The document provides information about several product failures by major companies:
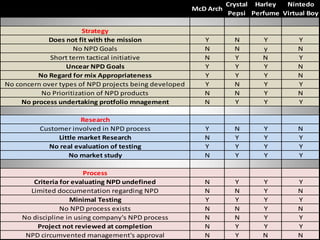
McDonald's Arch Deluxe burger failed in 1996 due to inappropriate marketing that targeted adults but showed kids rejecting it, high calorie content, and being too expensive. It showed McDonald's losing touch with its customers.
Crystal Pepsi, launched by PepsiCo in 1992, failed because it did not have a compelling difference from regular Pepsi and the "crystal" name was not appealing. The product and market were not well defined.
Nintendo's Virtual Boy game console from 1995 failed because it caused motion sickness, was uncomfortable to play, and lacked a "killer app" game. It also had an isolating gameplay experience

















![Nintendo
• Japanese multinational consumer electronics company
located in Kyoto, Japan.
• World's largest video game company by revenue
• Founded on September 23, 1889[2] by Fusajiro
Yamauchi
• Extensive experience in the video game industry
• First to introduce motion technology in video games
• Reasons for Launch:
• Slowdown of the Japanese, the US and European
economies
• Short products lifecycle
• Growing US games software market](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/npds-121224150526-phpapp02/85/Product-Failure-Evaluation-18-320.jpg)