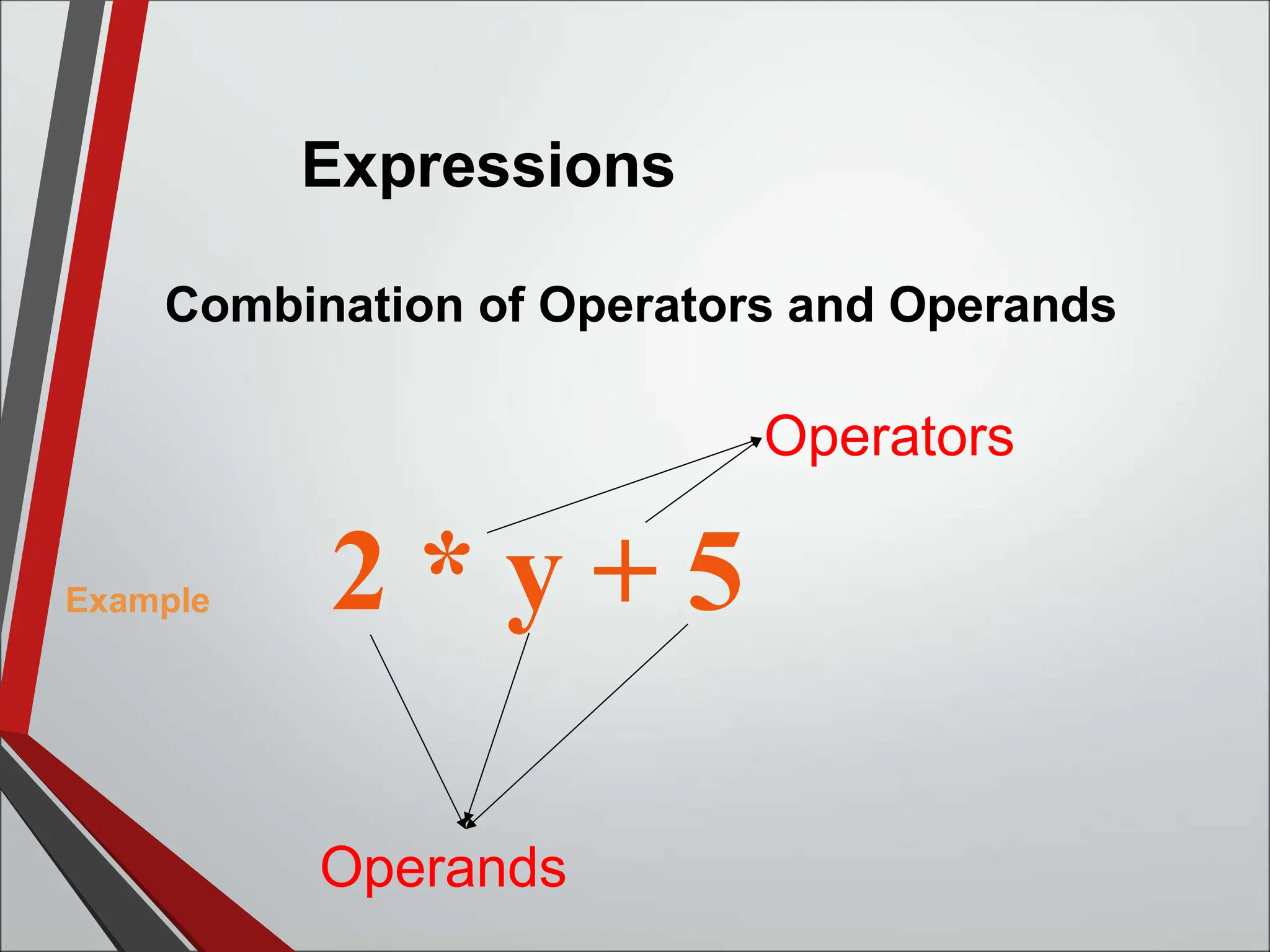
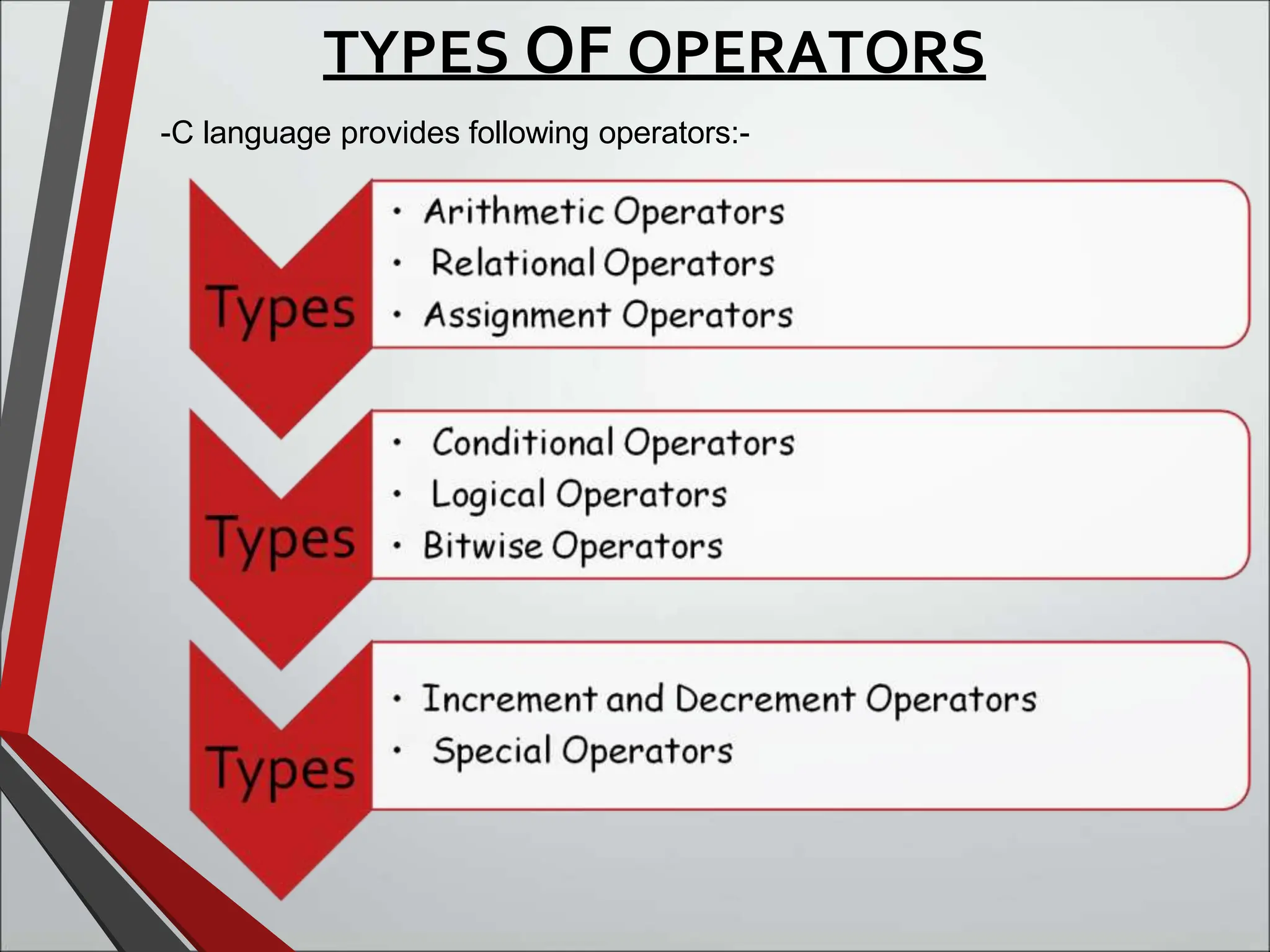
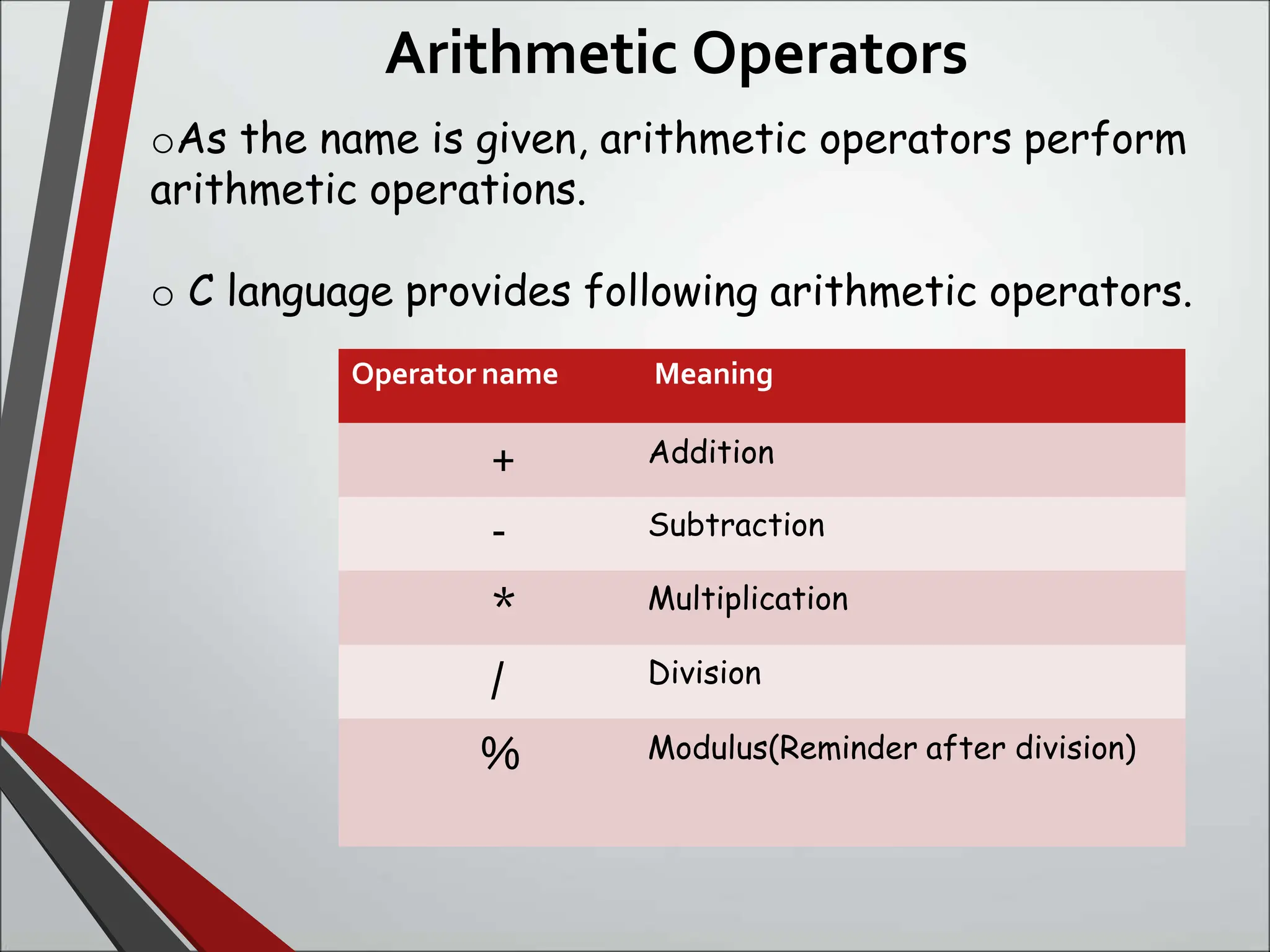
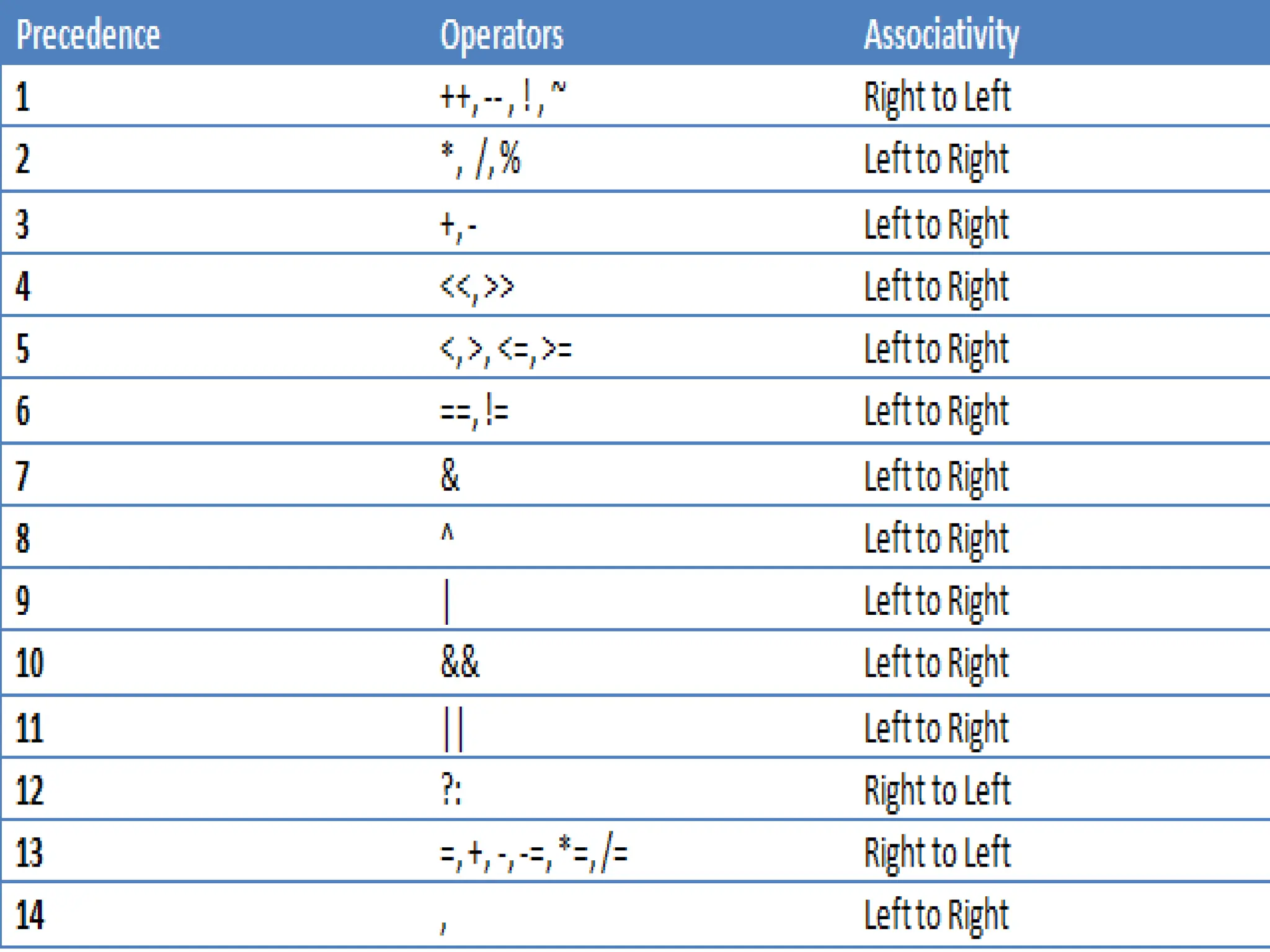
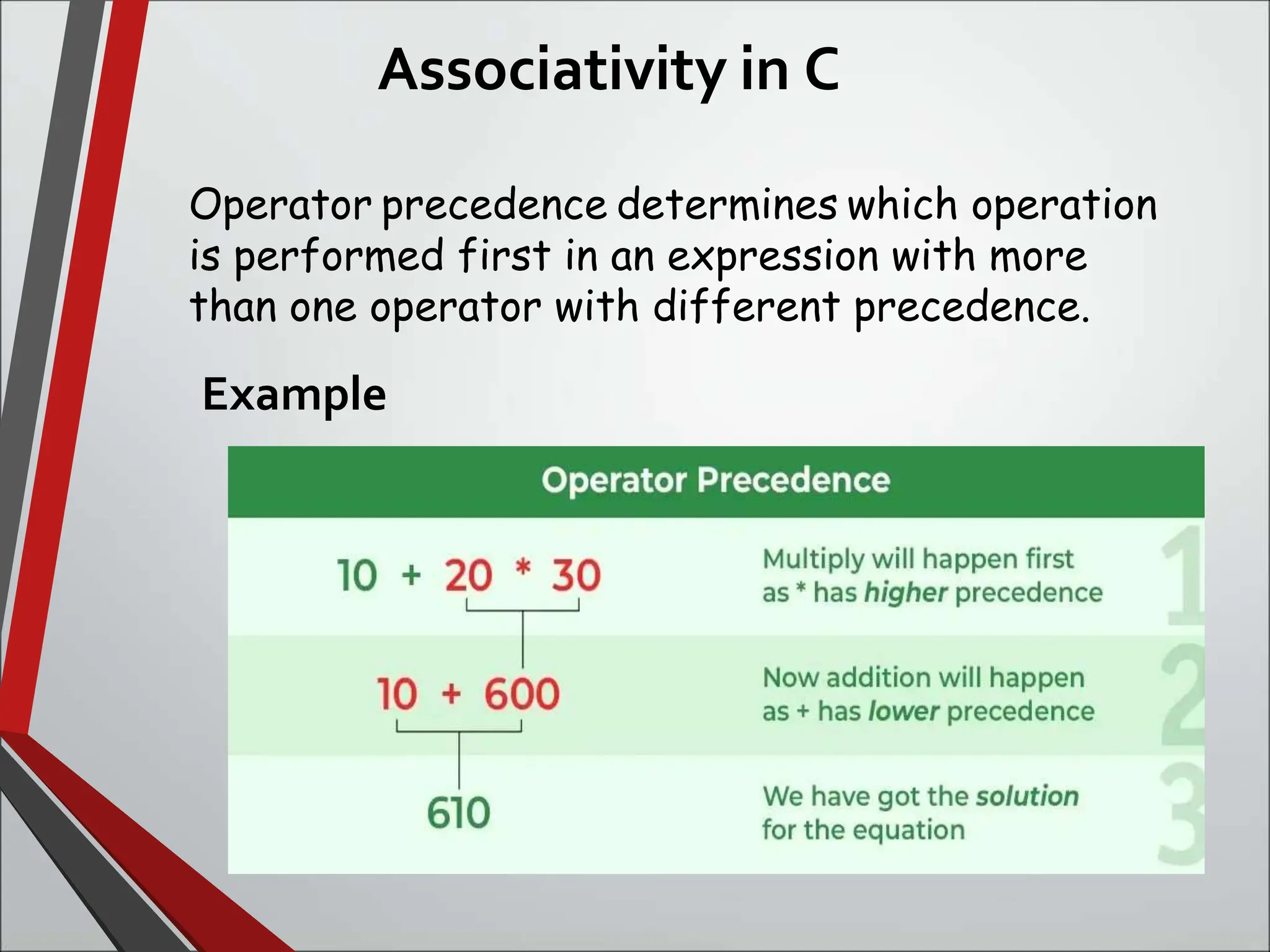
This document discusses arithmetic operators in C language. It defines operators as symbols that take operands and perform computations. Operands are variables or expressions used with operators. Combining operands and operators forms expressions. Arithmetic operators are binary operators that take two numeric operands and perform addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and modulus operations. The order in which operators are evaluated, known as precedence and associativity, is also discussed along with an example program demonstrating arithmetic operators.