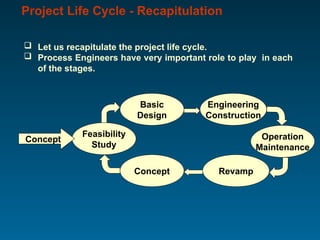
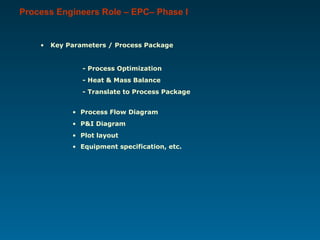
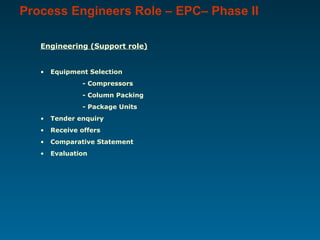
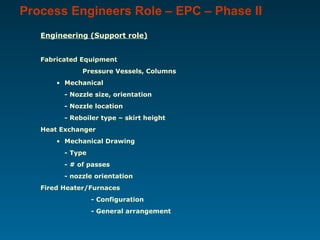
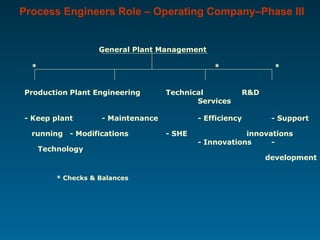
The document outlines the vital role of process engineers throughout the project life cycle, emphasizing their responsibilities in the phases of engineering, construction, operation, and maintenance. It discusses their involvement in key activities such as feasibility studies, technology selection, equipment design, and plant commissioning. Additionally, it highlights the importance of research and development for continuous improvement in efficiency and innovation within the industry.