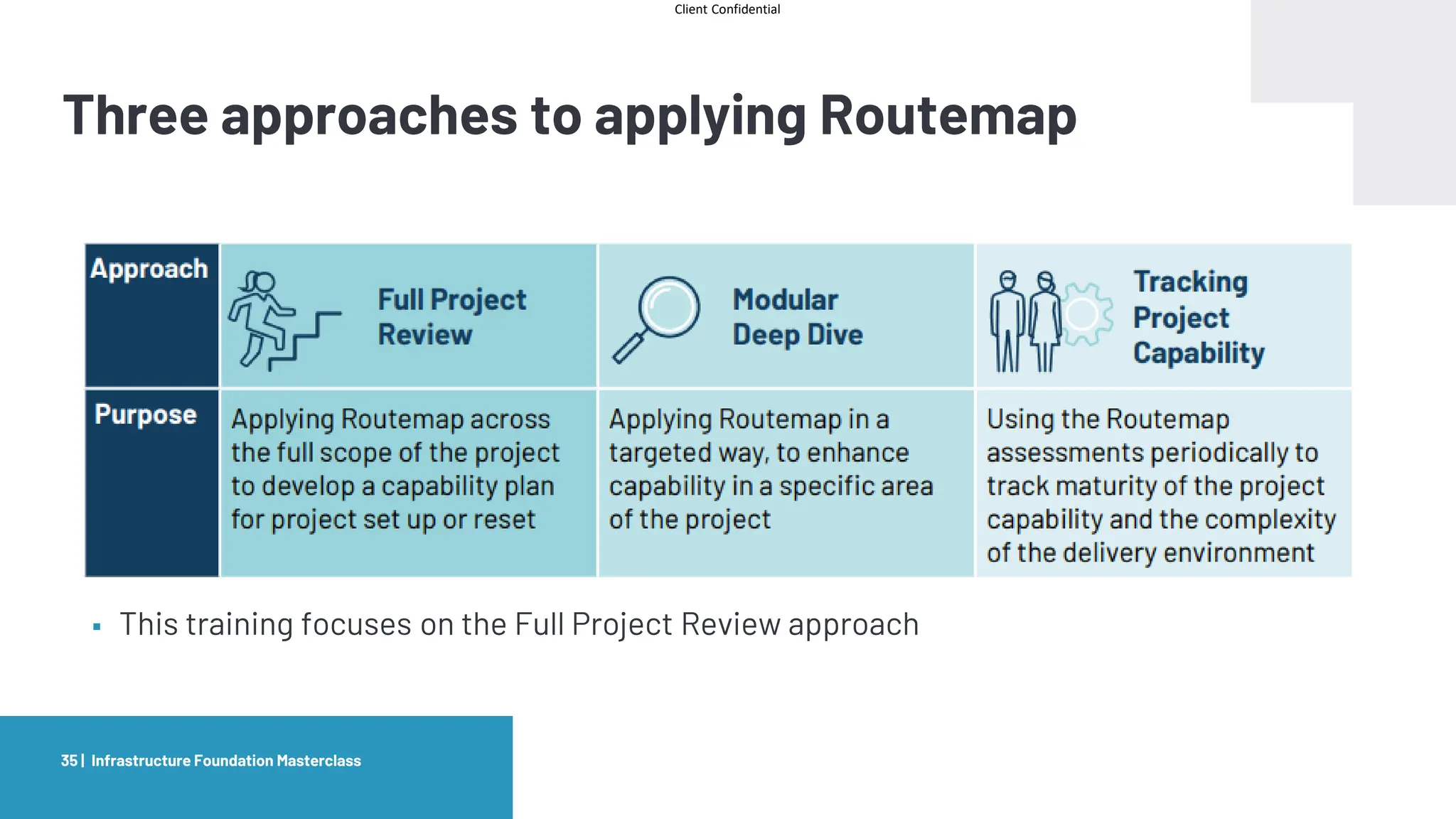
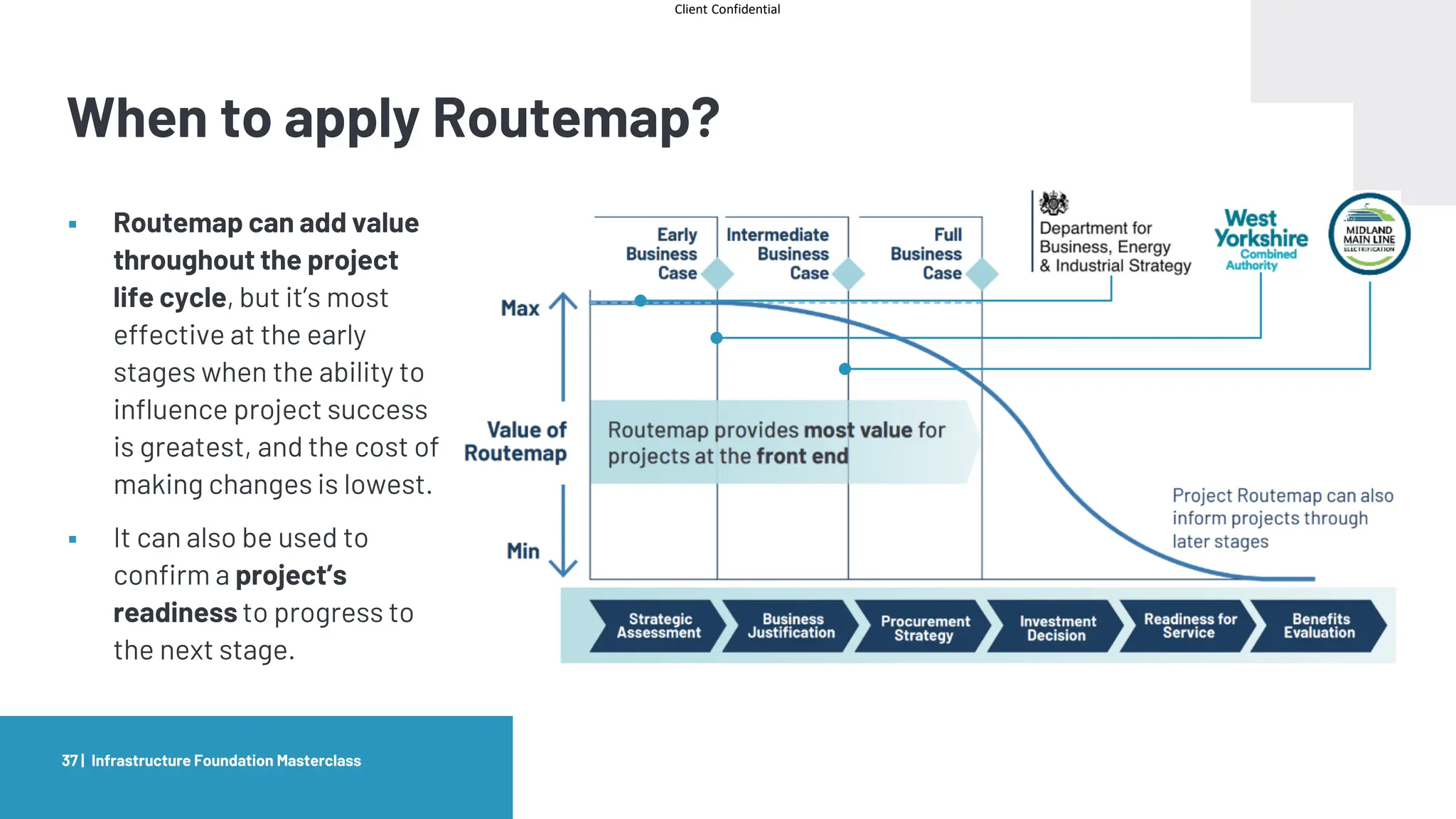
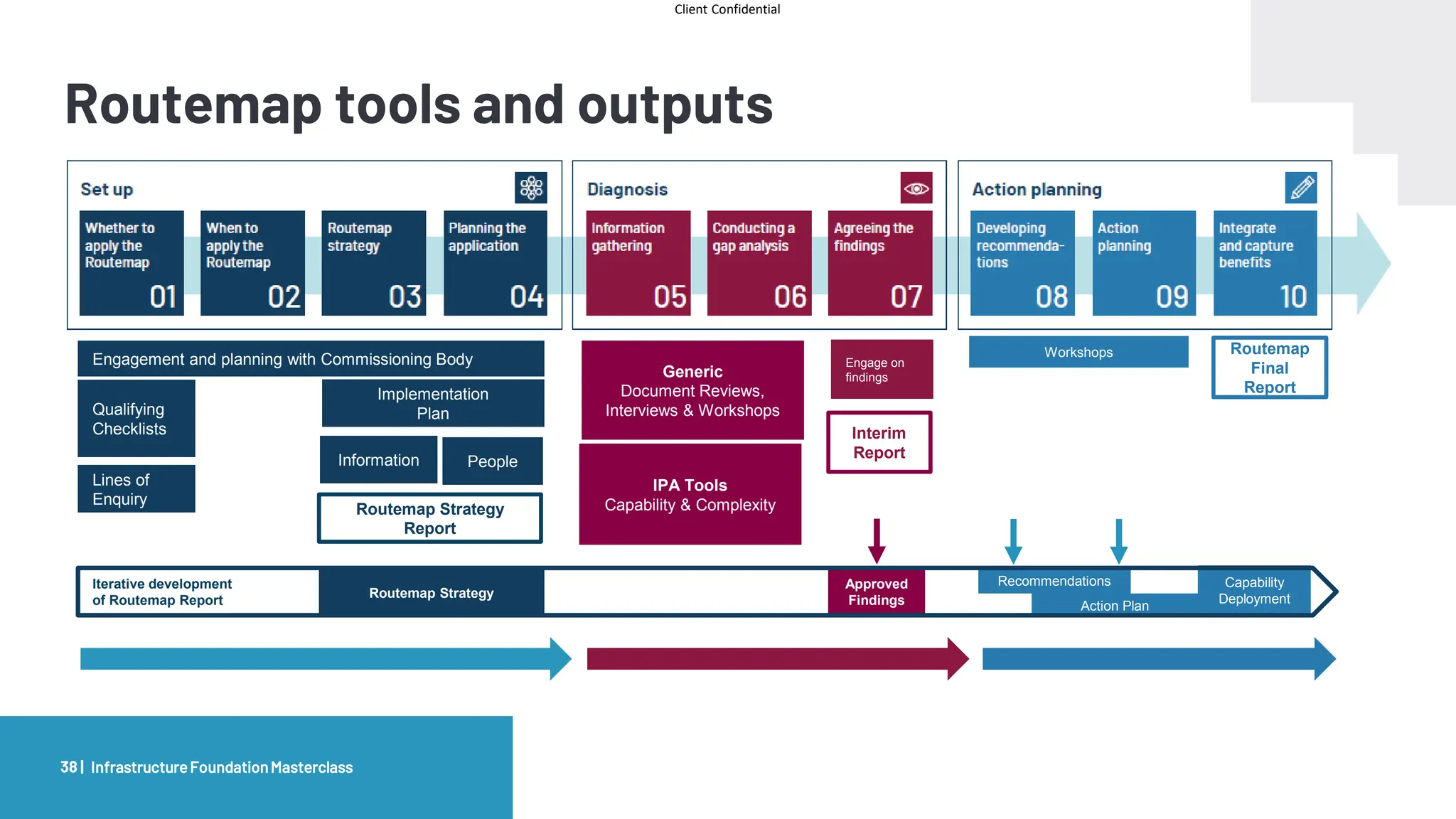
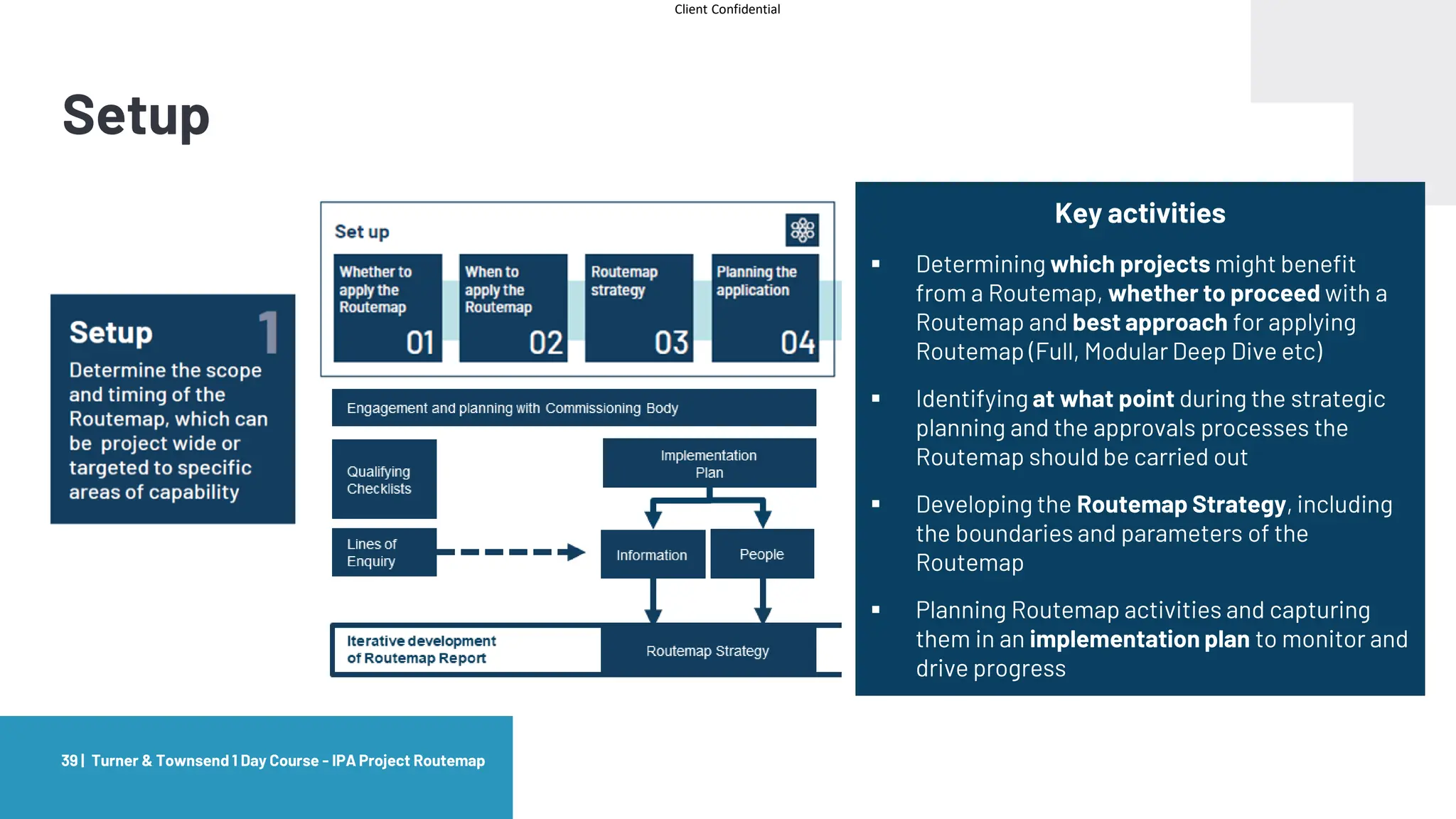
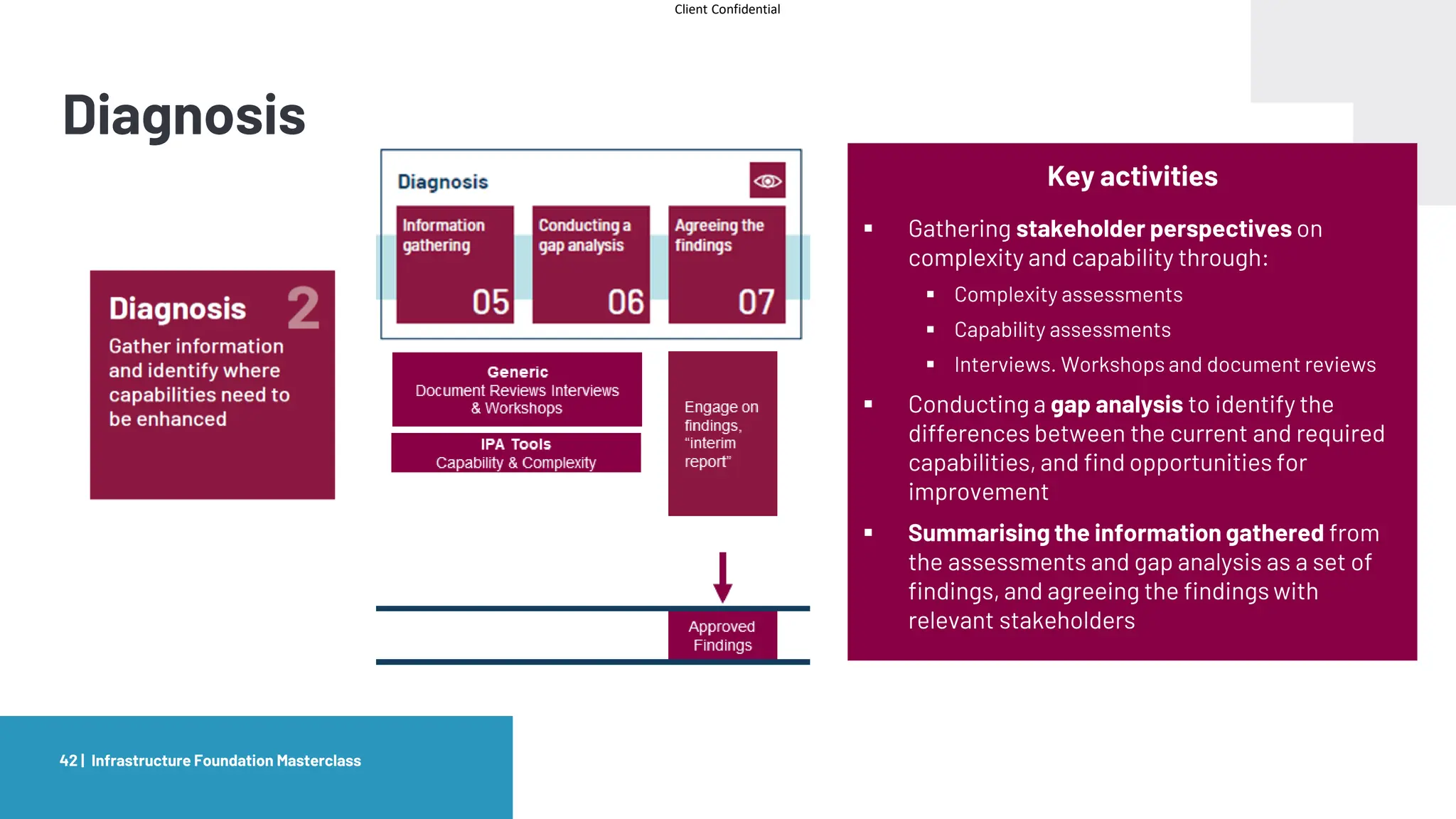
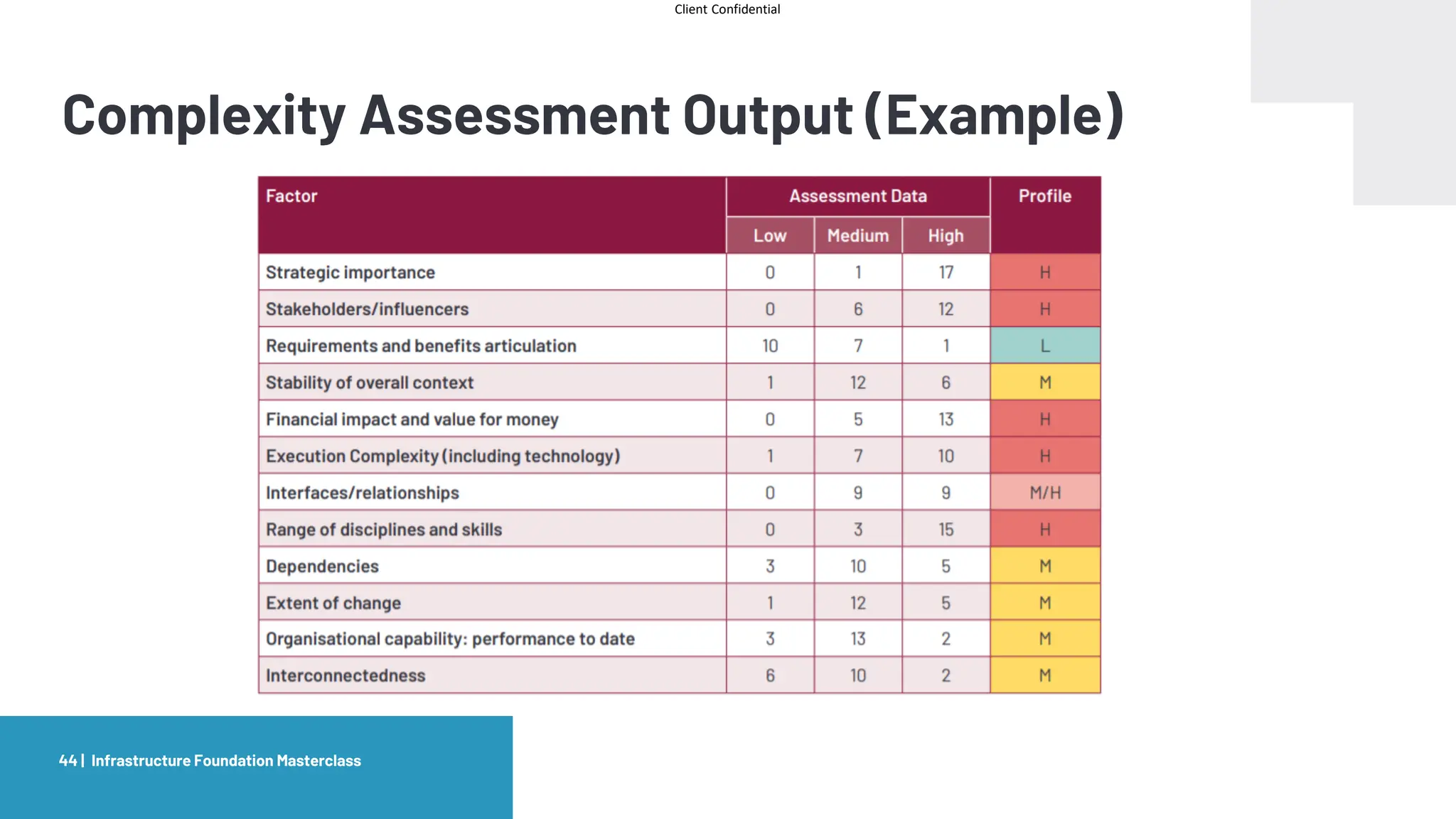
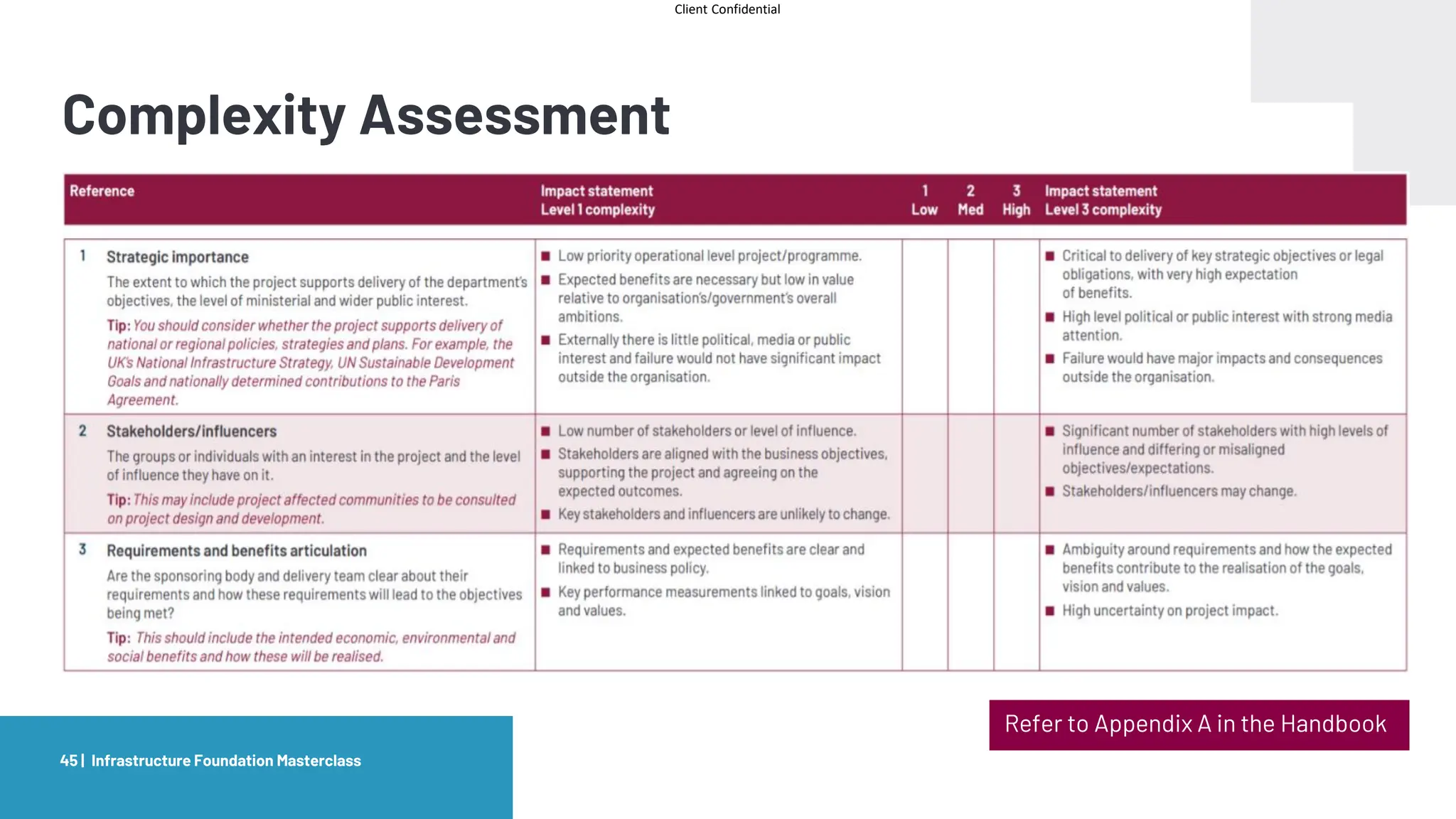
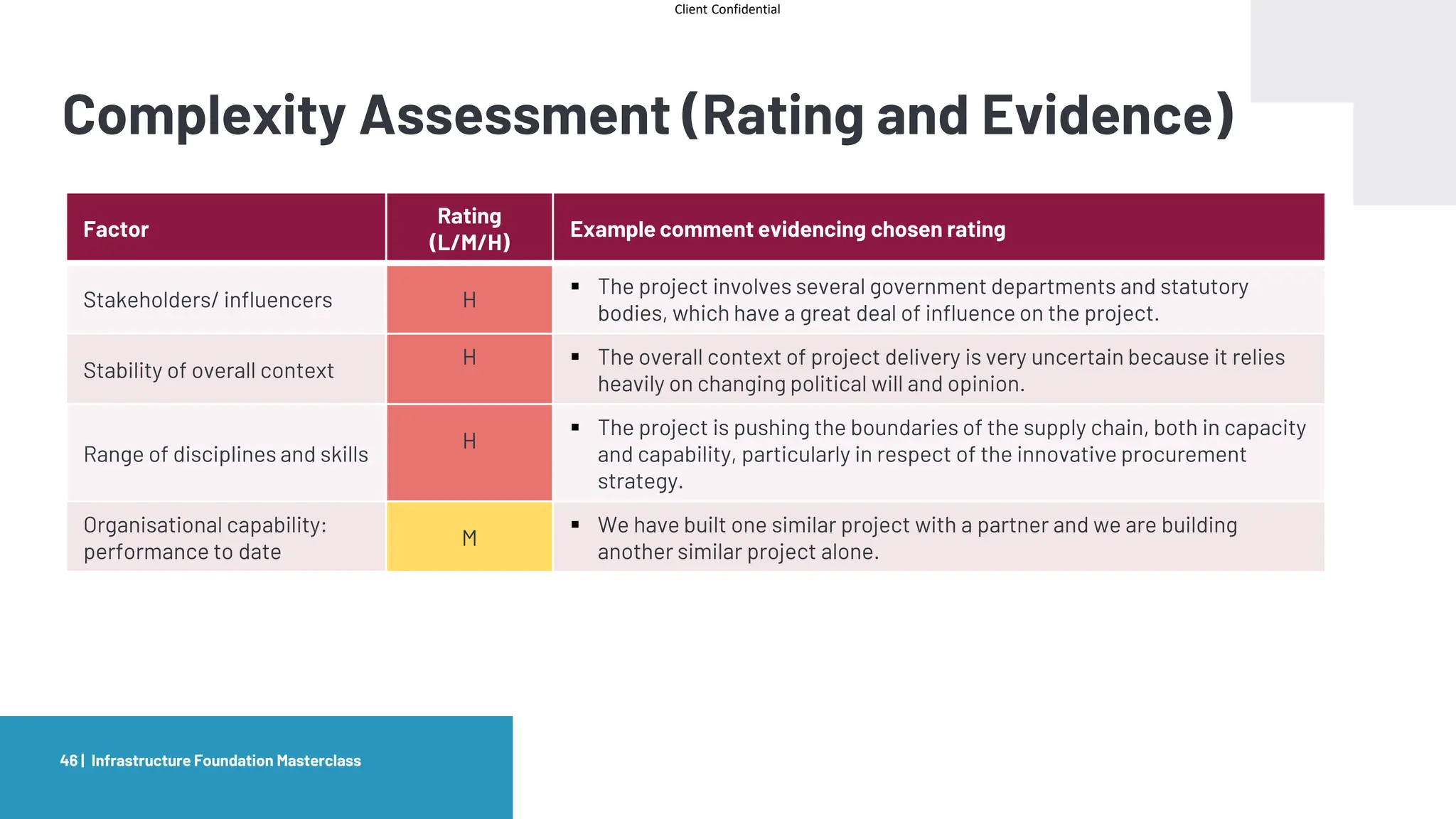
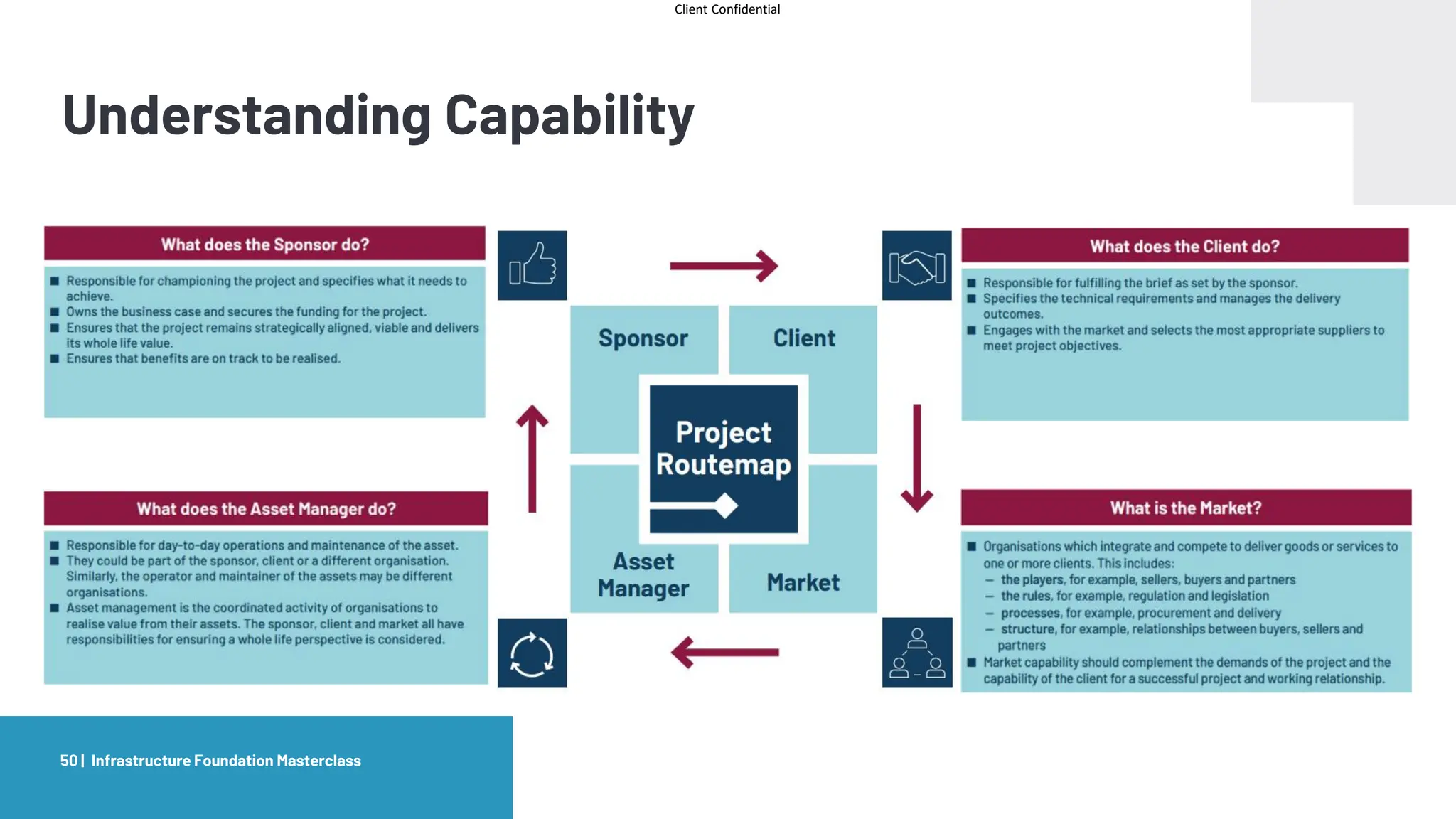
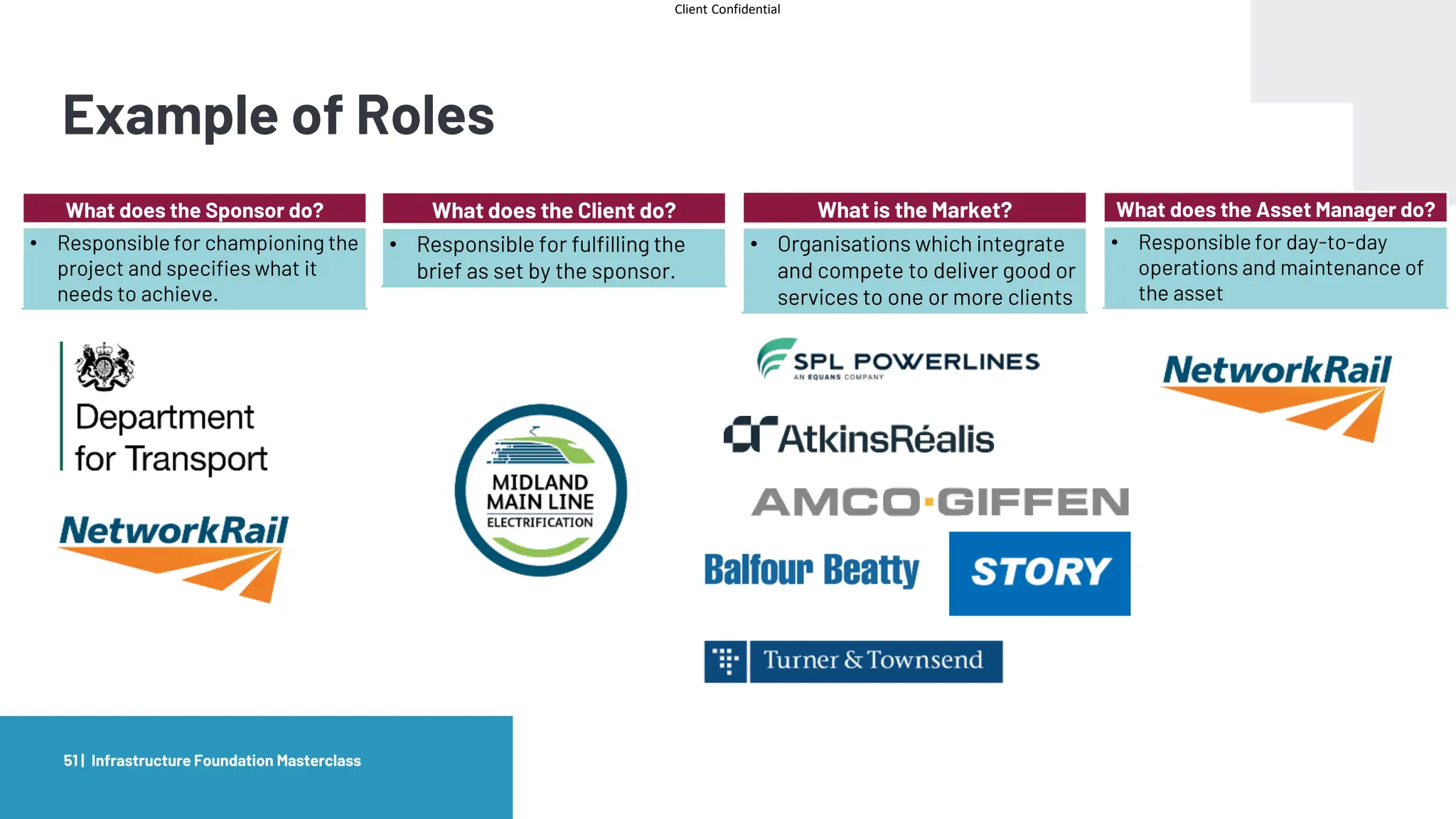
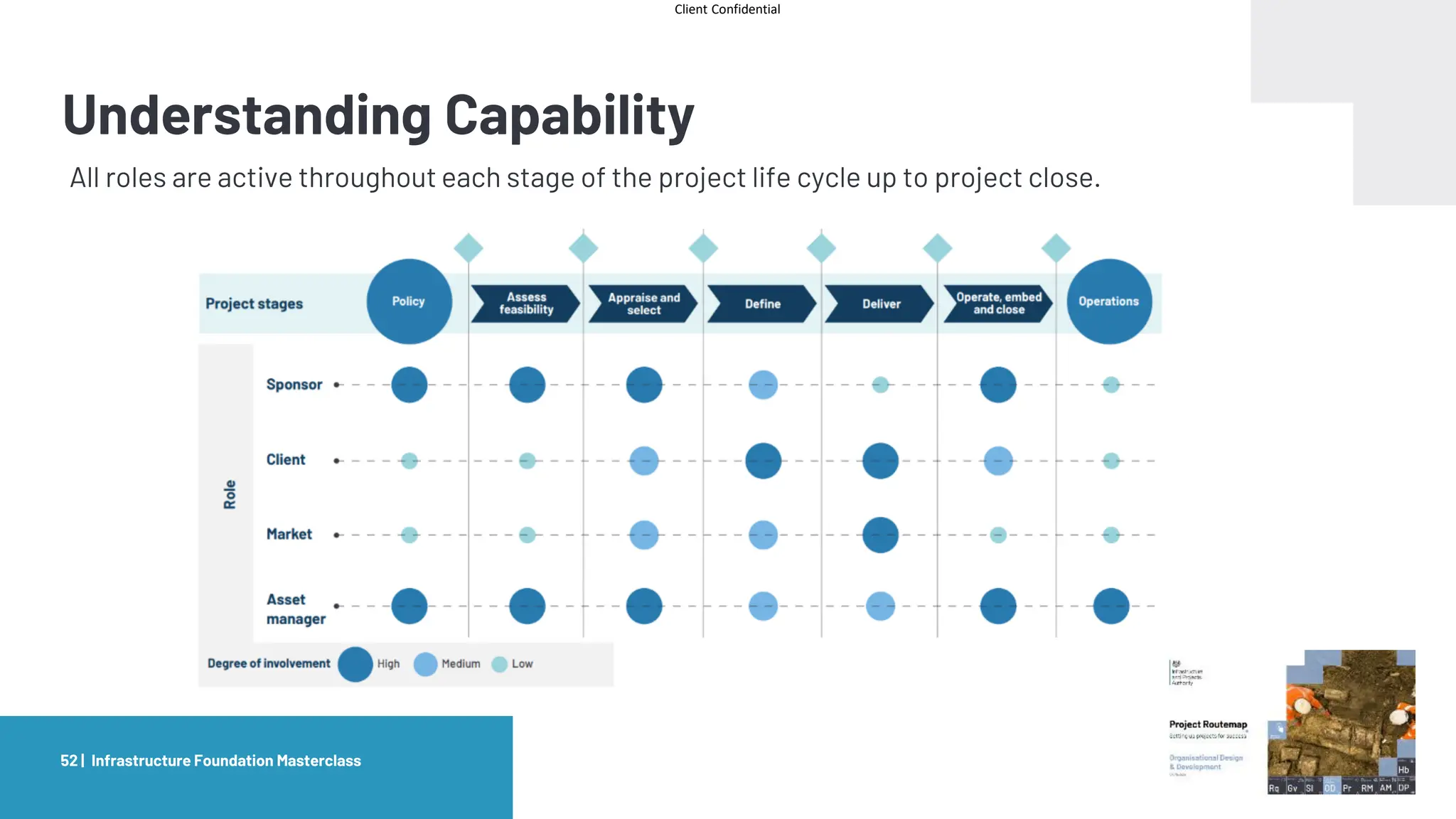
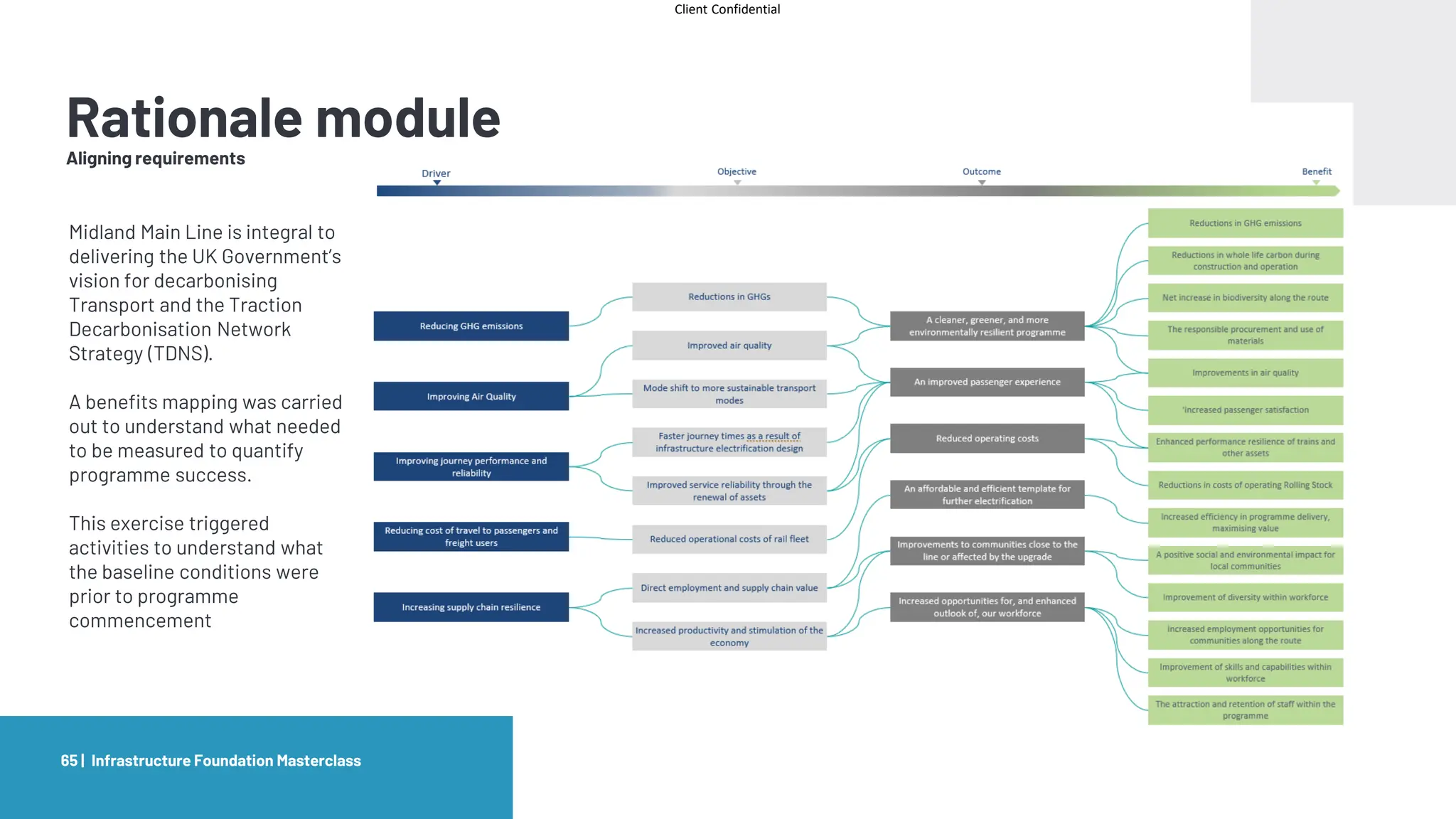
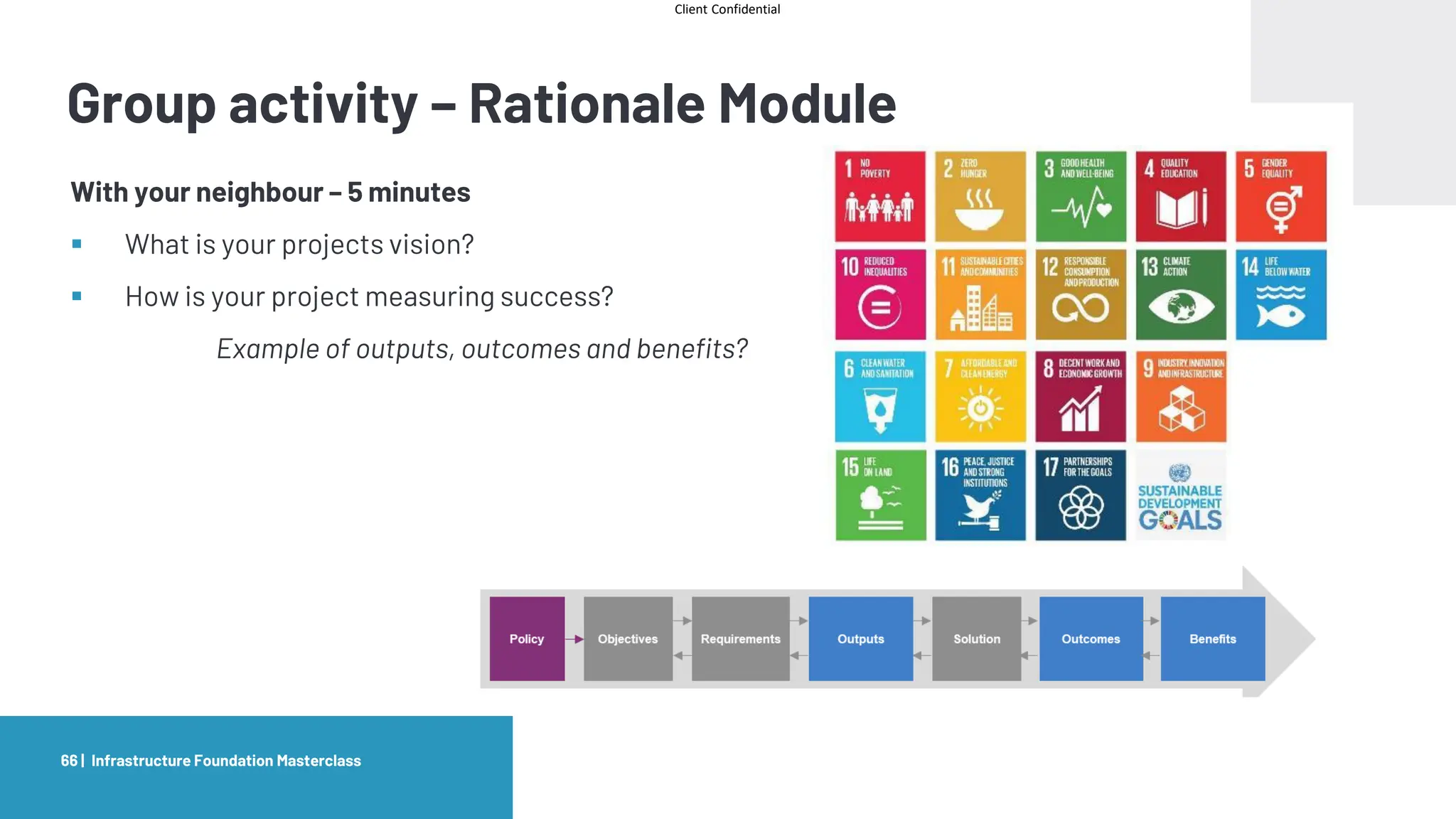
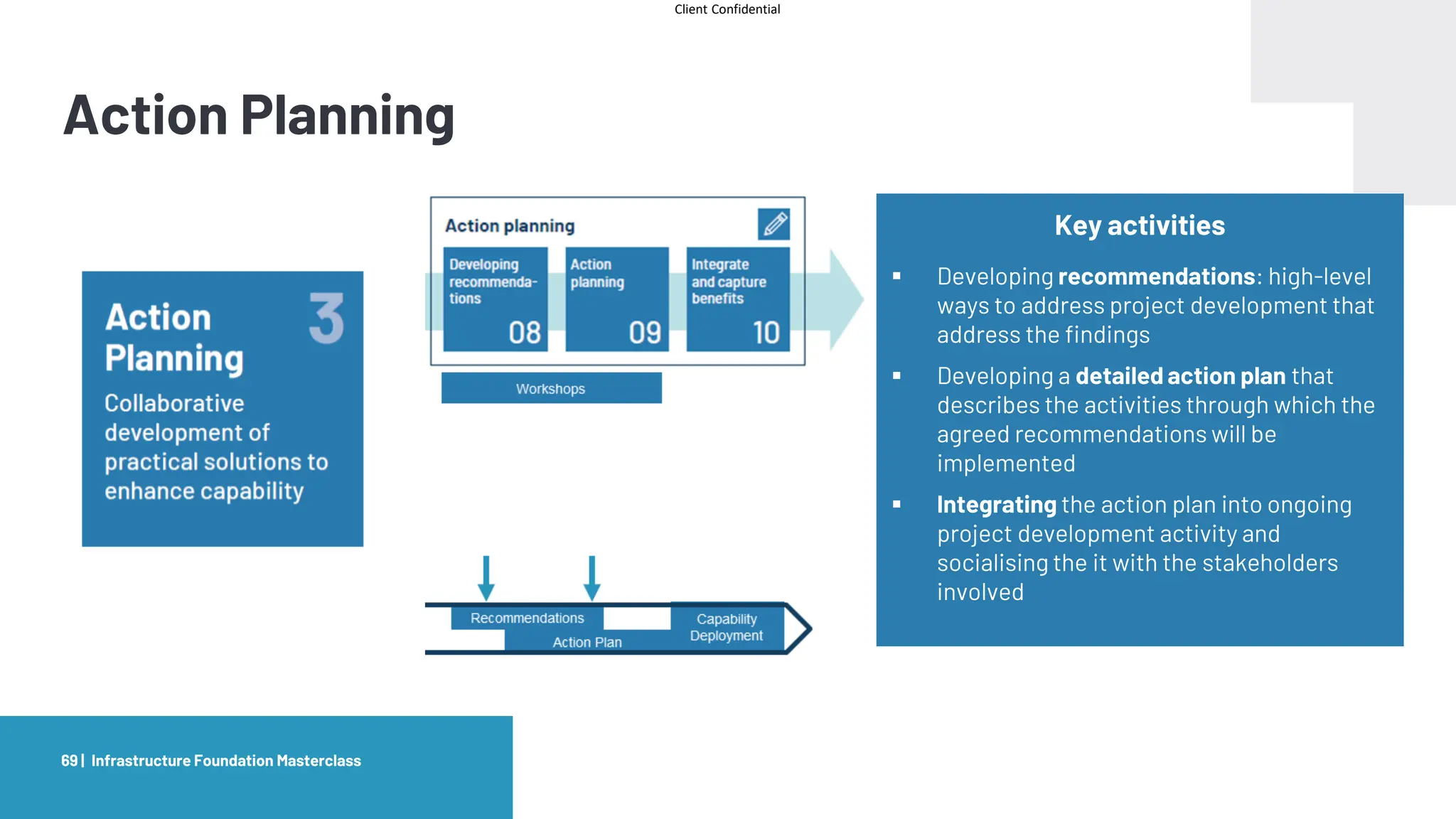
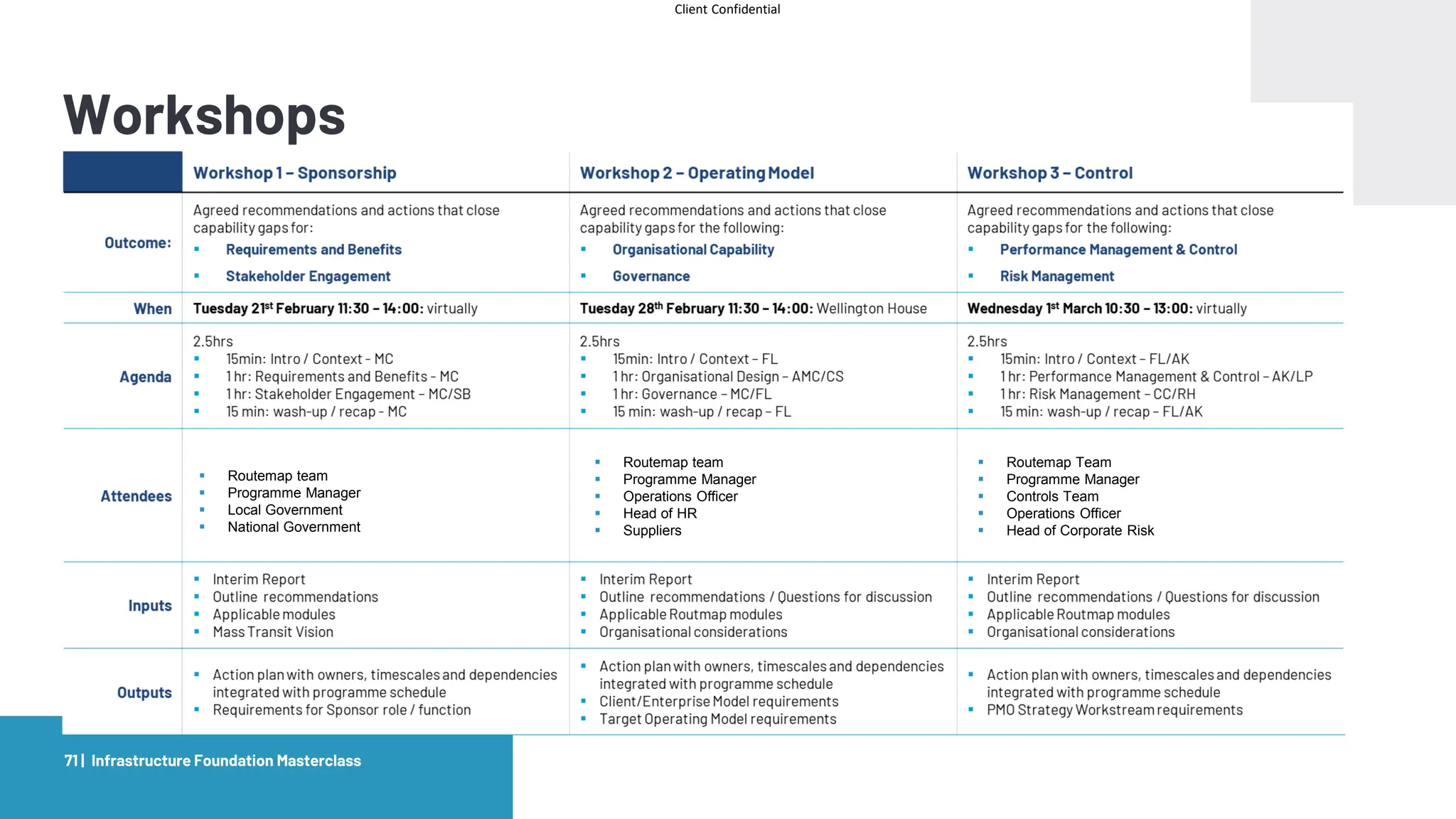
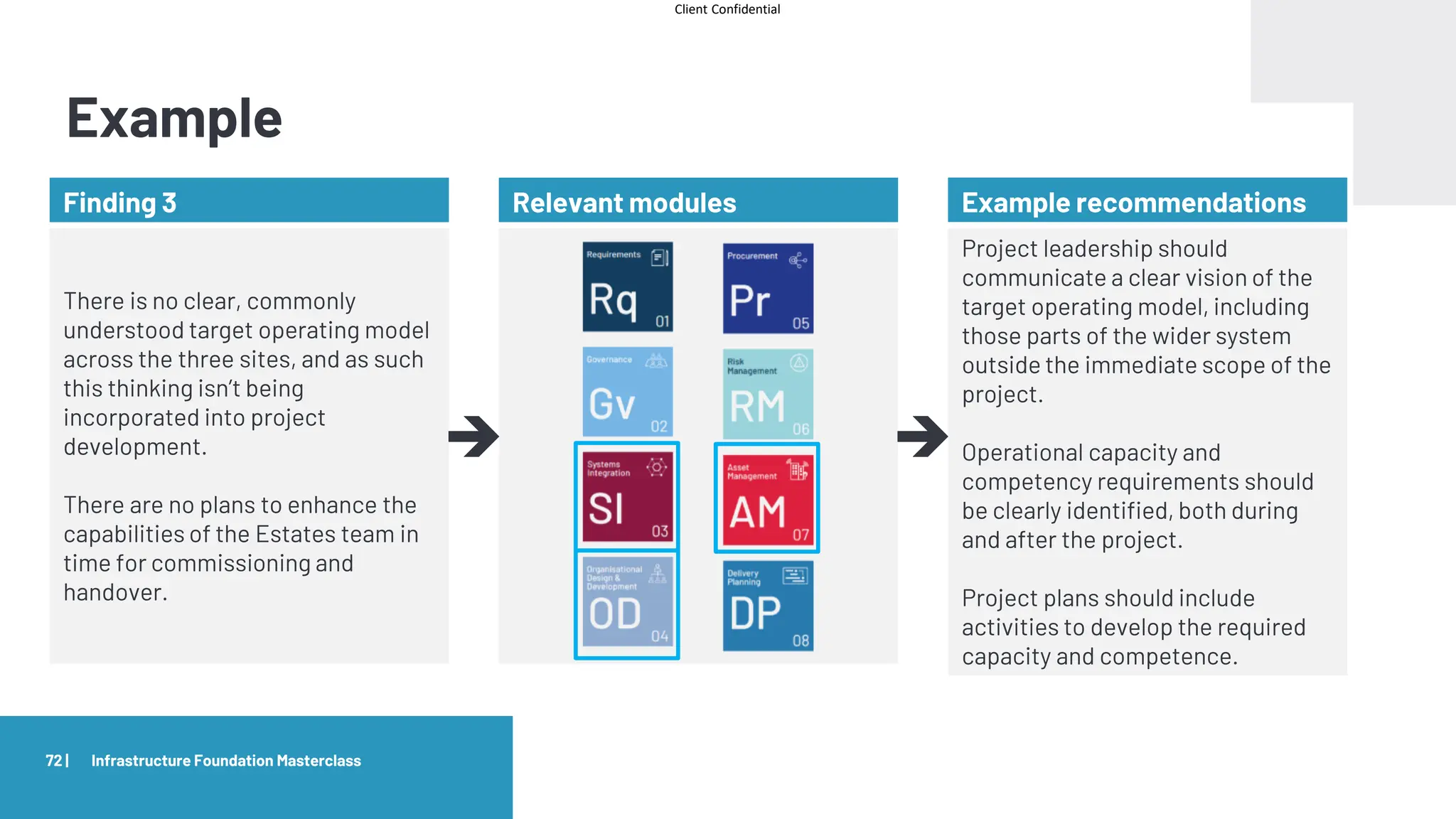
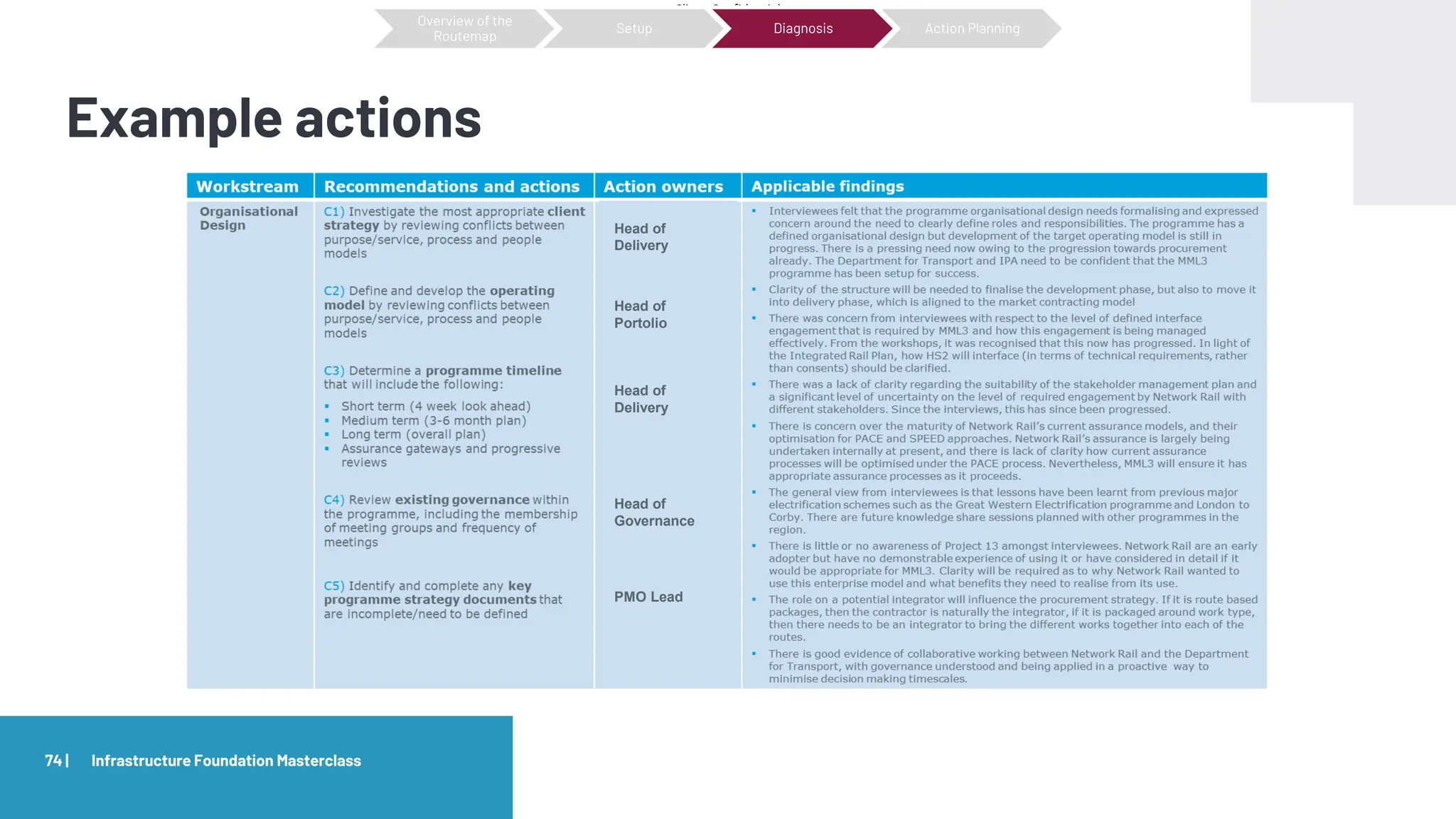
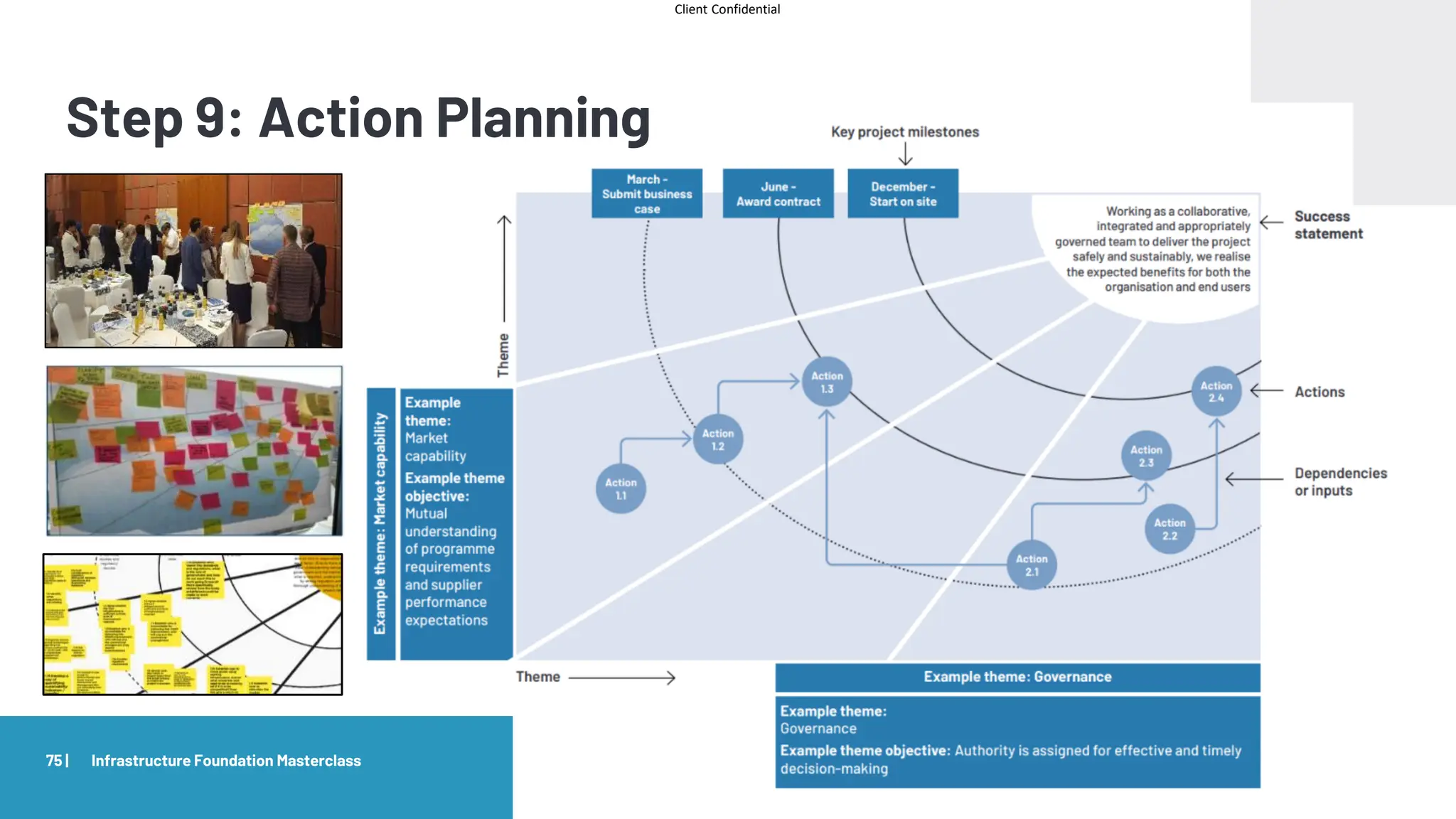
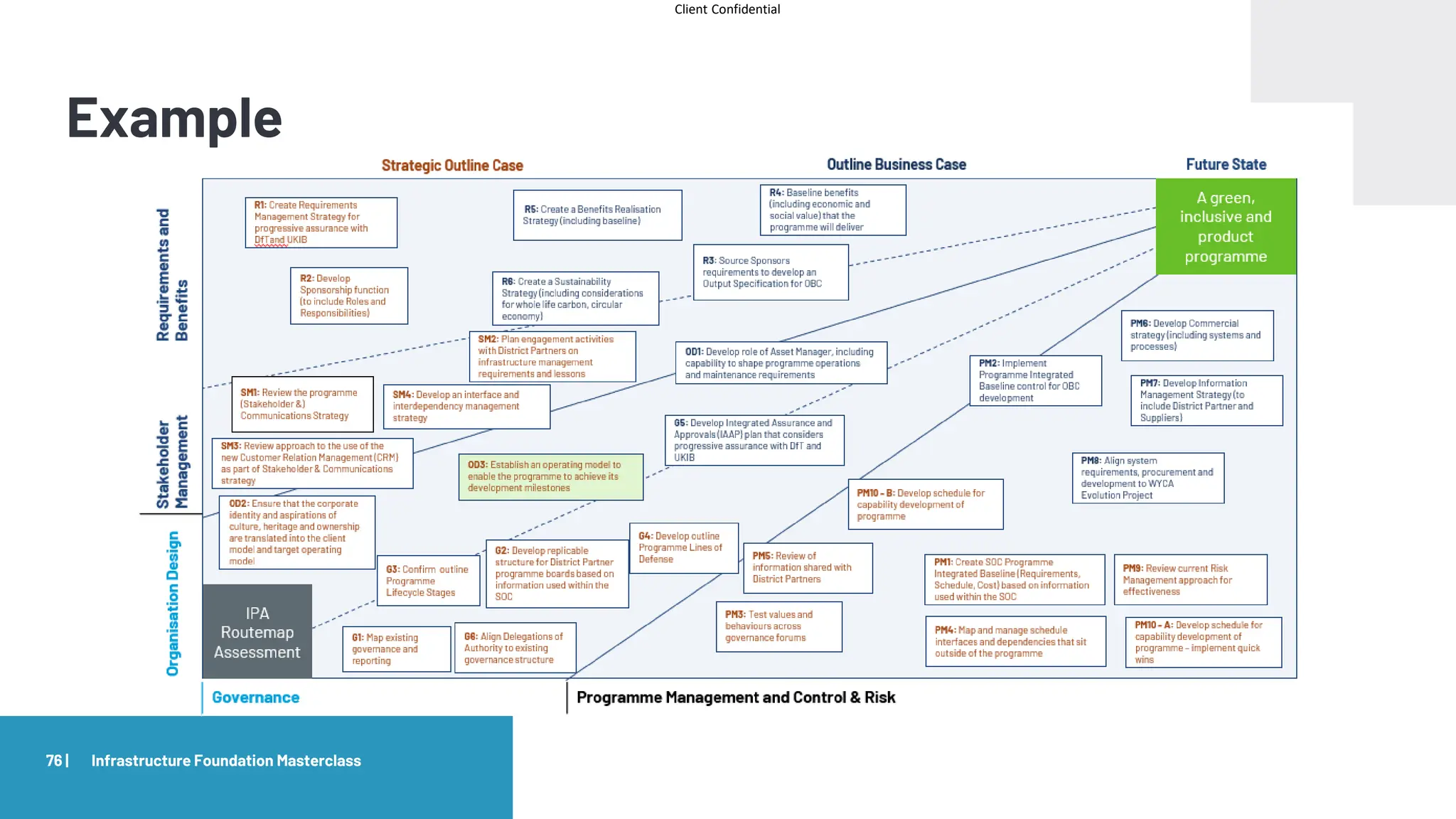
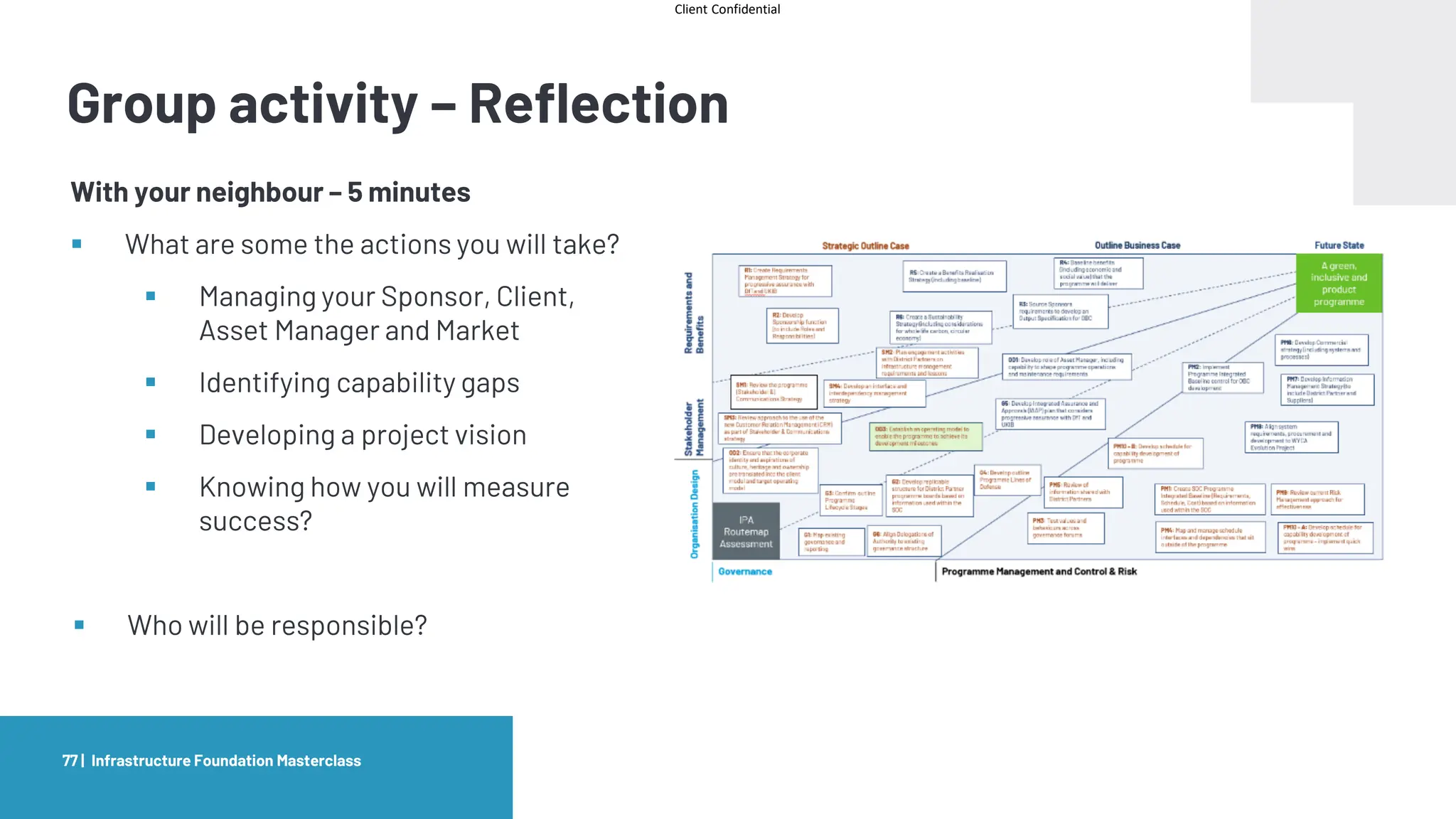
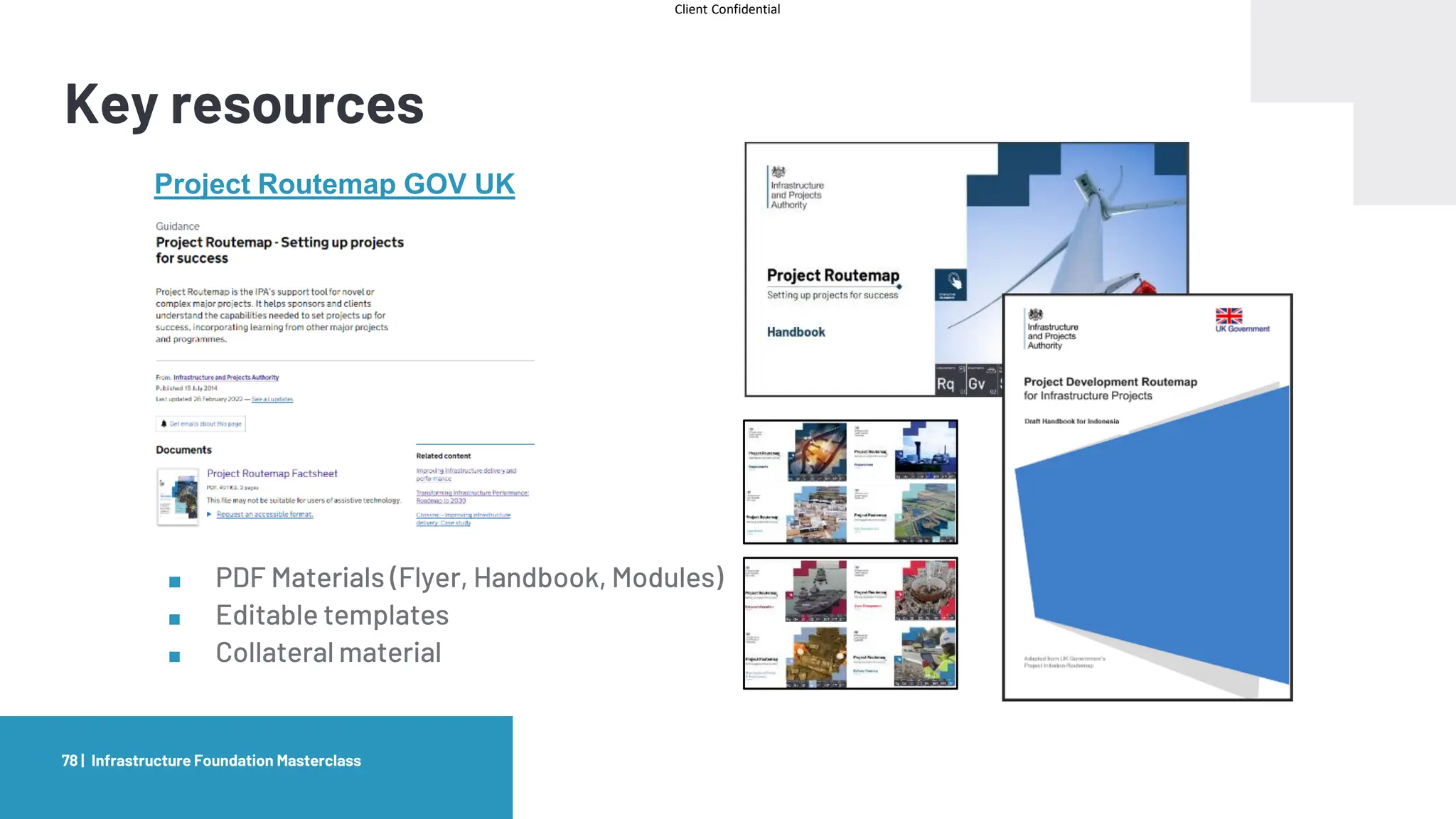
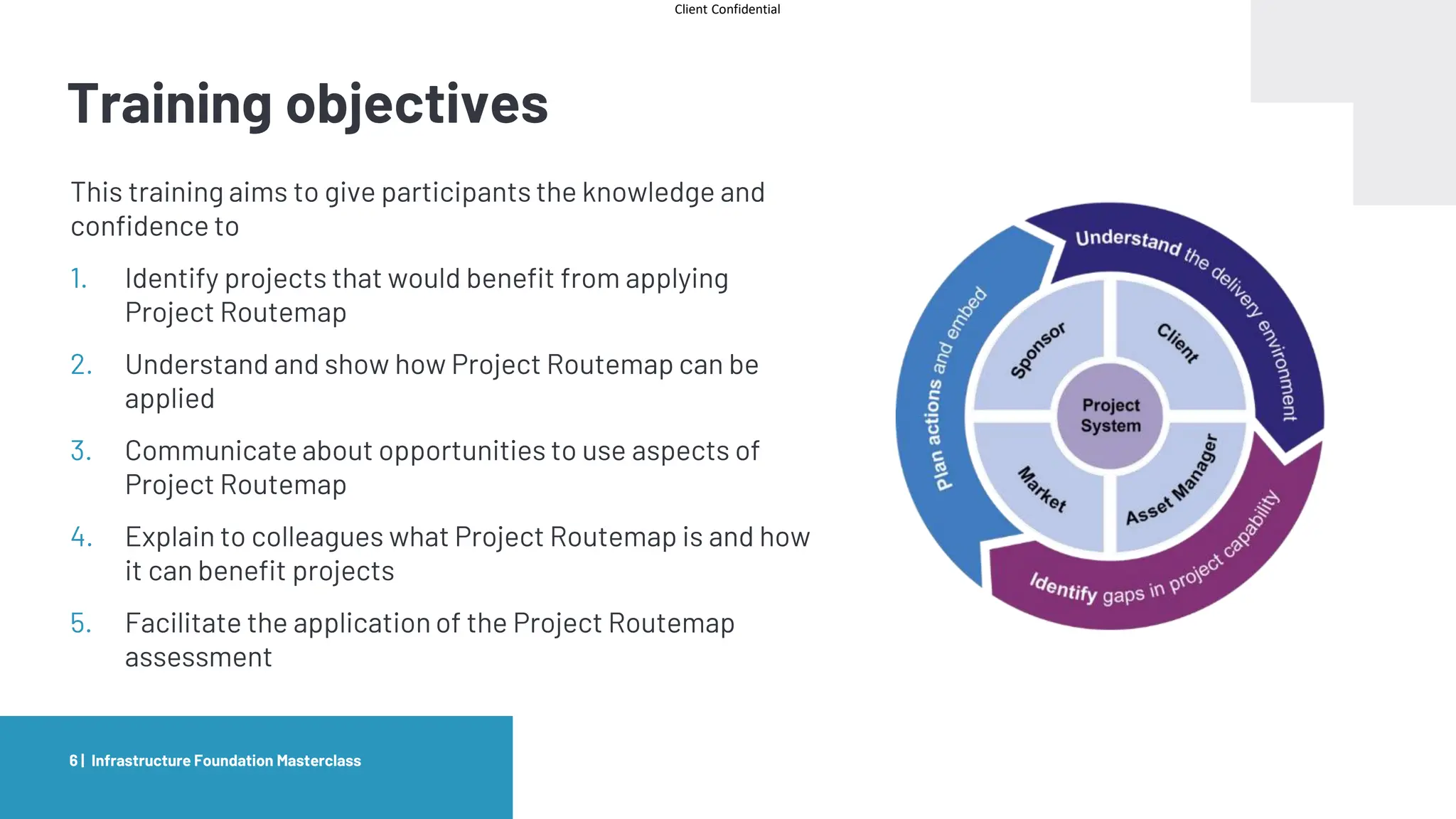
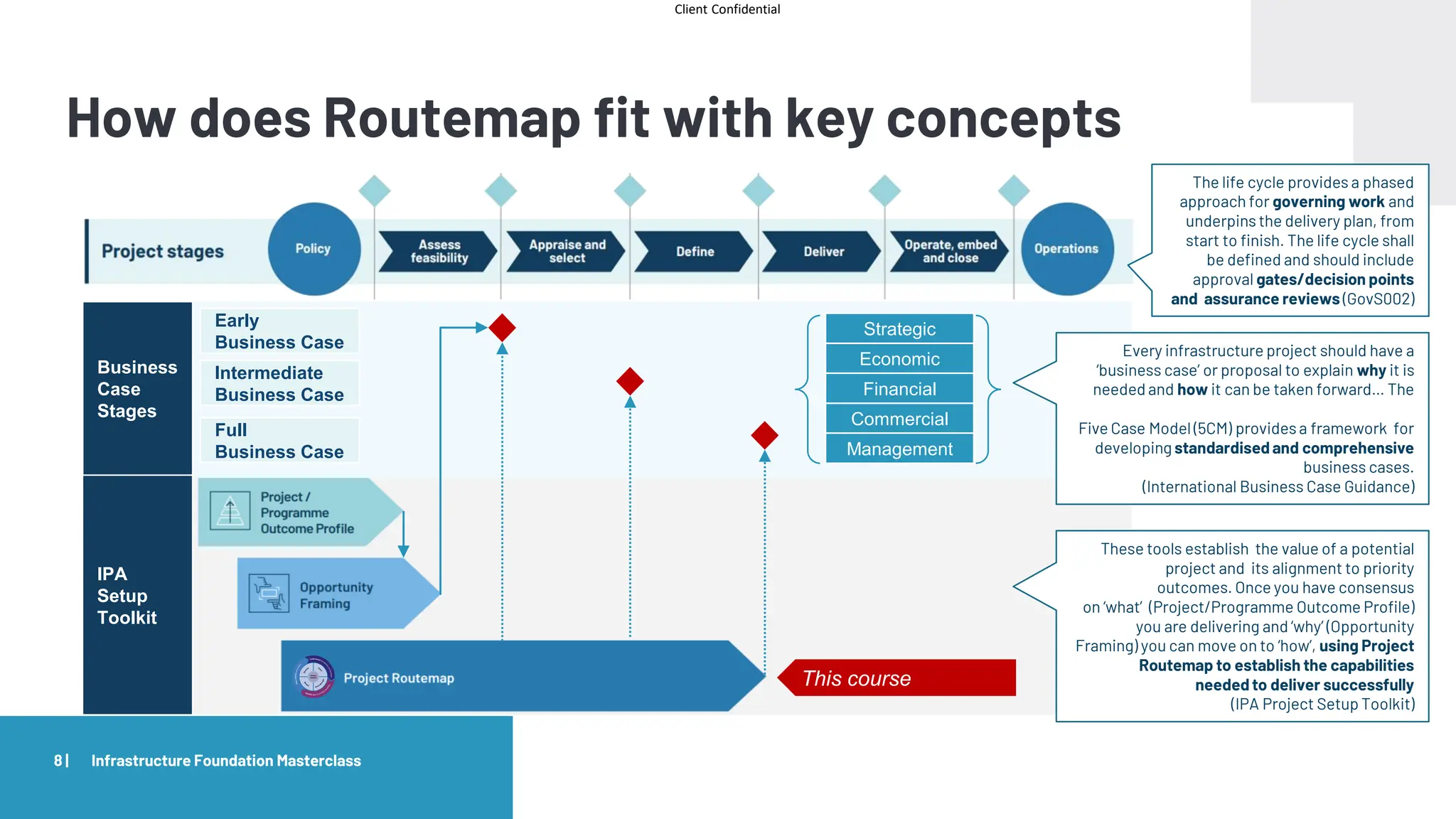
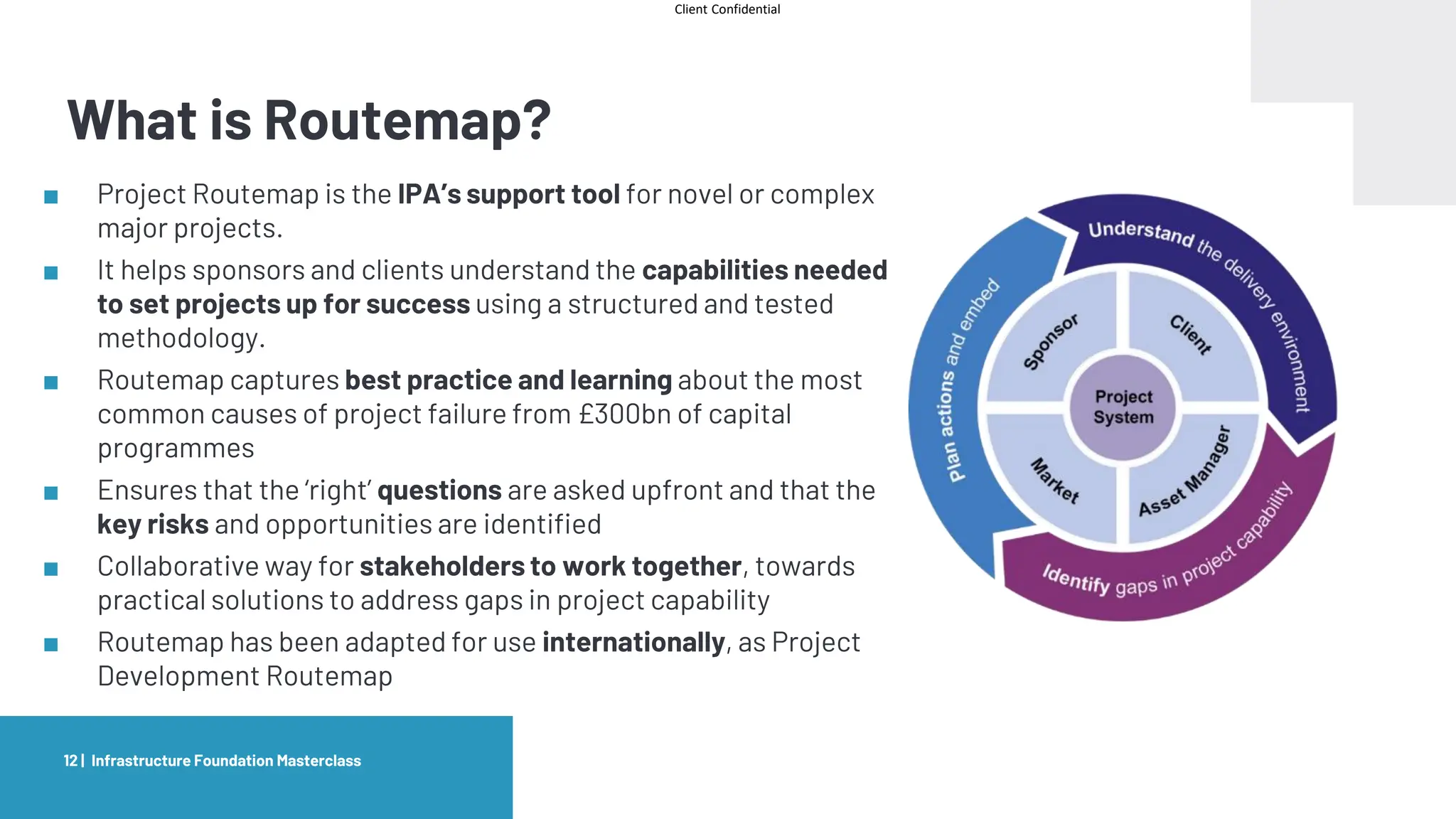
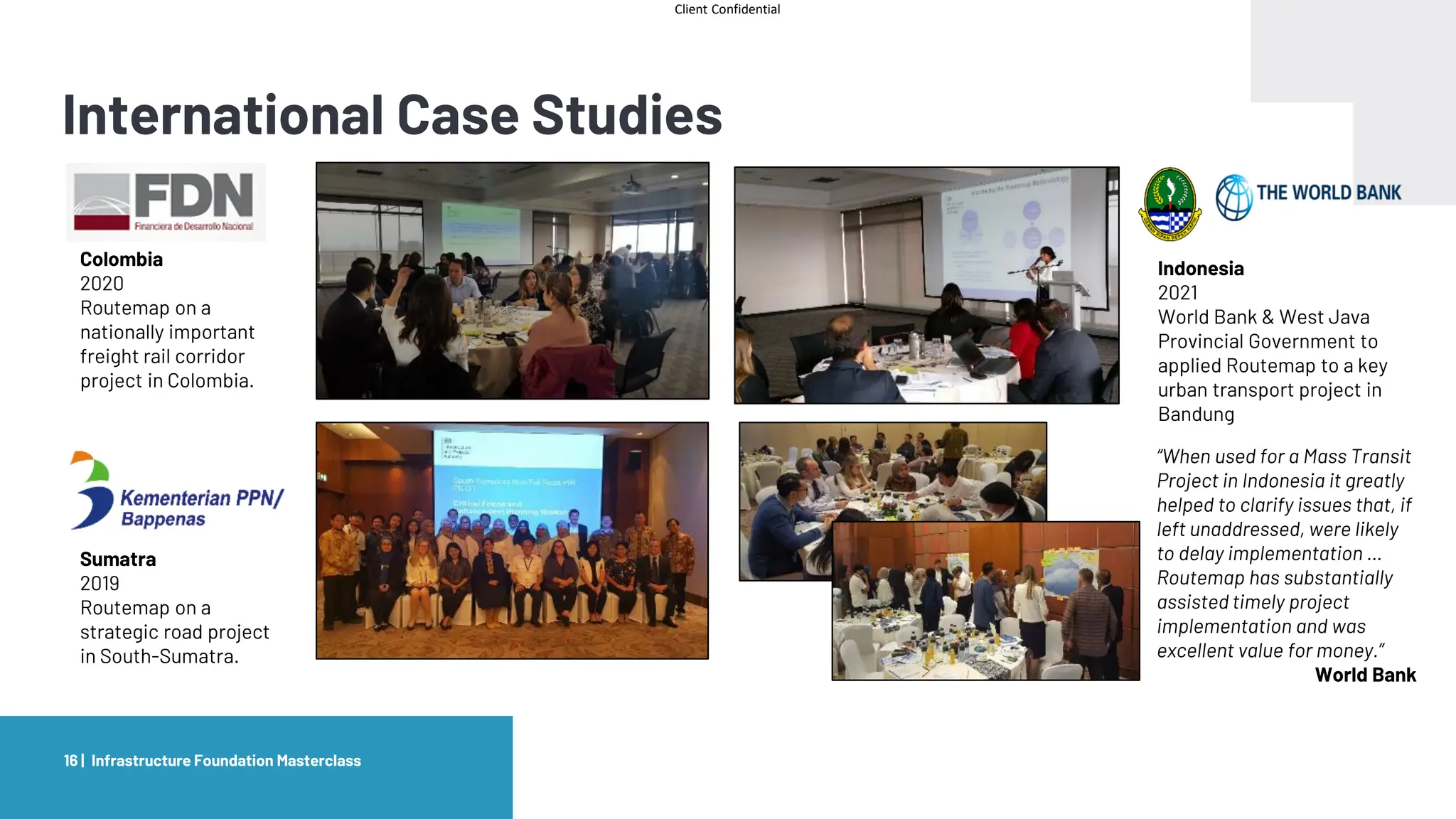
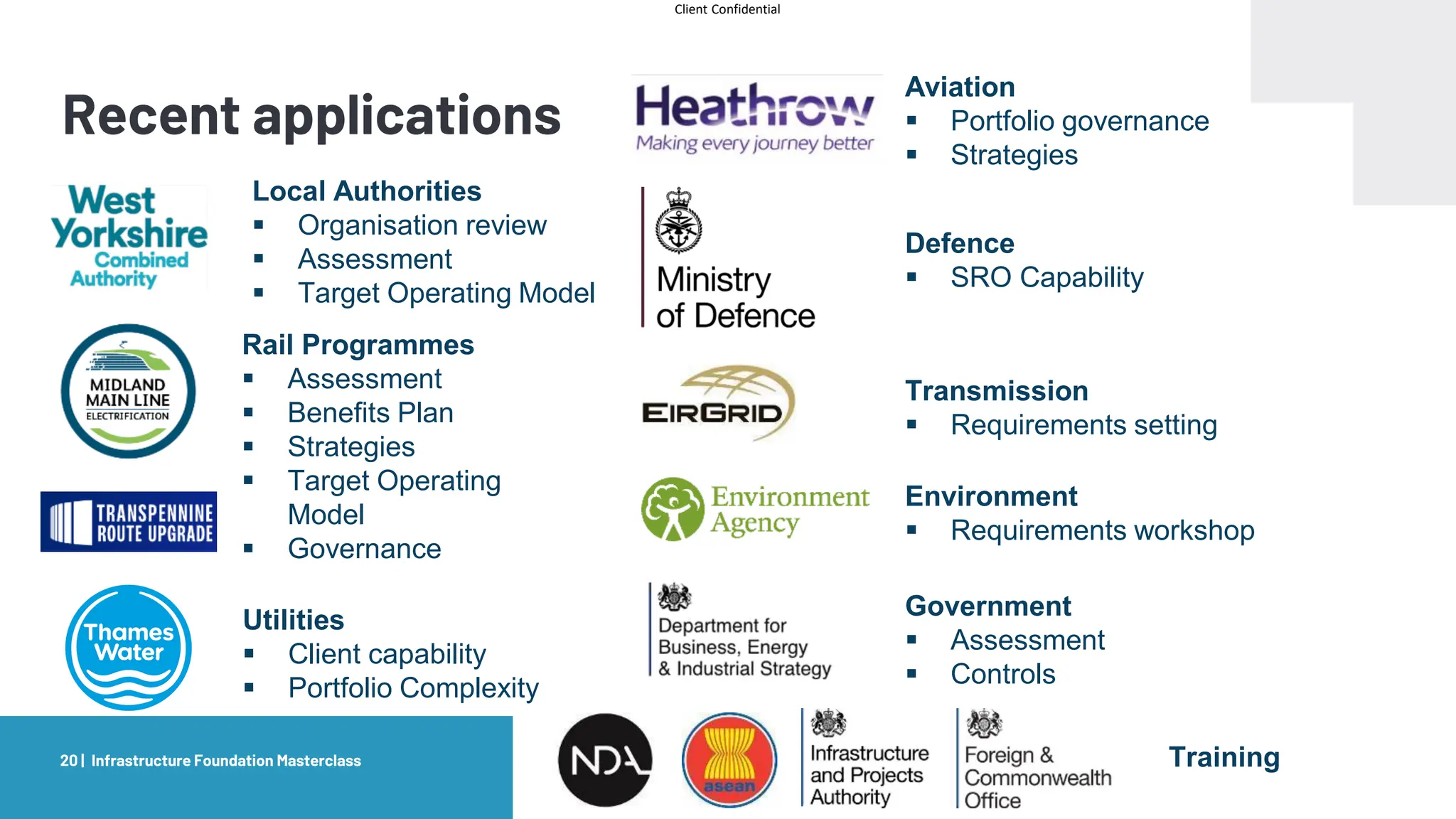
The document provides an agenda and overview for a masterclass training on the IPA Project Routemap methodology. The training aims to help participants understand how Routemap can be applied to identify capability needs for complex infrastructure projects. It discusses the Routemap modules, case studies of international applications, and the multi-step process for conducting a Routemap assessment. The document also outlines the roles involved and how Routemap fits within the overall project lifecycle and setup tools.

















![Client Confidential
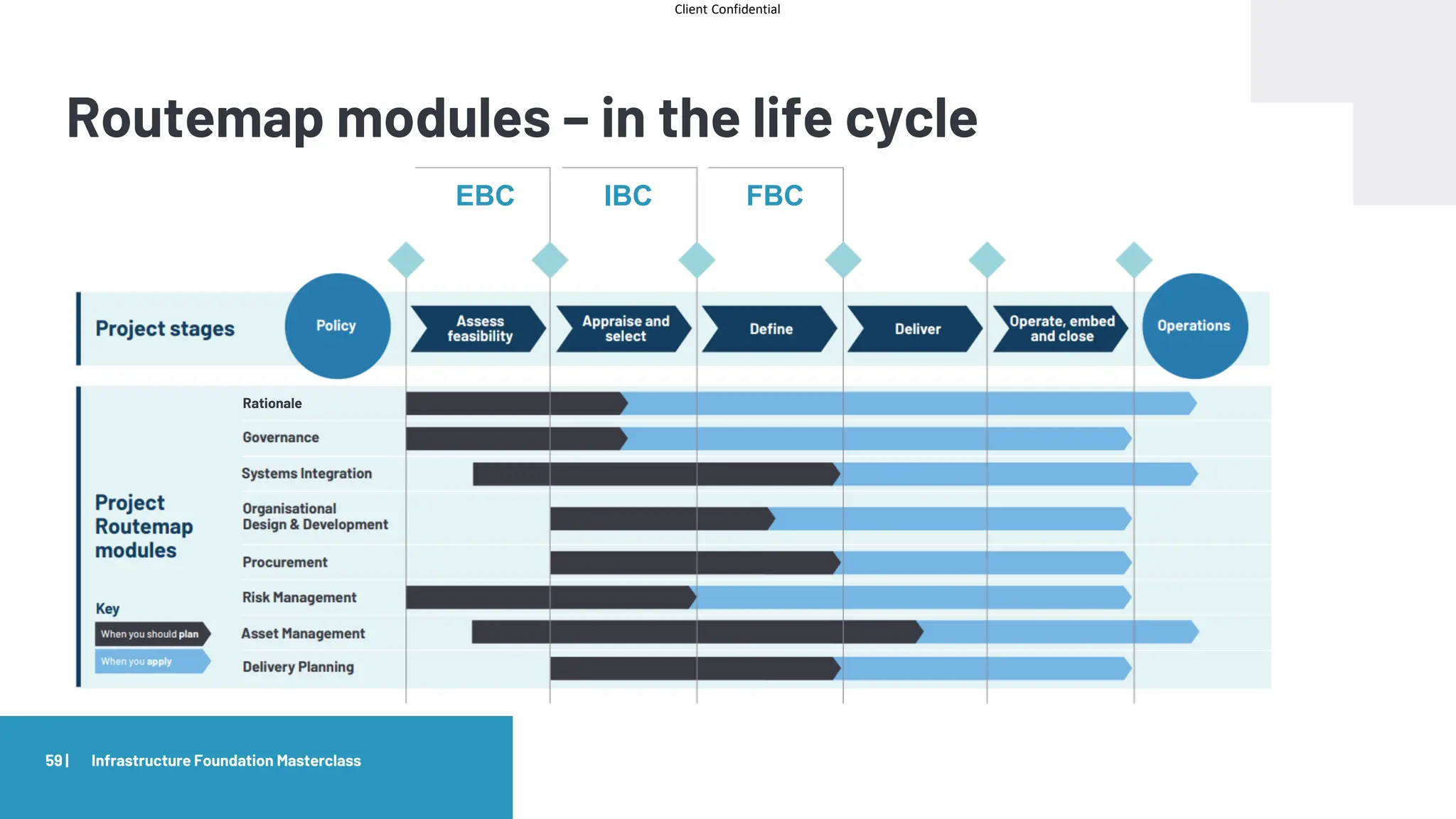
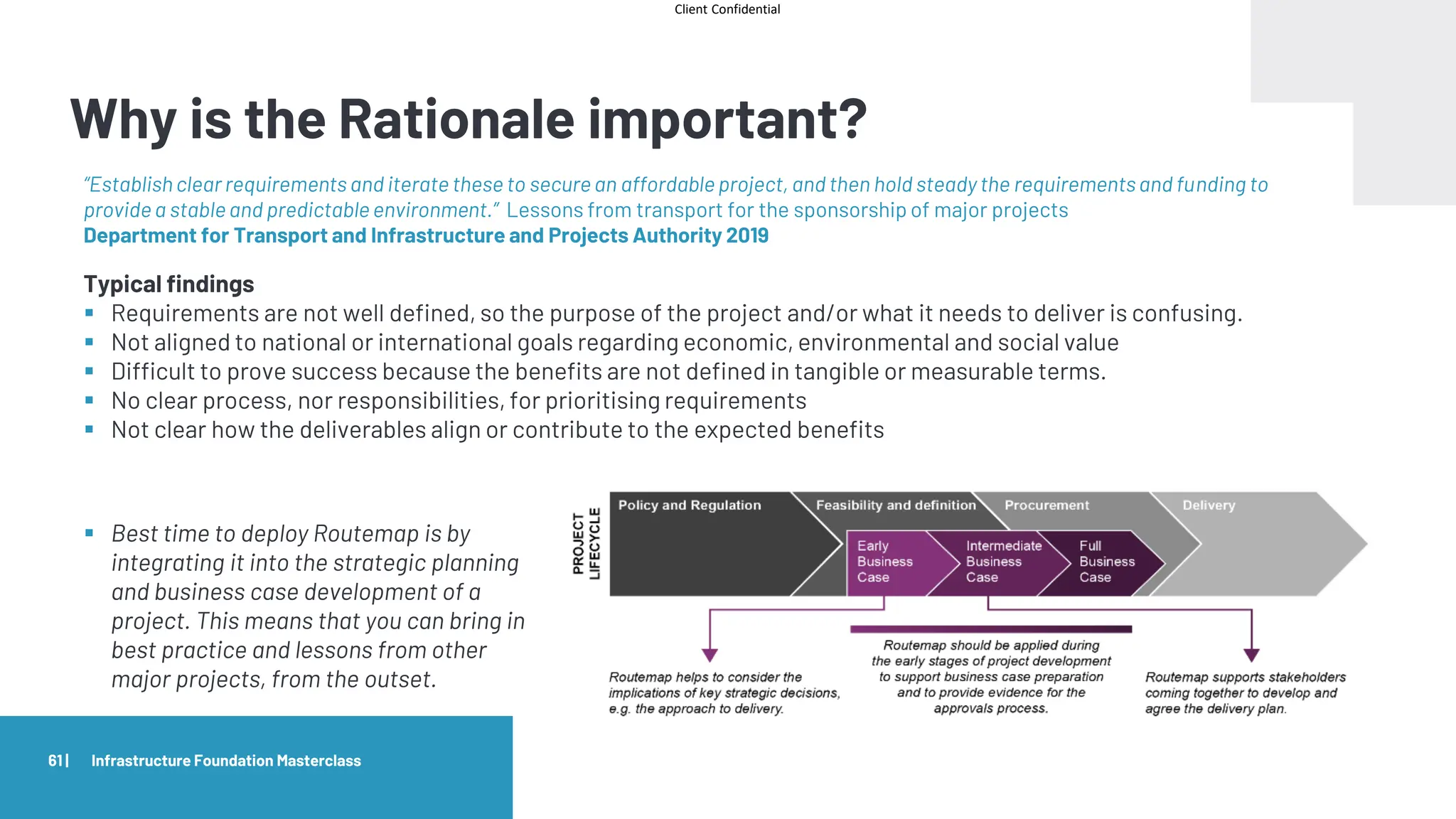
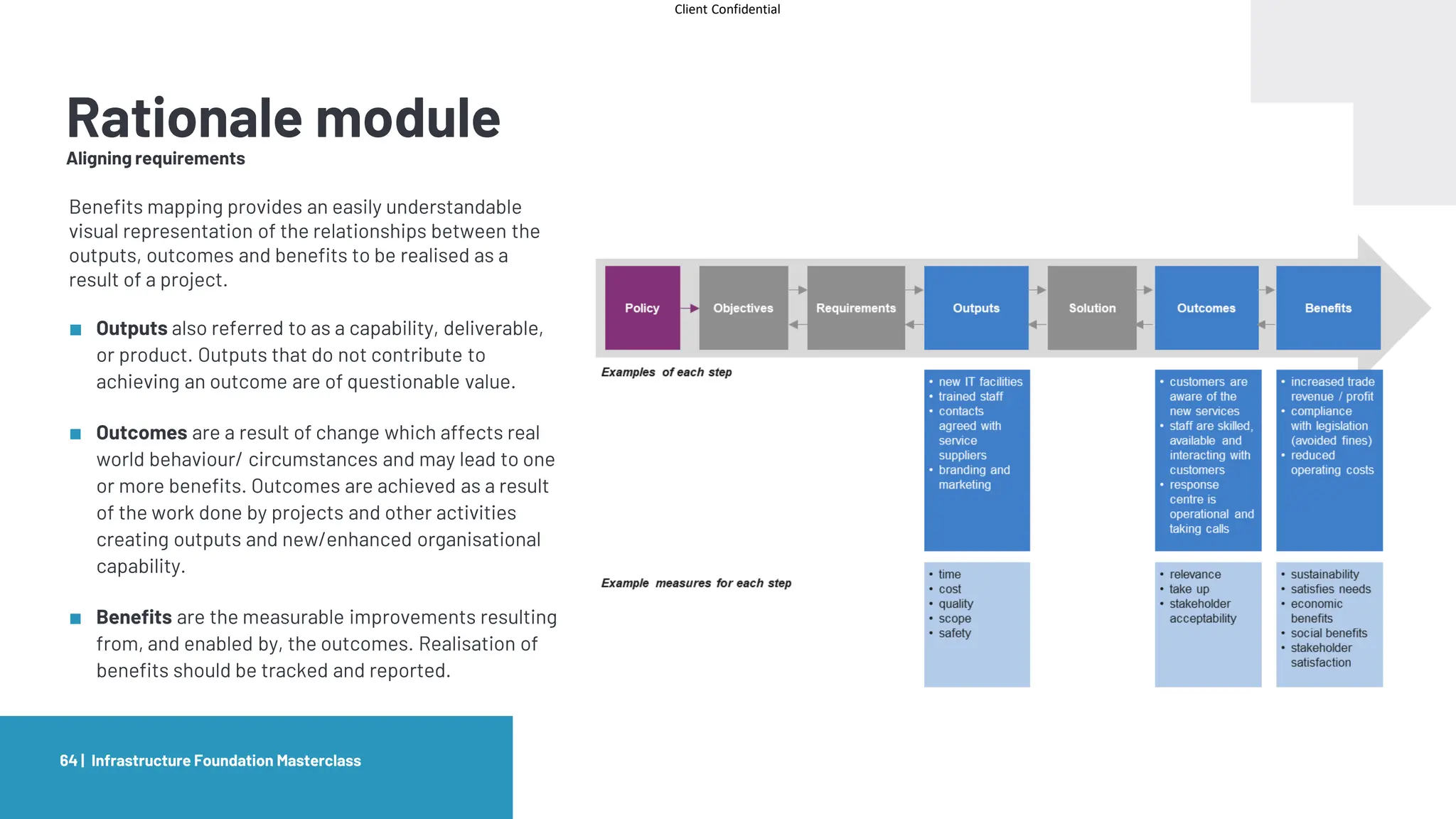
Routemap modules
[…], and why it’s important
Introduction to the topic of the module
including a list of key documents that will
help you to understand how this area is
managed on your project
Typical findings
Indicators that issues might arise
during delivery
Pillars of effective […]
Hallmarks of effective project set up
Considerations
Detailed list of questions to understand
root causes and suggest improvements.
Together with signposts to other
materials you may find helpful.
Good practice examples and suggested
reading
Context to support your wider understanding
Overview of the
Routemap
Setup Diagnosis Action Planning
Infrastructure Foundation Masterclass
25 |](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20231122routemapinfrafoundationcourse-231214201456-f3a55d40/75/Project-Development-Routemap-Infrastructure-Foundation-Masterclass-25-2048.jpg)