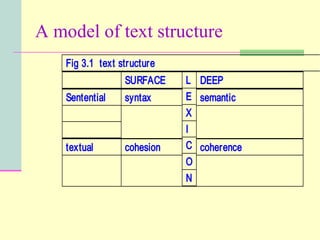
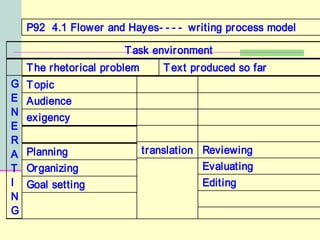
The document discusses process writing and its importance for composition success. It summarizes key aspects of the writing process such as planning, organizing, drafting, revising and editing. Process writing models are presented including Flower and Hayes' cognitive process theory of writing. Research on elementary school writing processes is discussed emphasizing the importance of viewing writing as a problem-solving process and providing student choice, feedback and opportunities to write for different audiences.