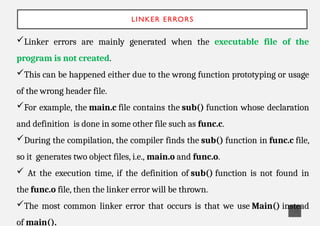
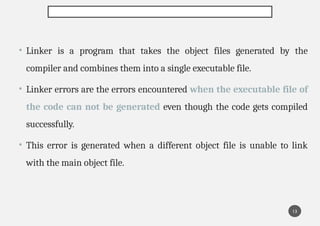
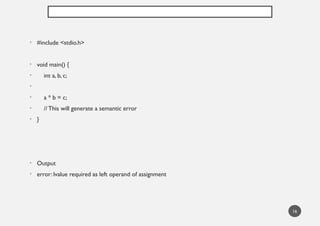
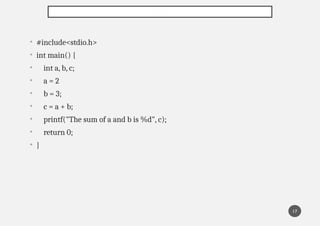
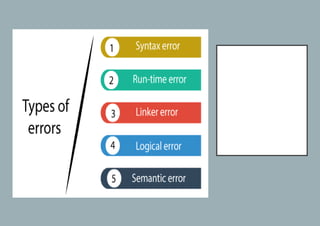
The document explains five types of errors in C programming: syntax errors, runtime errors, logical errors, linker errors, and semantic errors, detailing their definitions and examples. Syntax errors occur during compilation due to incorrect code structure, runtime errors happen during execution, logical errors produce incorrect output despite valid code, linker errors prevent executable creation, and semantic errors arise from unrecognized code meaning. Each error type is illustrated with programming examples to enhance understanding.





![RUNTIME ERRORS
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int array[5];
printf("%d", array[10]);
return 0;
}
9
Some common examples of runtime
errors are:
• Division by zero
• Null pointer dereferencing
• Array index out of bounds
• Resource leaks (e.g., memory or
open file handles)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/typesoferror-241211061106-10abd595/85/Programming-in-C-Types-of-Errorss-pptx-9-320.jpg)