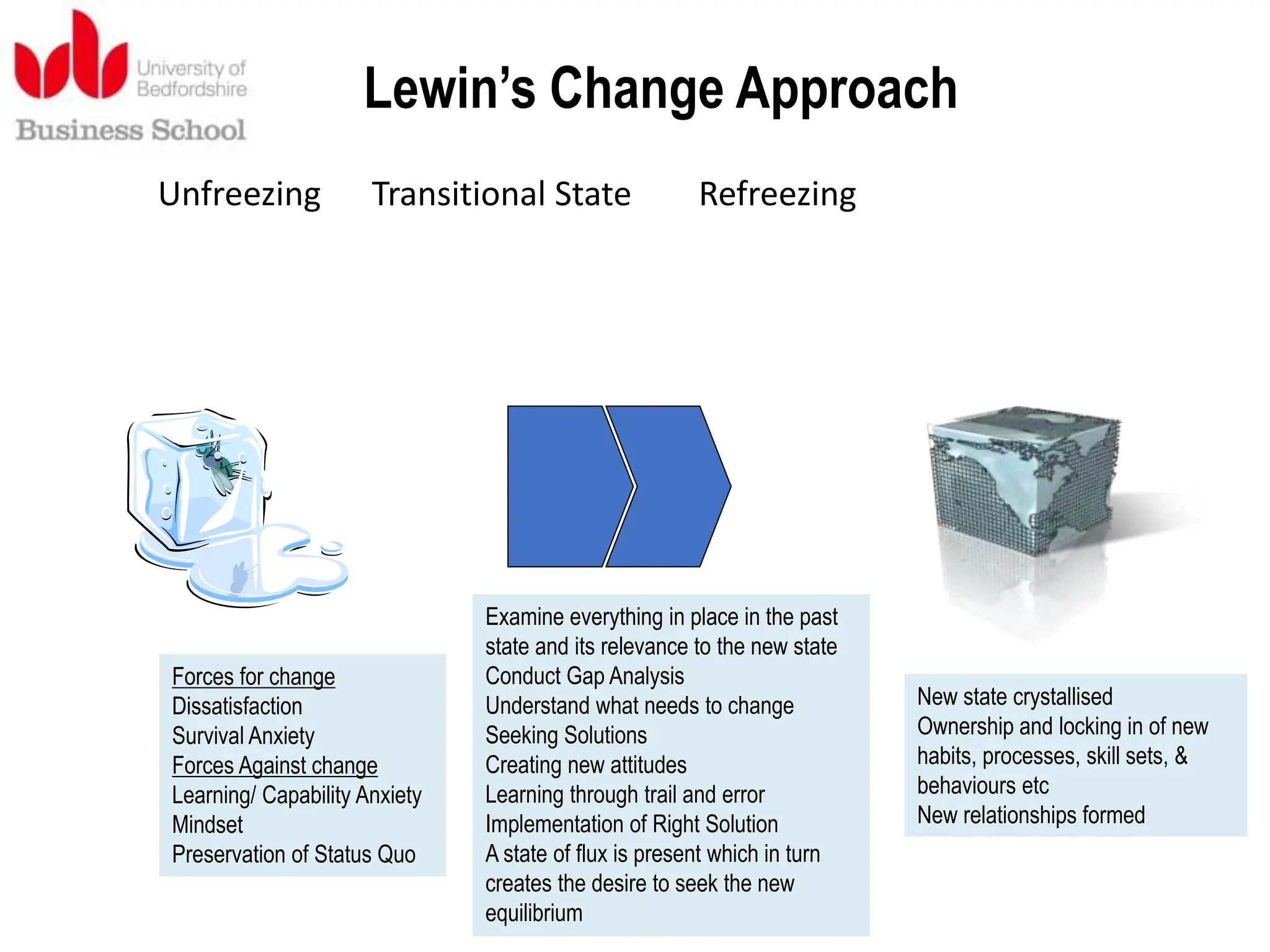
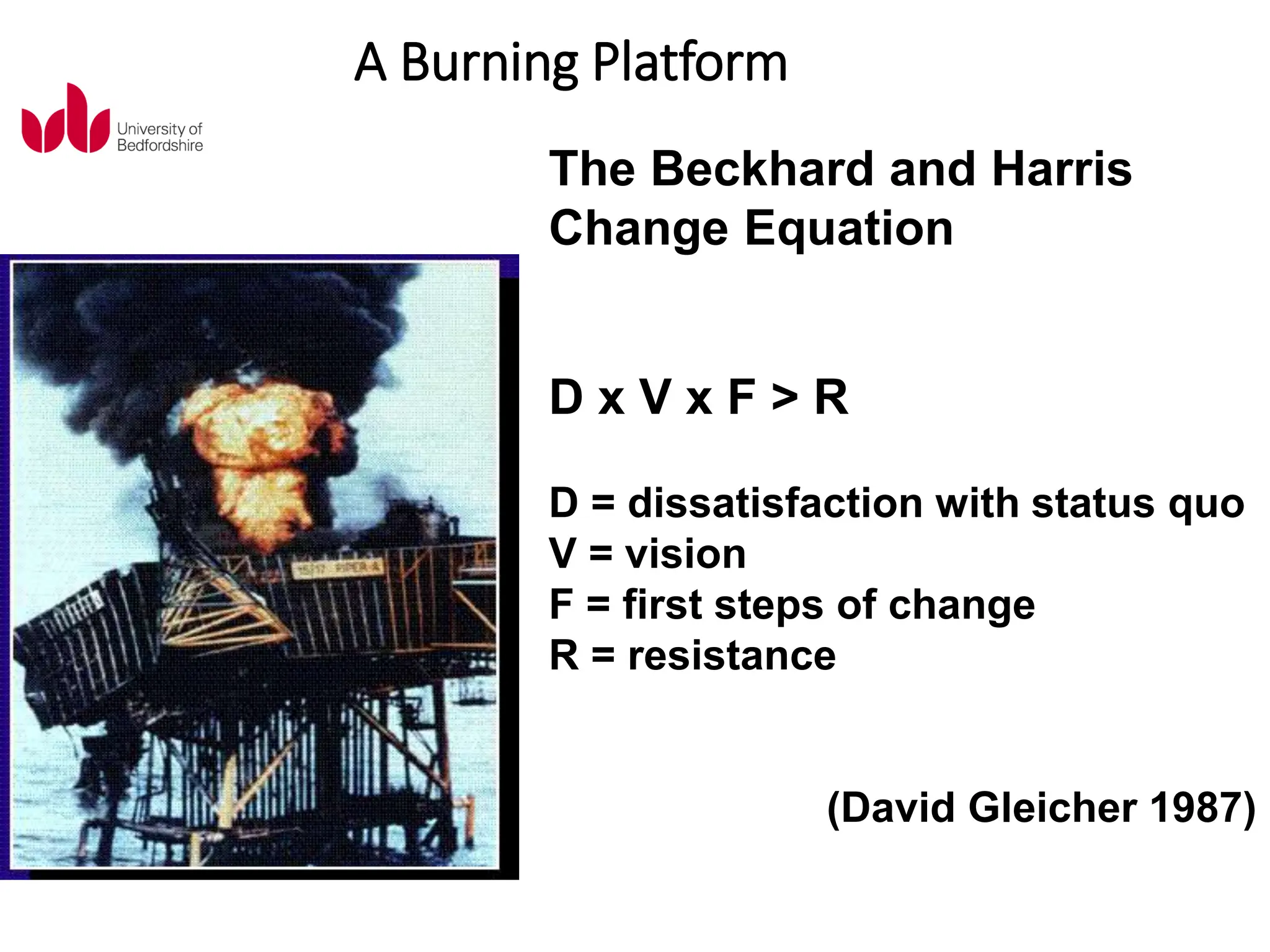
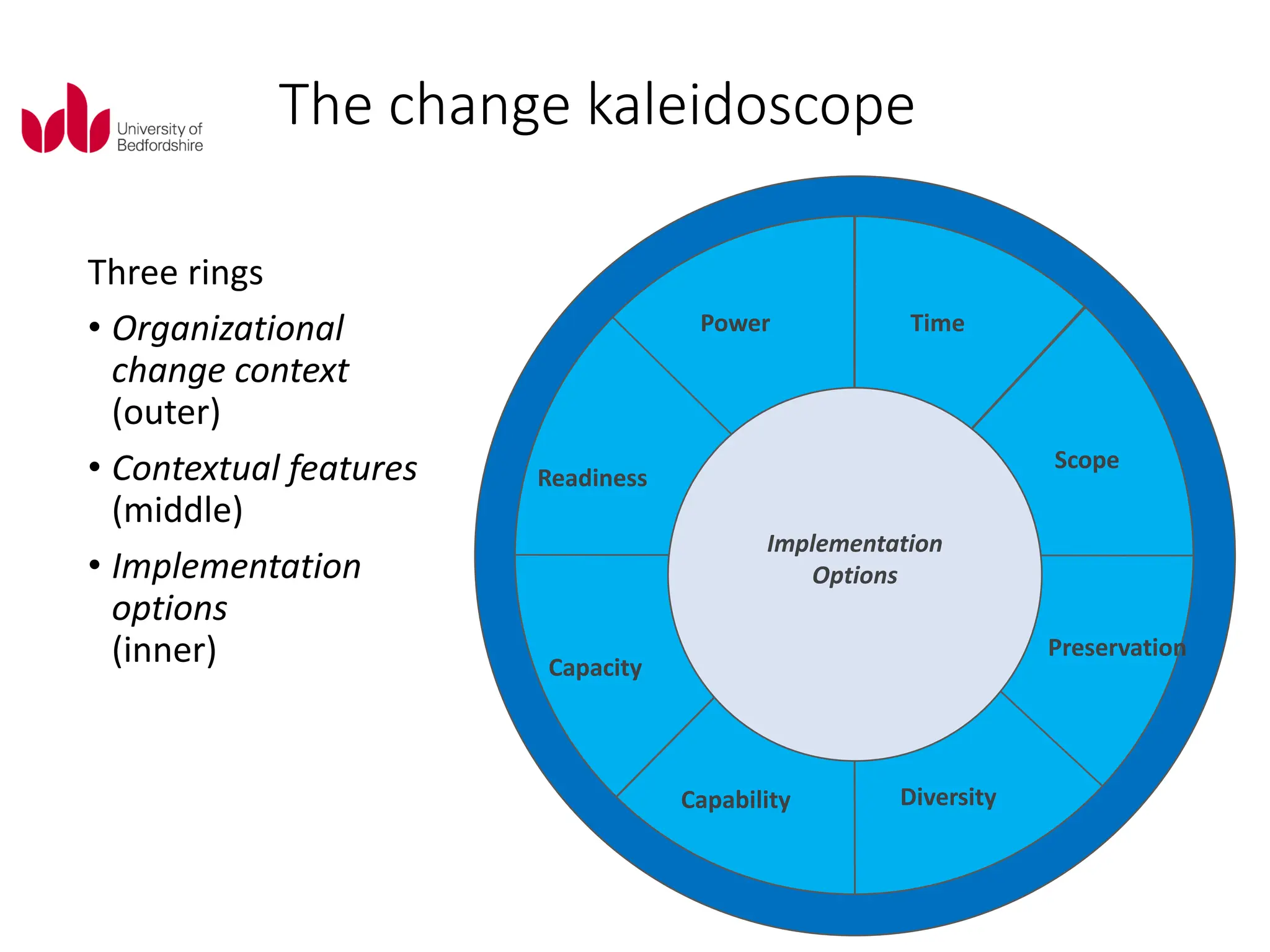
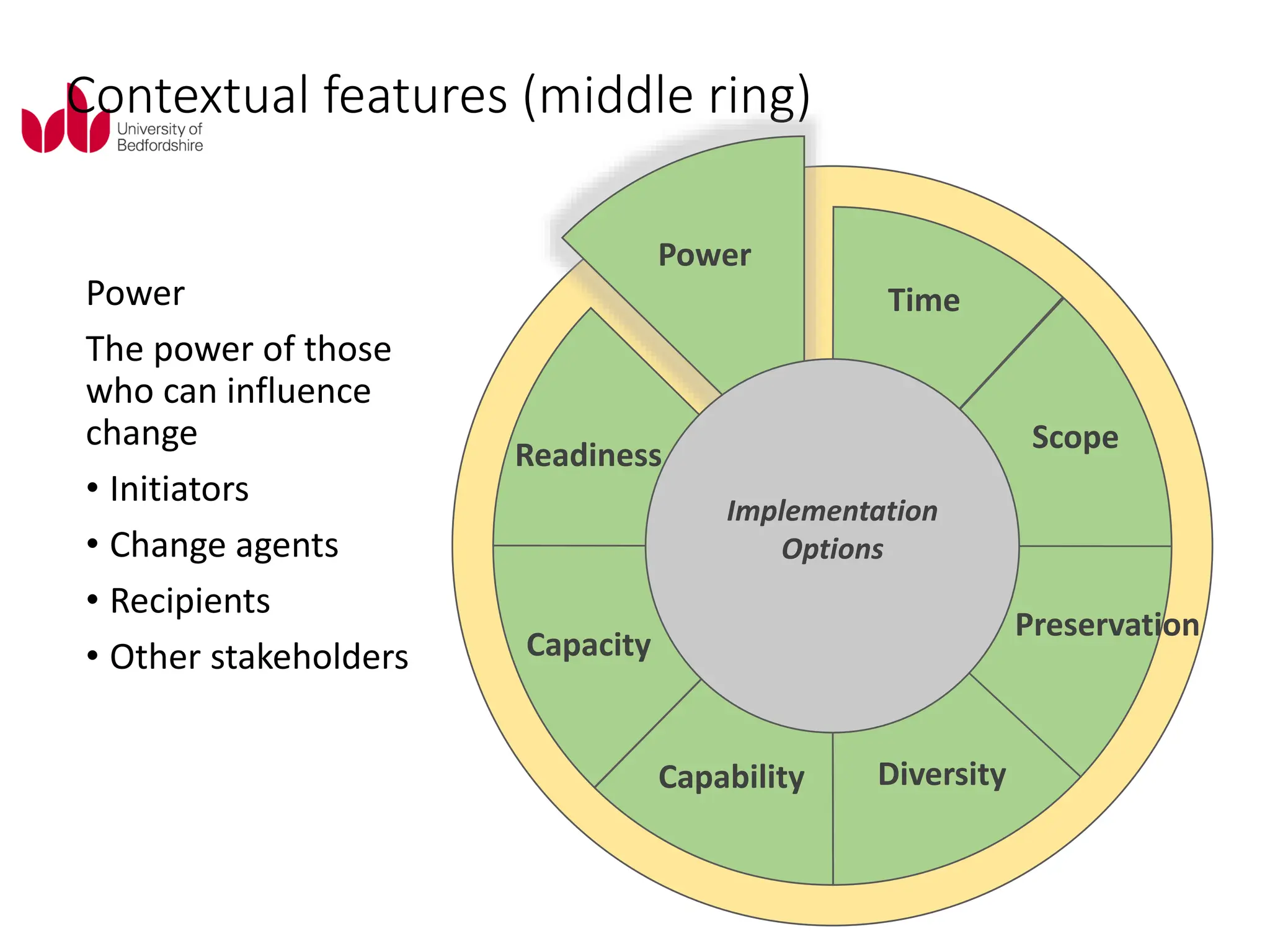
This document discusses various planned and process approaches to change management. It describes Lewin's three-step model of unfreezing, transitioning, and refreezing. Kotter's eight-step model and dual operating system are also discussed. Process approaches covered include Senge's learning organization, the thinking organization, the change kaleidoscope, and the storying process. Contextual features like time, scope, diversity, and power that influence change implementation are also summarized.