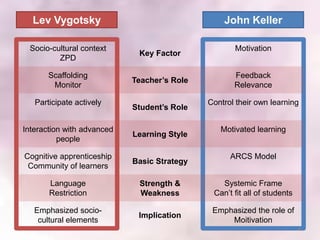
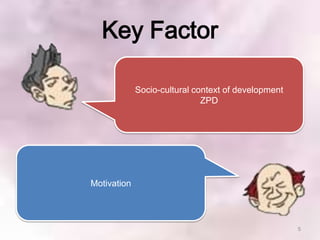
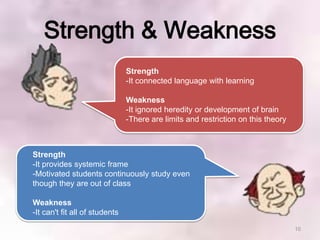
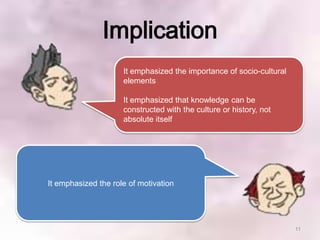
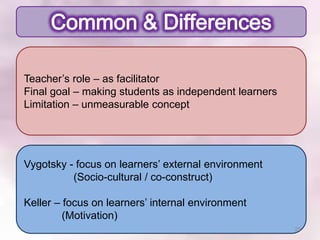
This document summarizes Vygotsky and Keller's learning theories and how they can be applied to a Scrooge project. According to Vygotsky, learning occurs through social interaction and within one's zone of proximal development with guidance from teachers and more capable peers. Keller's theory emphasizes motivation, with teachers providing feedback, varying difficulty levels, and making lessons relevant. The Scrooge project will apply these theories by having students work collaboratively, with teachers providing scaffolding and feedback to help students learn independently.