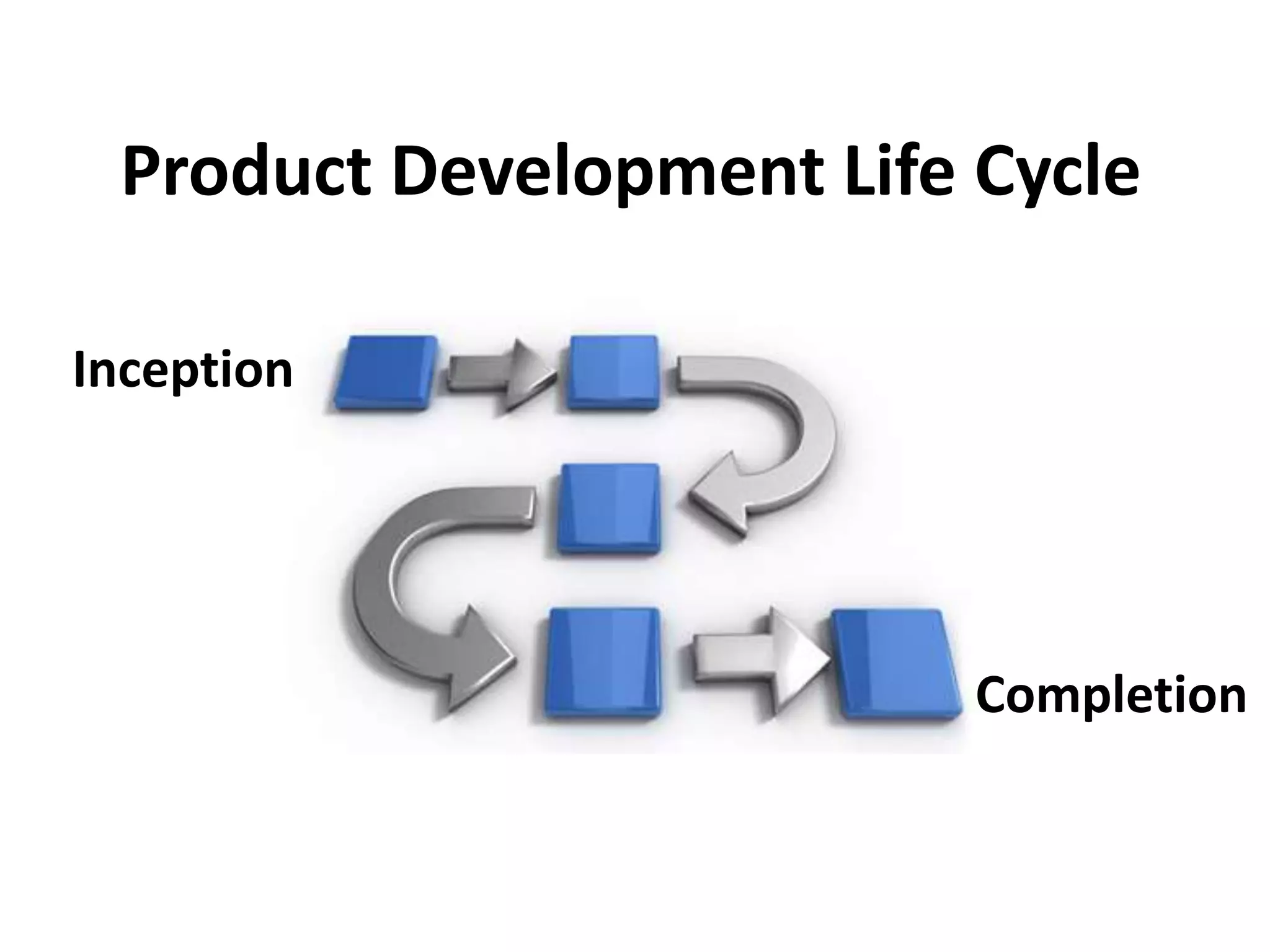
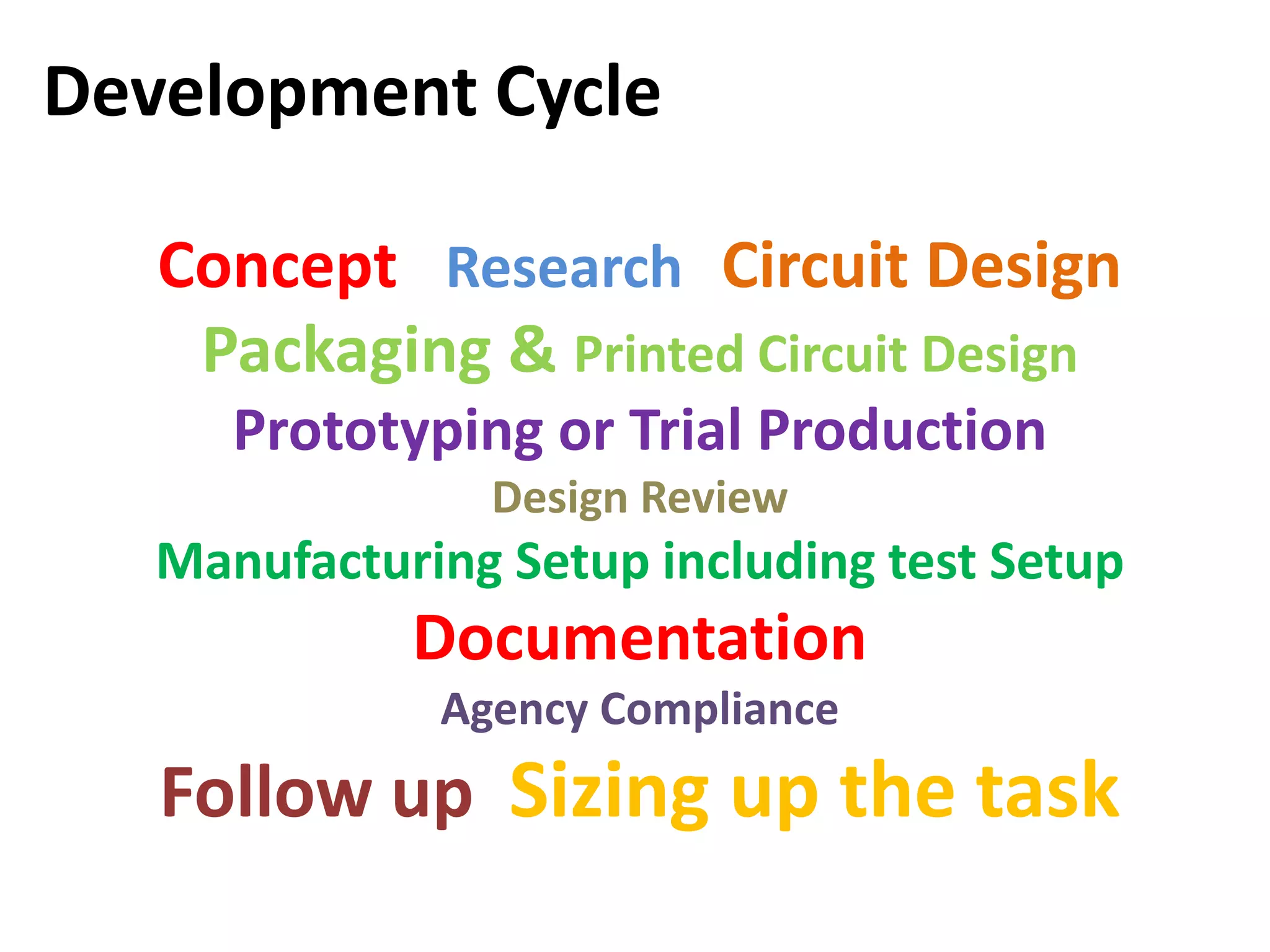
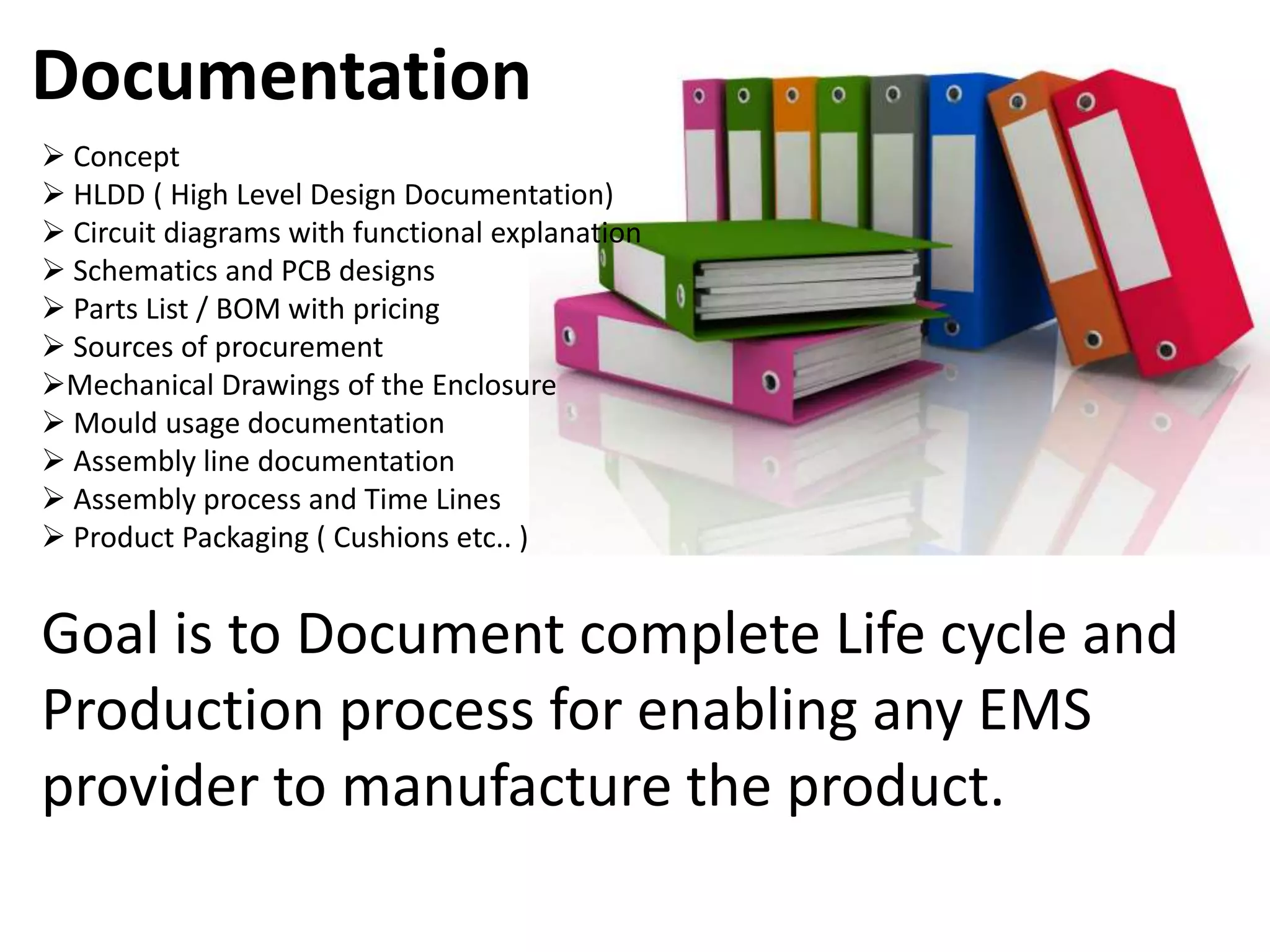
The document outlines the key steps in a typical product development life cycle from concept to realization including:
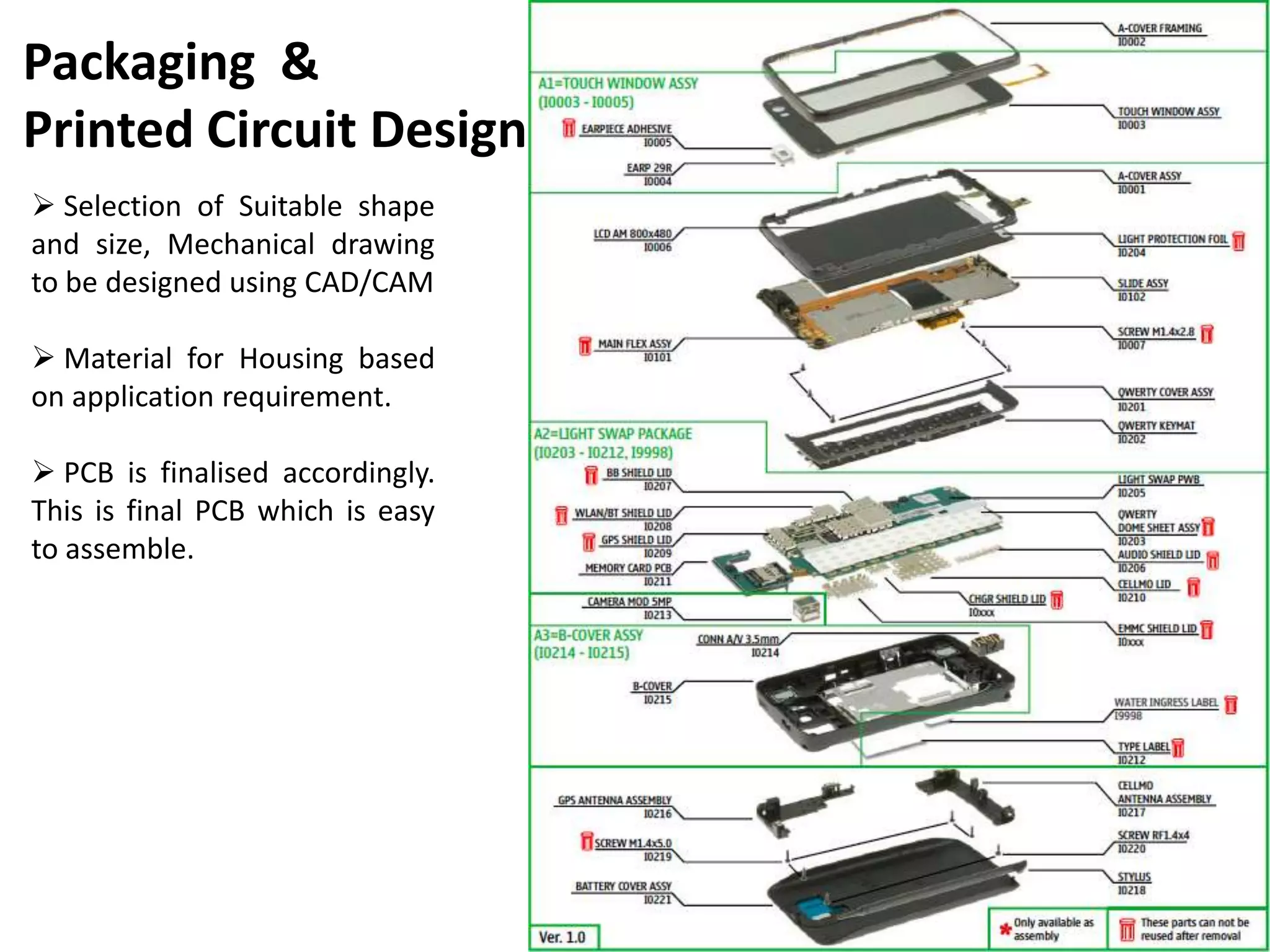
1. Concept development, research, circuit design, packaging design, and prototyping.
2. Design review, manufacturing setup, documentation, and compliance with relevant agencies.
3. Follow up which includes reviewing manufacturing experience, product support data, and user responses to improve future designs and marketing.