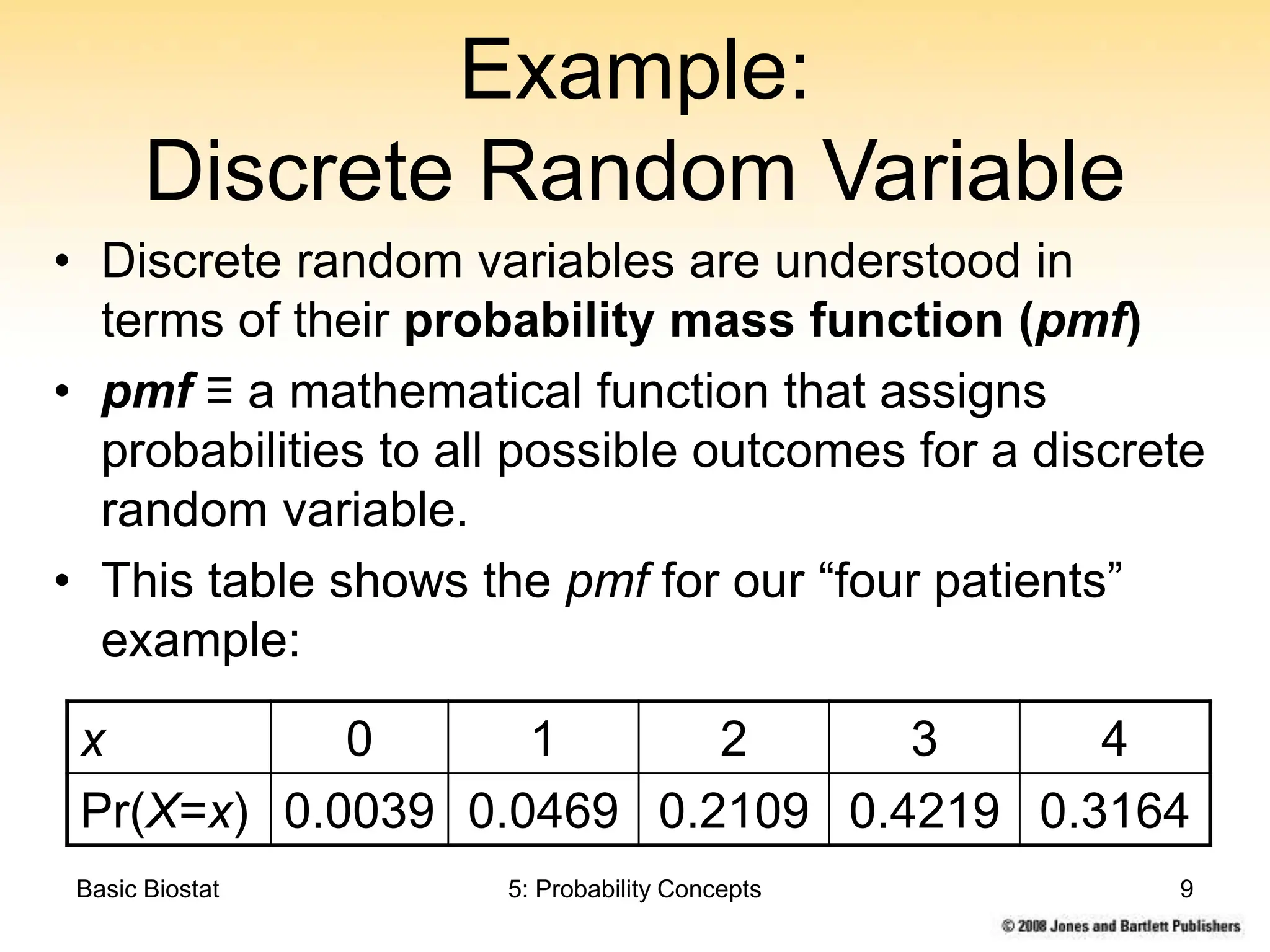
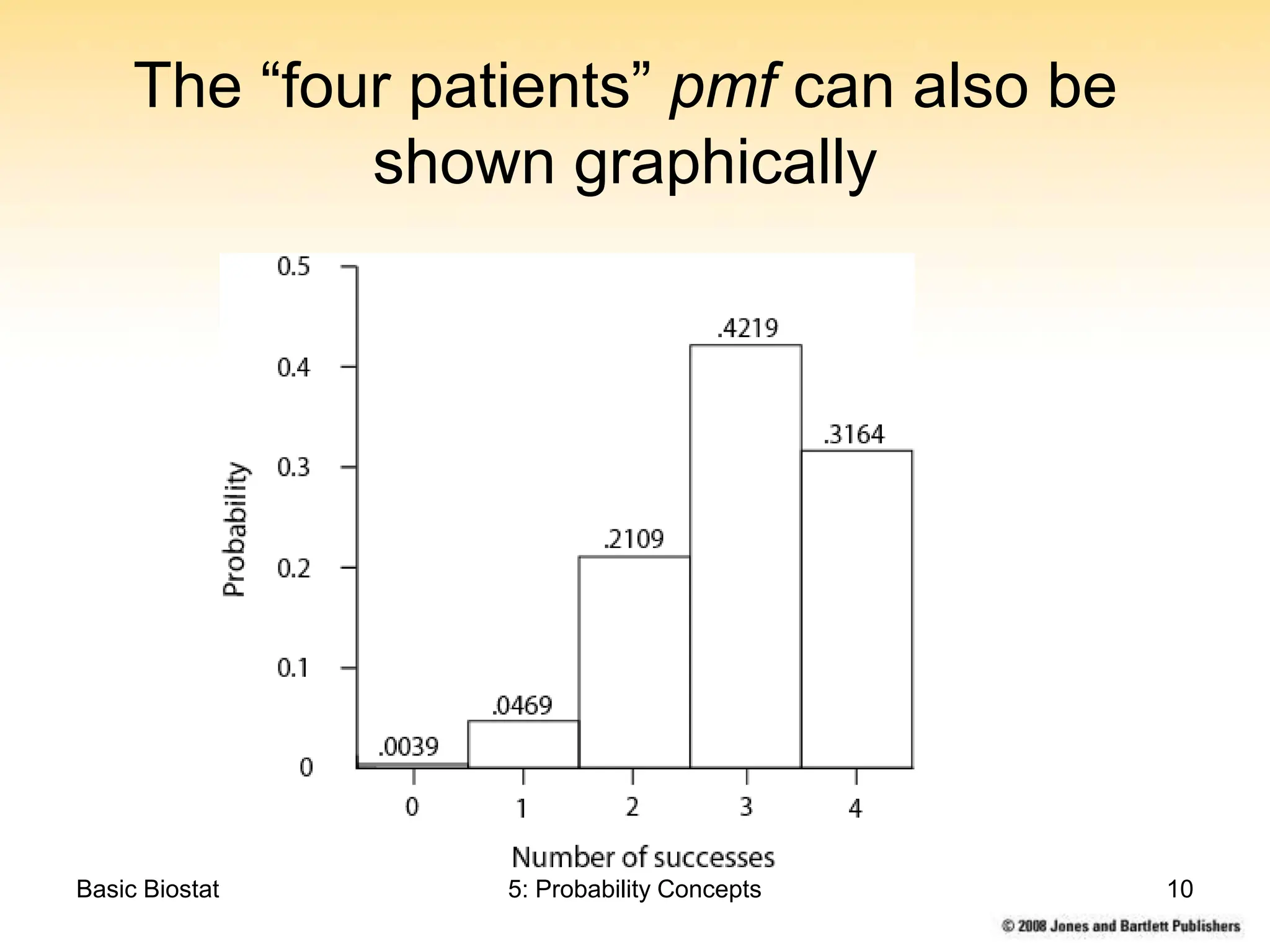
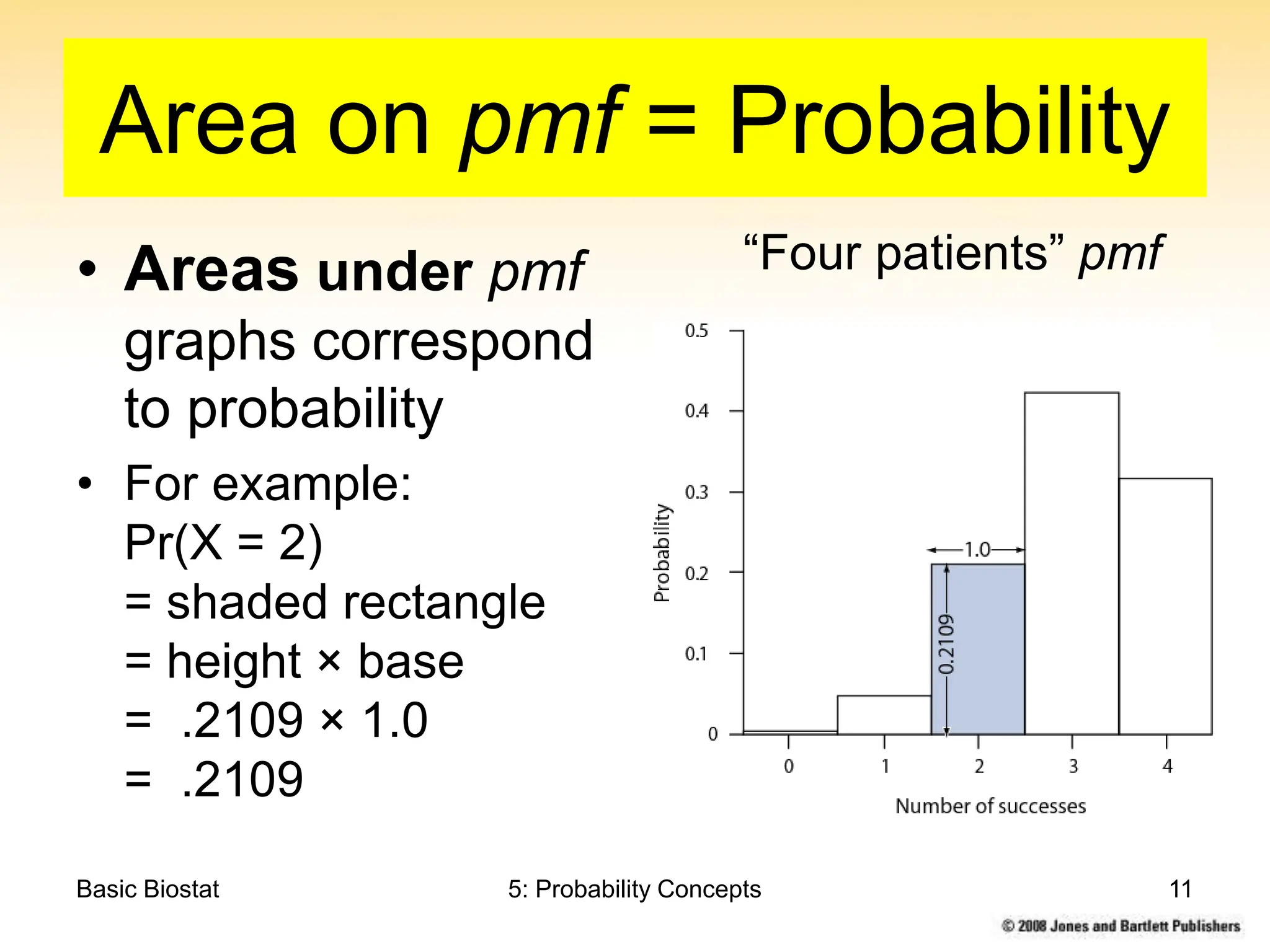
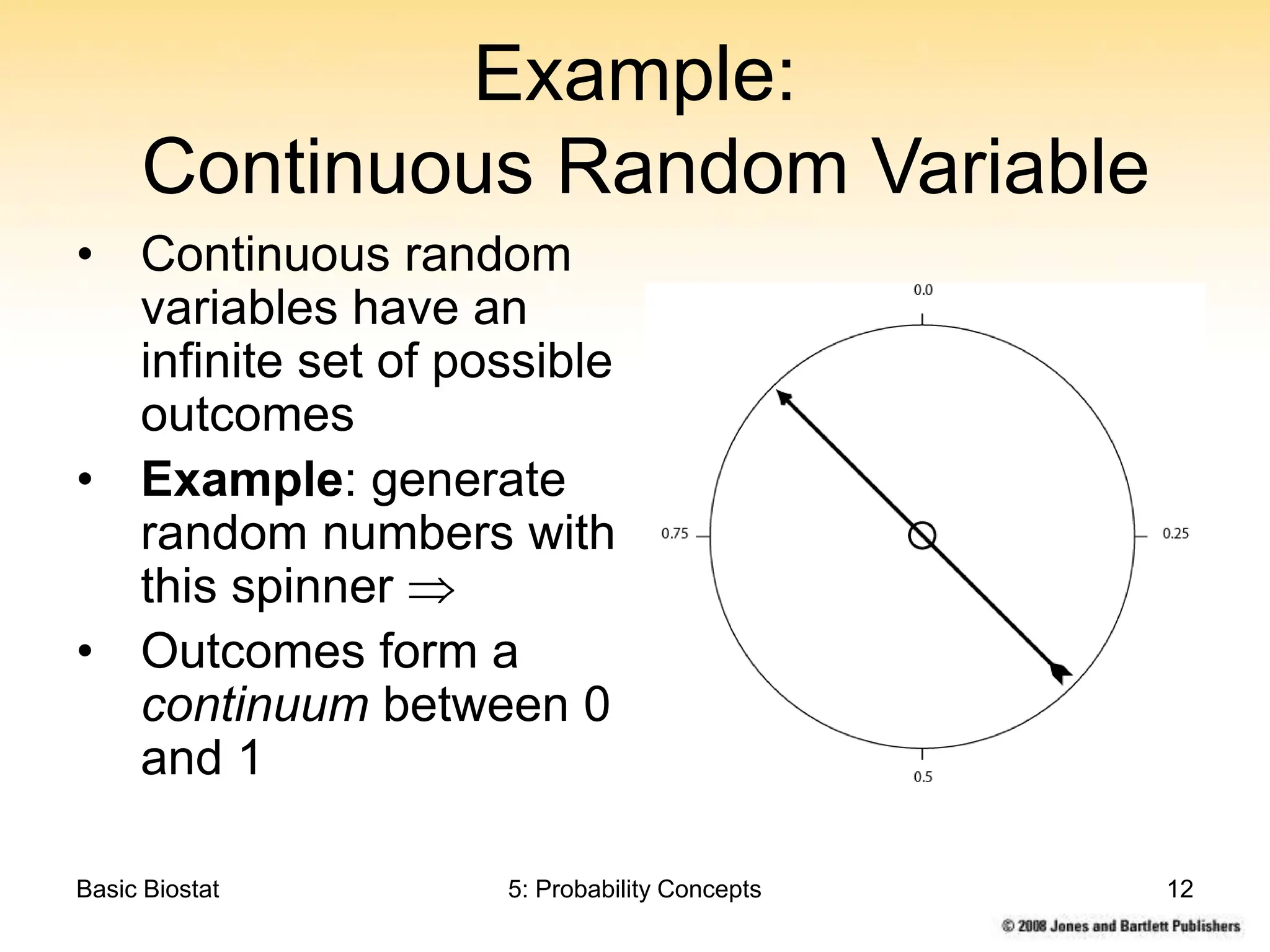
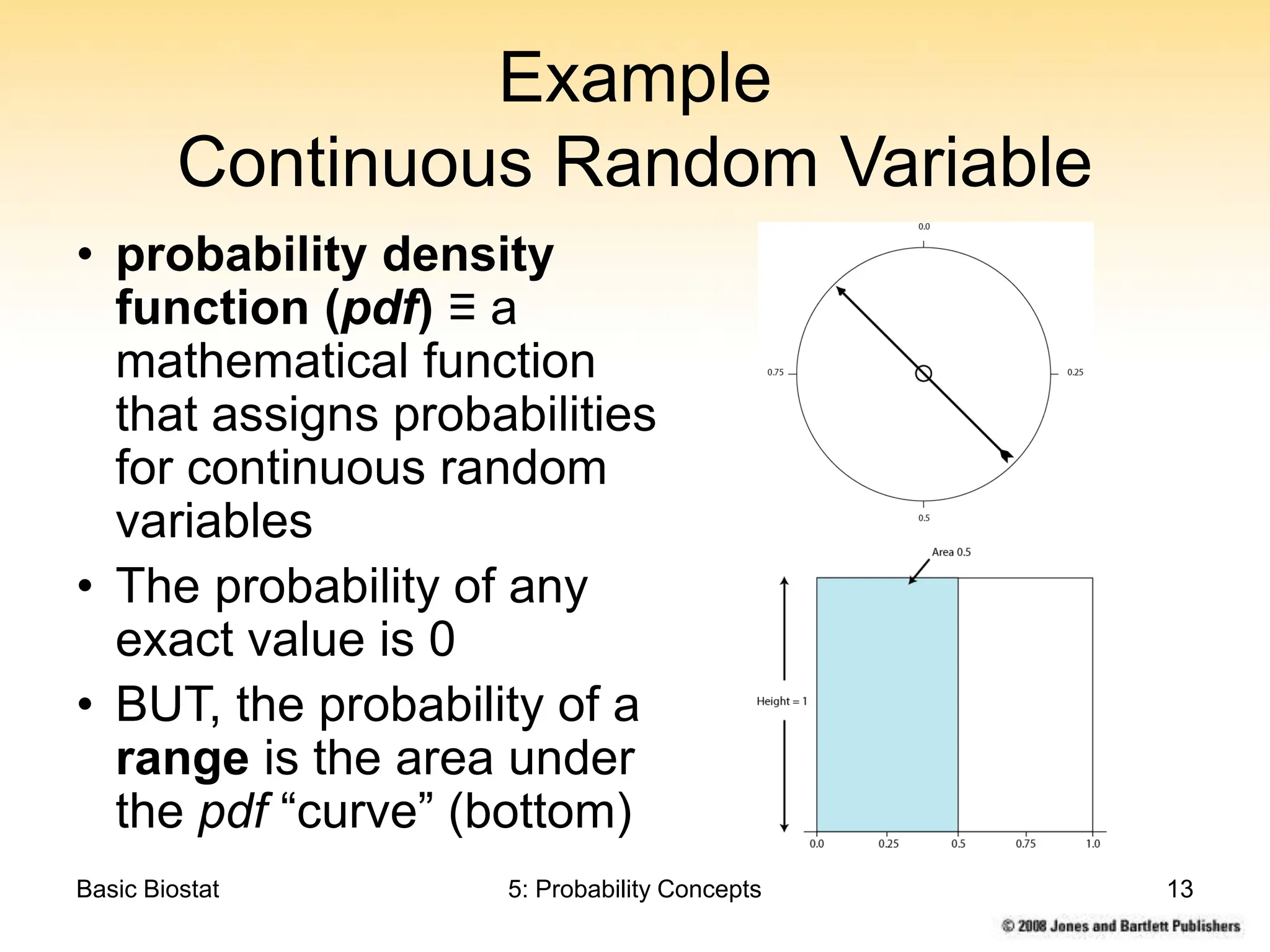
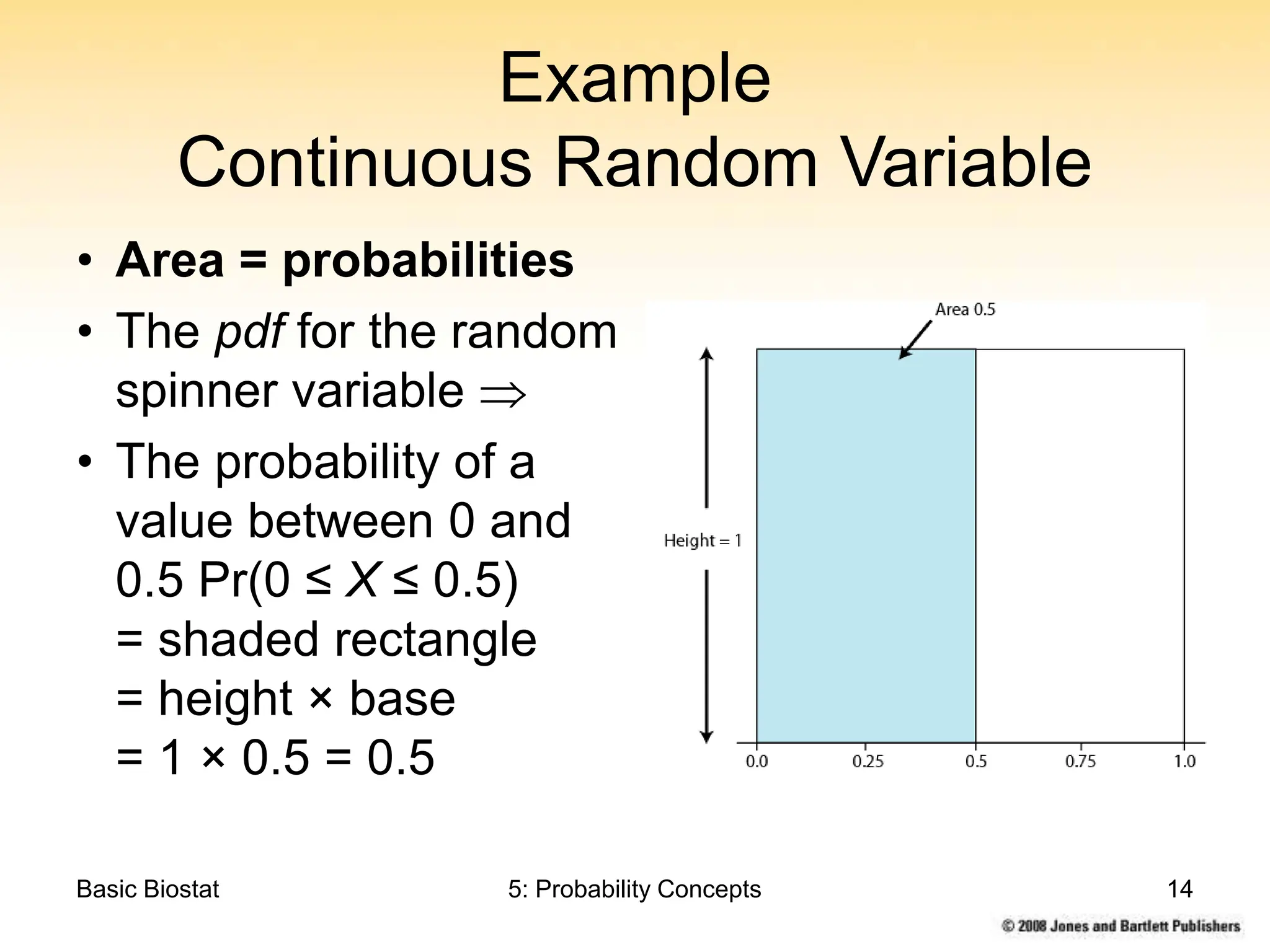
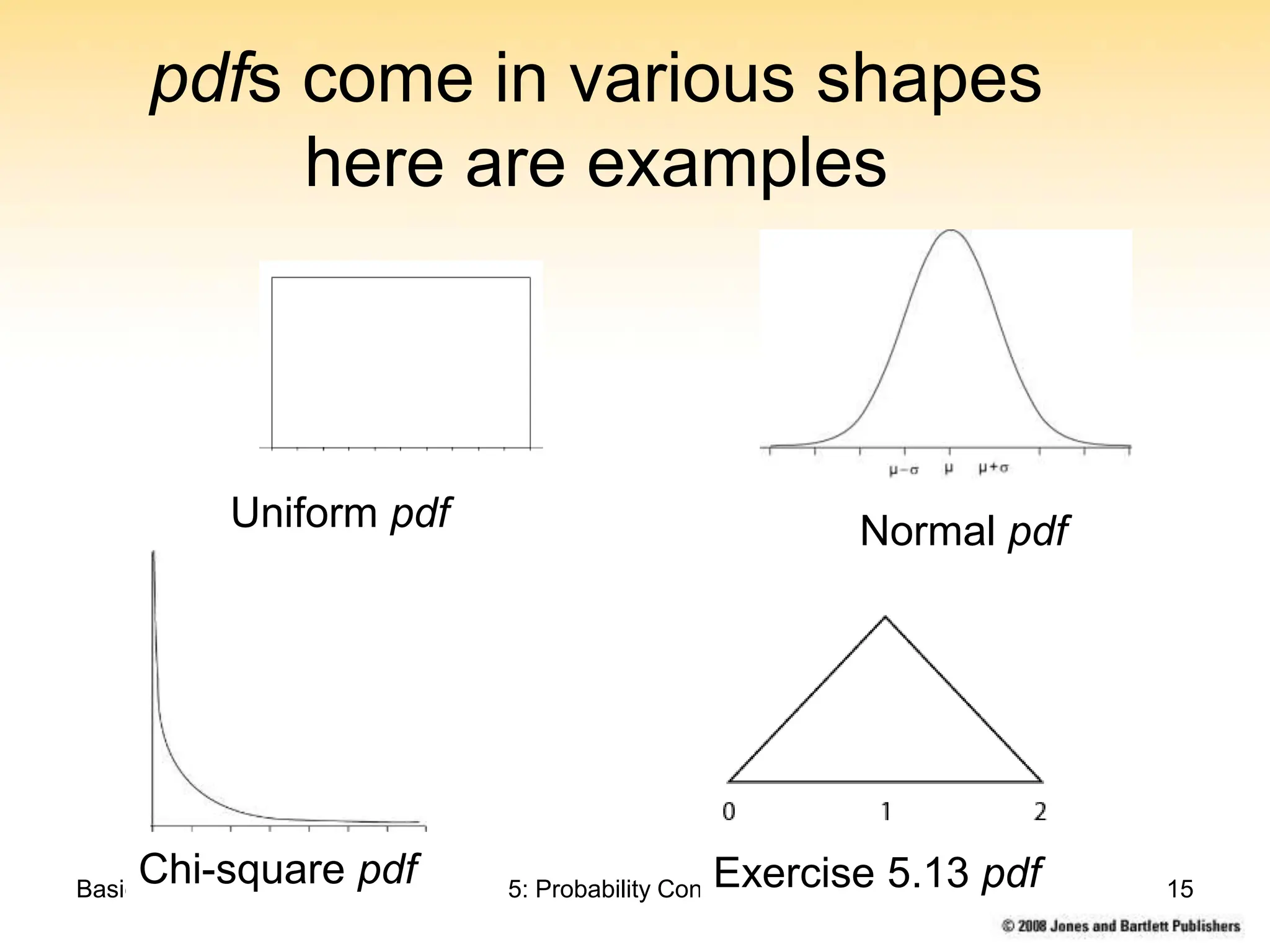
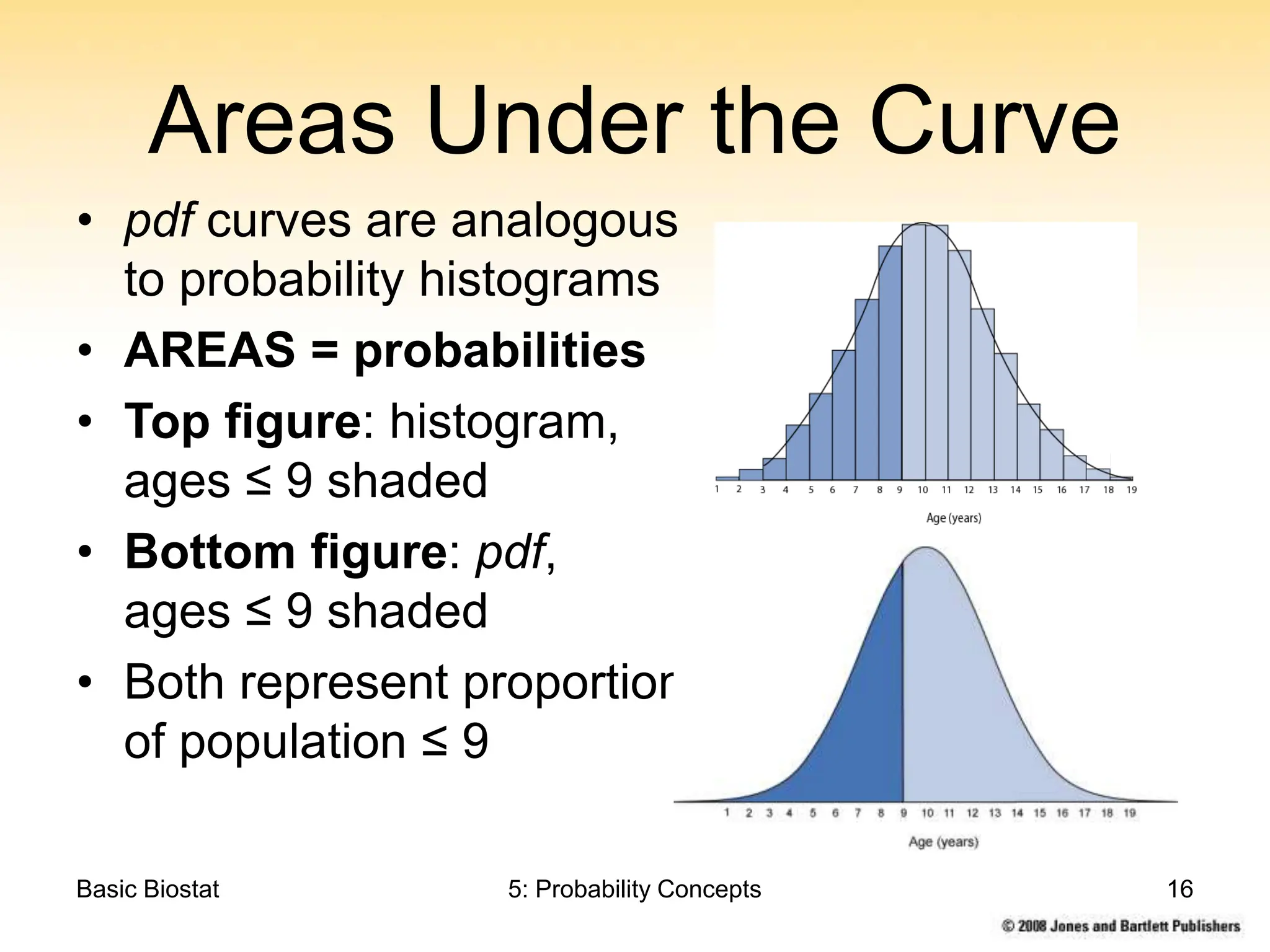
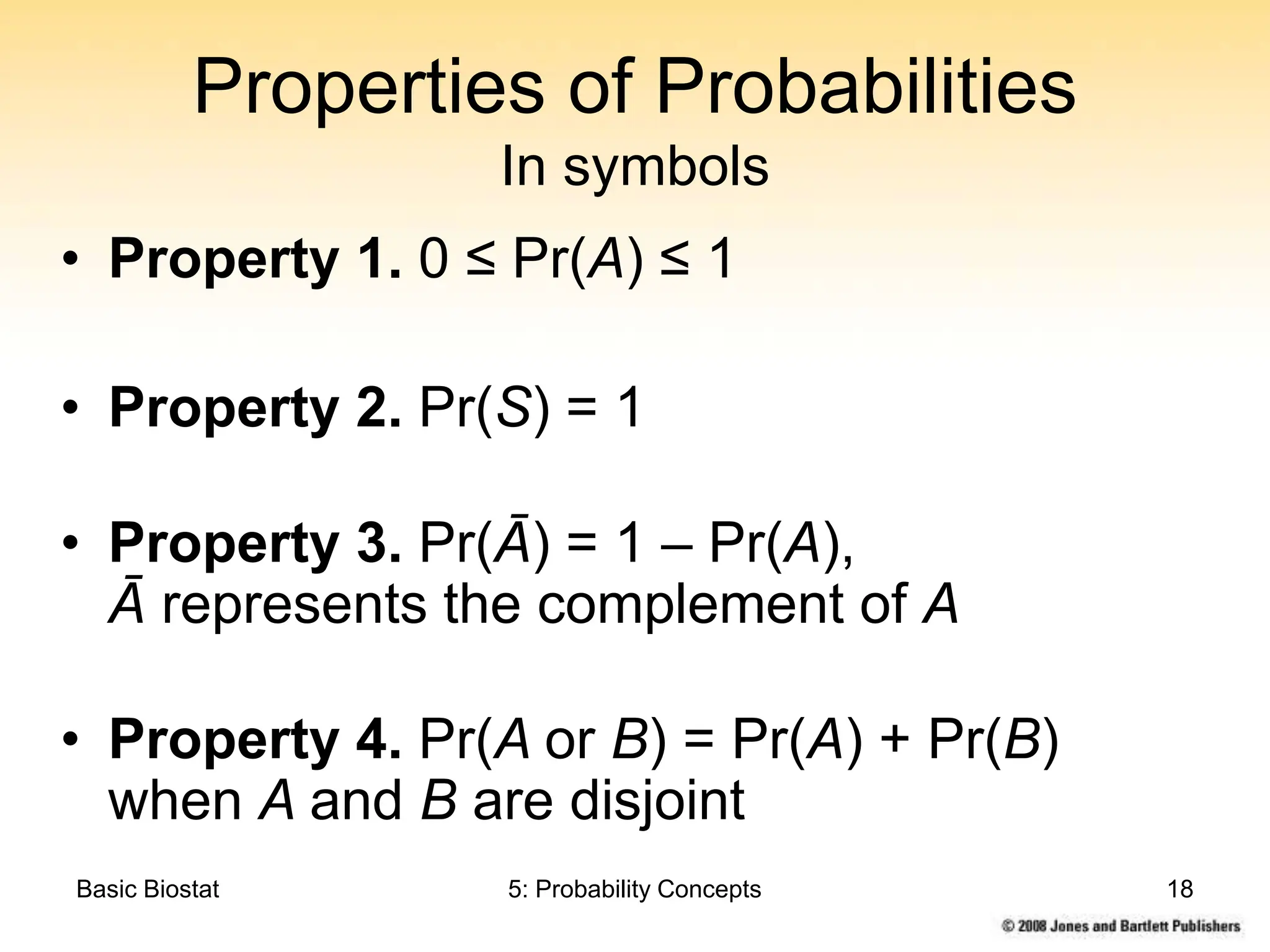
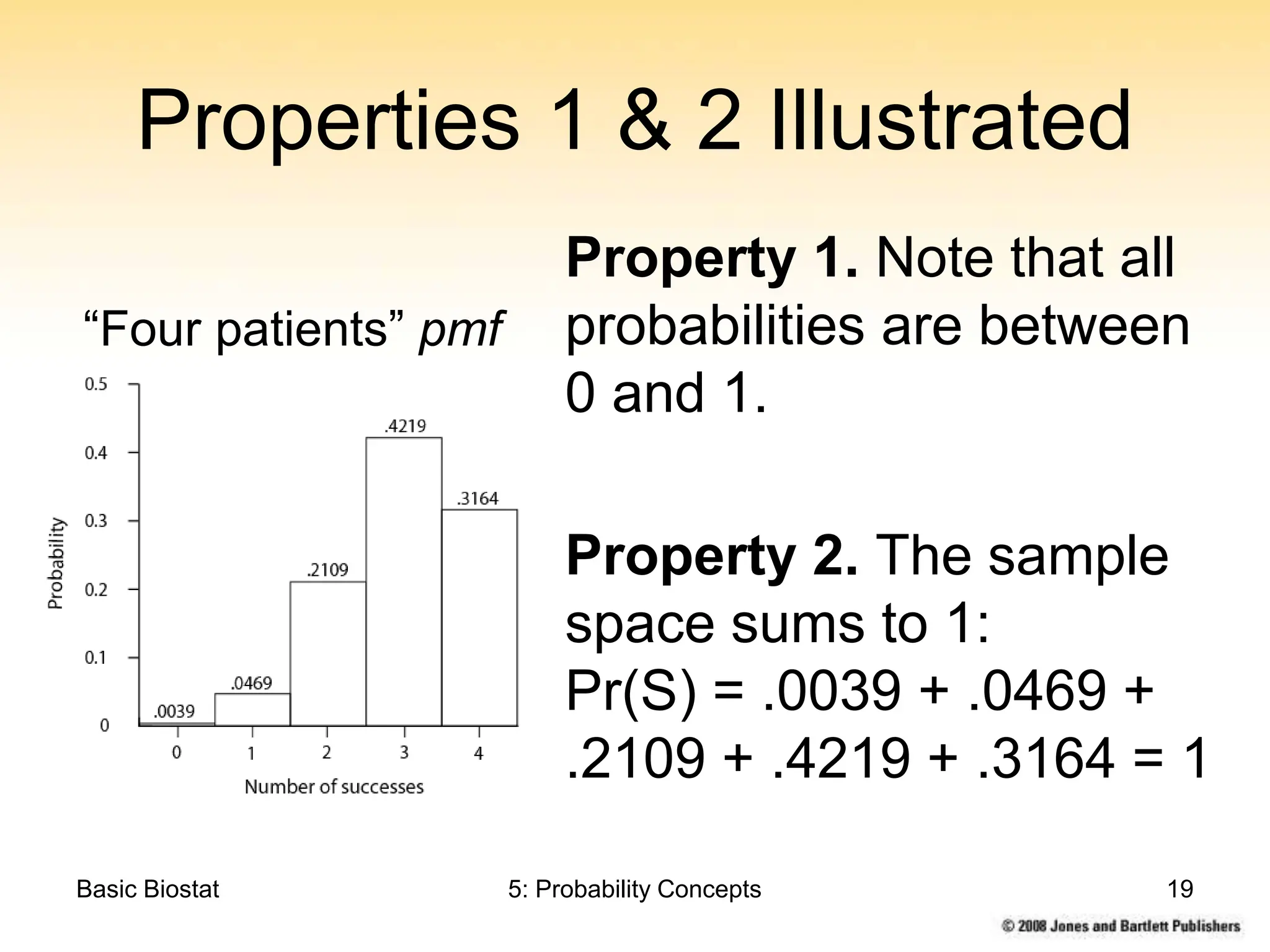
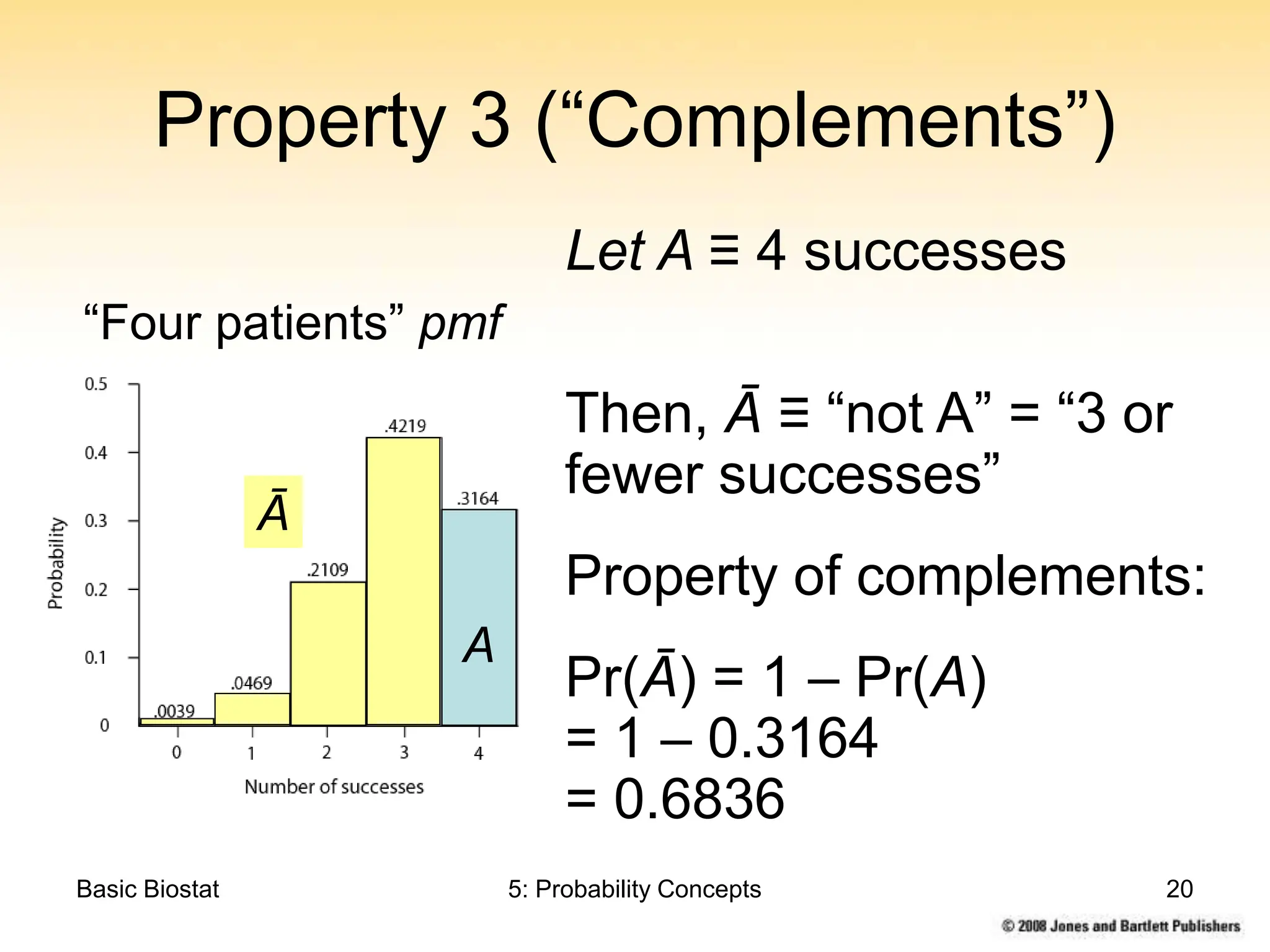
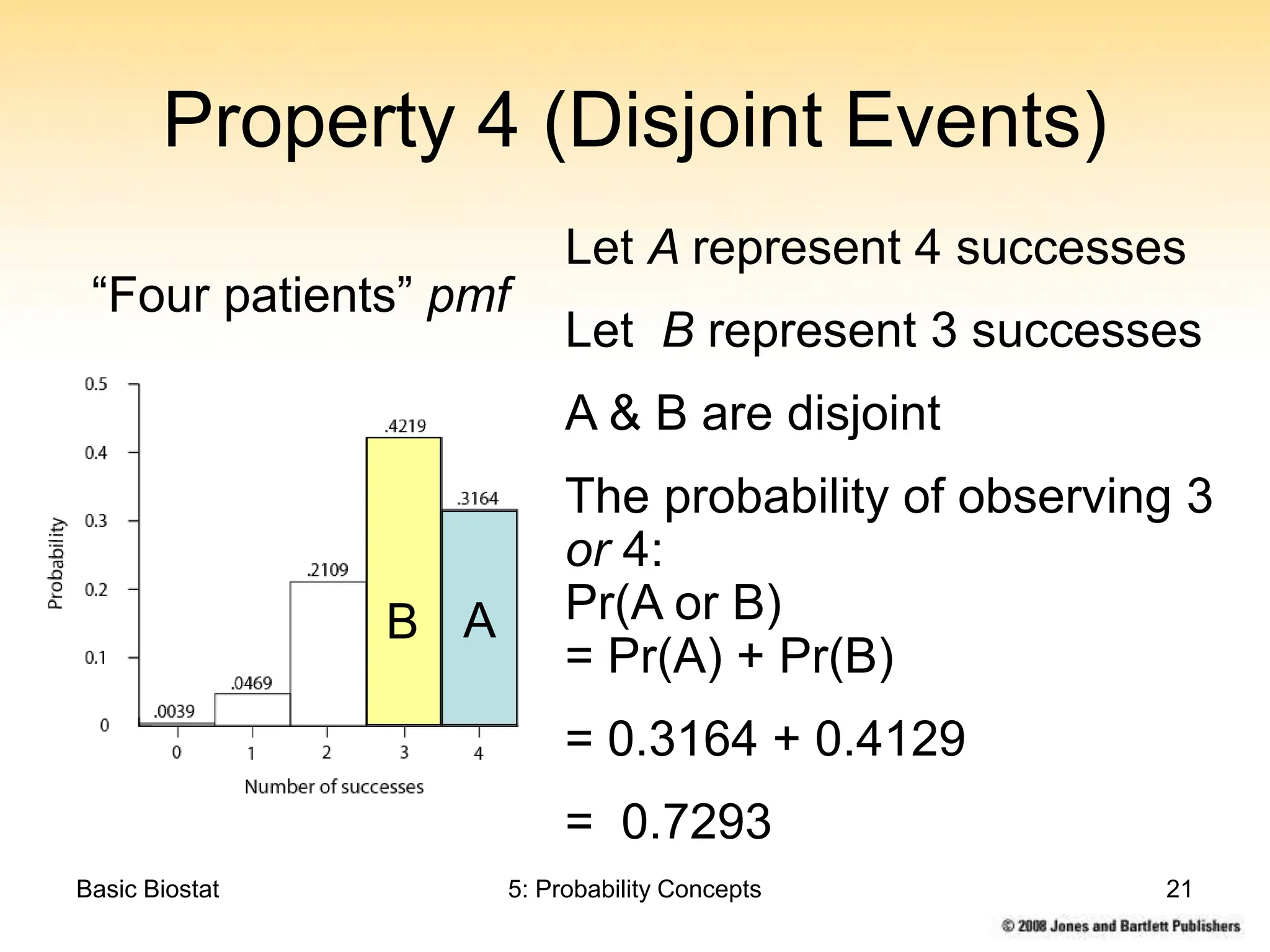
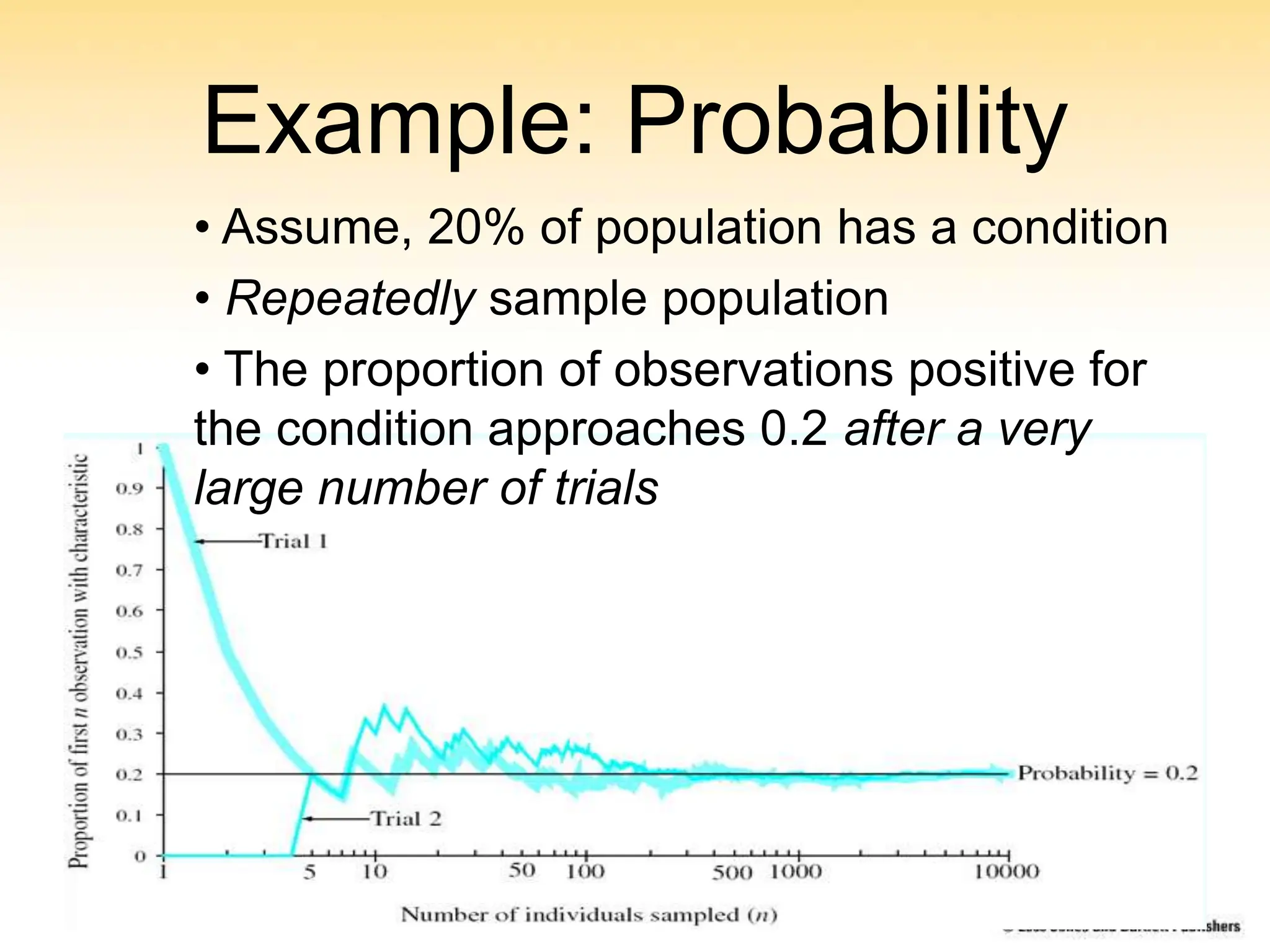
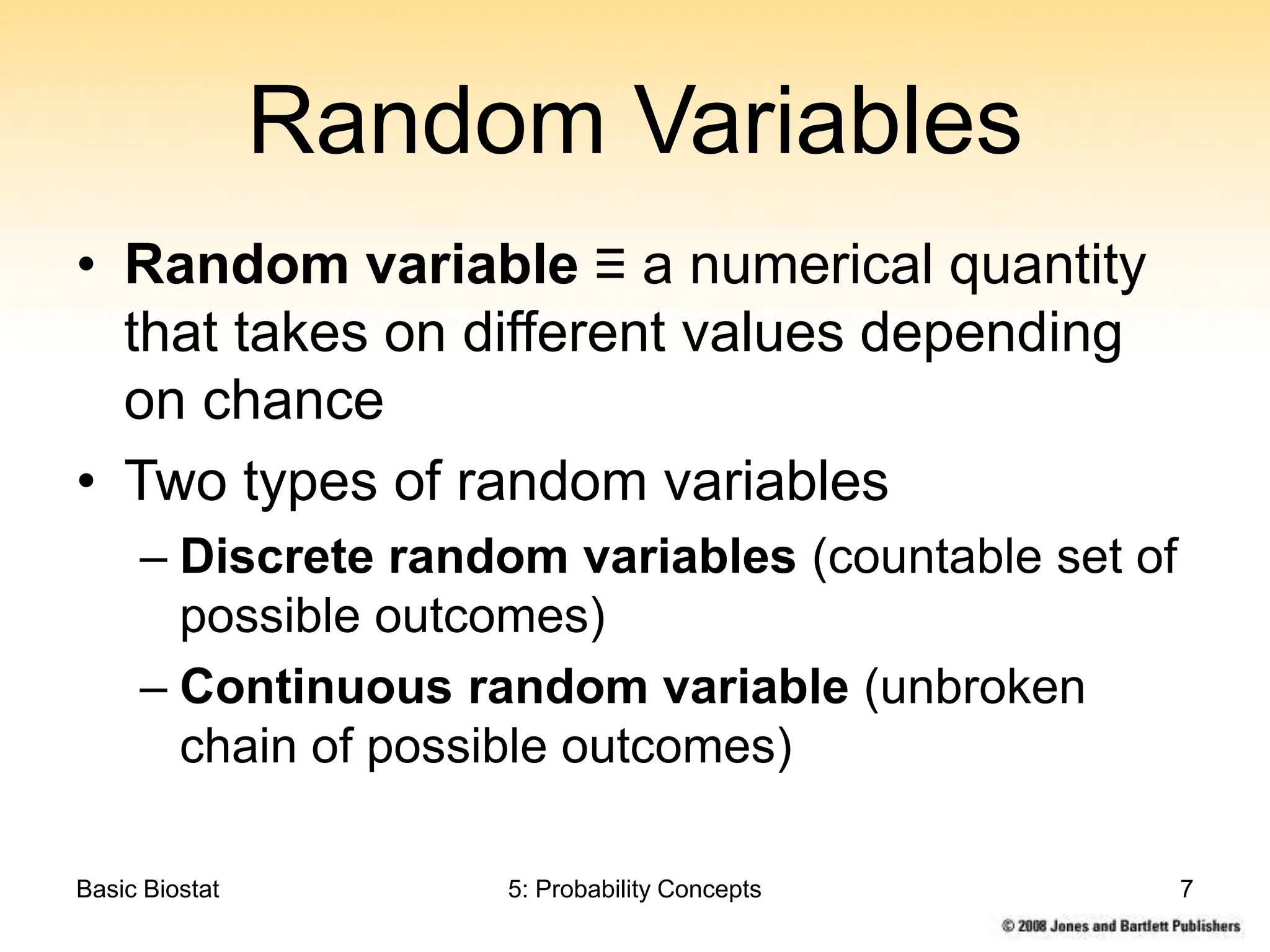
This chapter discusses probability concepts including random variables, events, and probability. It defines two types of random variables - discrete and continuous. Discrete random variables take on countable values while continuous random variables have an unbroken range of possible outcomes. Probability is defined as the relative frequency of an event occurring in the long run. Properties of probability include being between 0 and 1, the sample space summing to 1, complements summing to 1, and adding probabilities of disjoint events. Examples illustrate probability mass functions for discrete variables and probability density functions for continuous variables.




![Basic Biostat 5: Probability Concepts 8
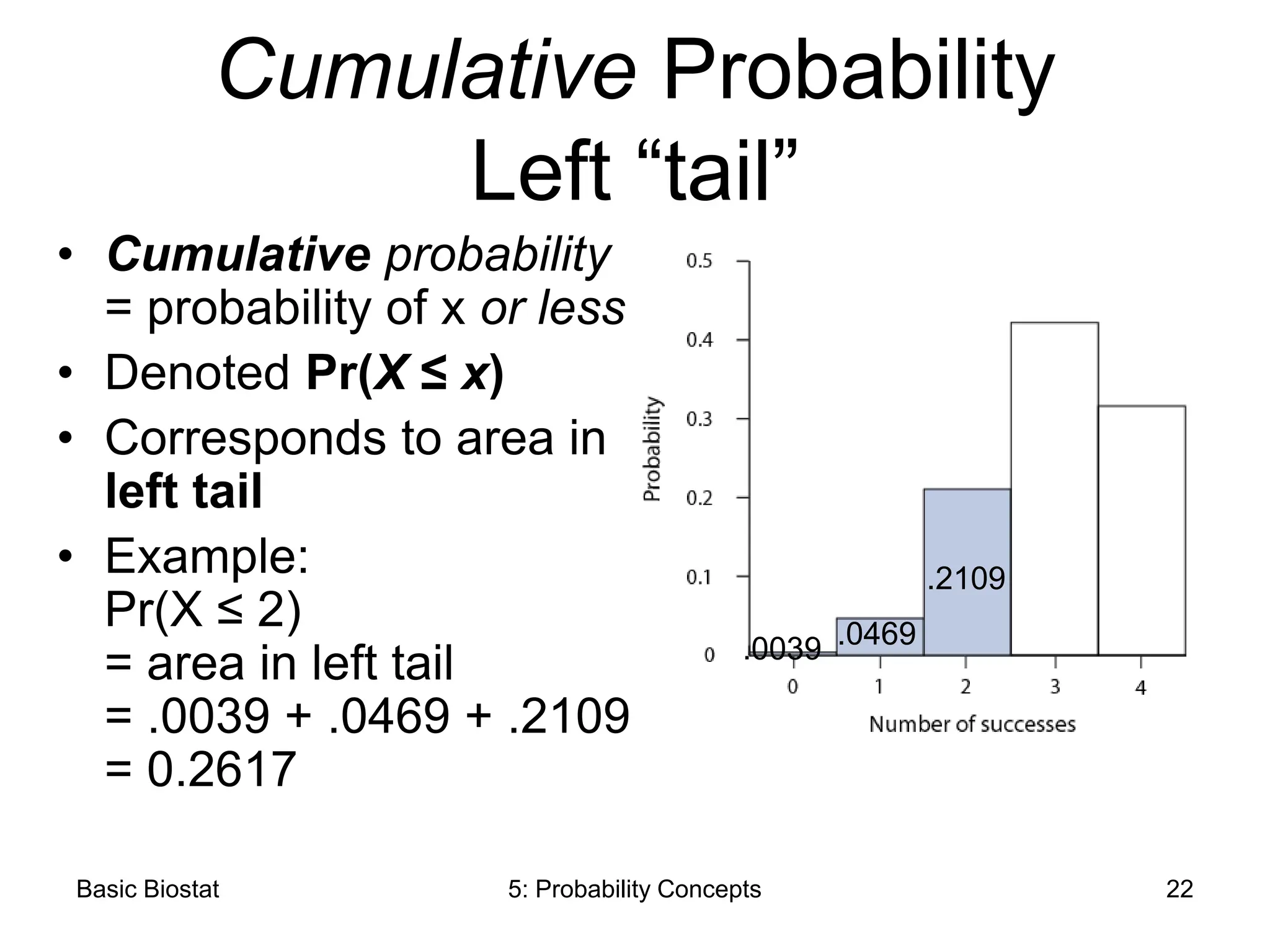
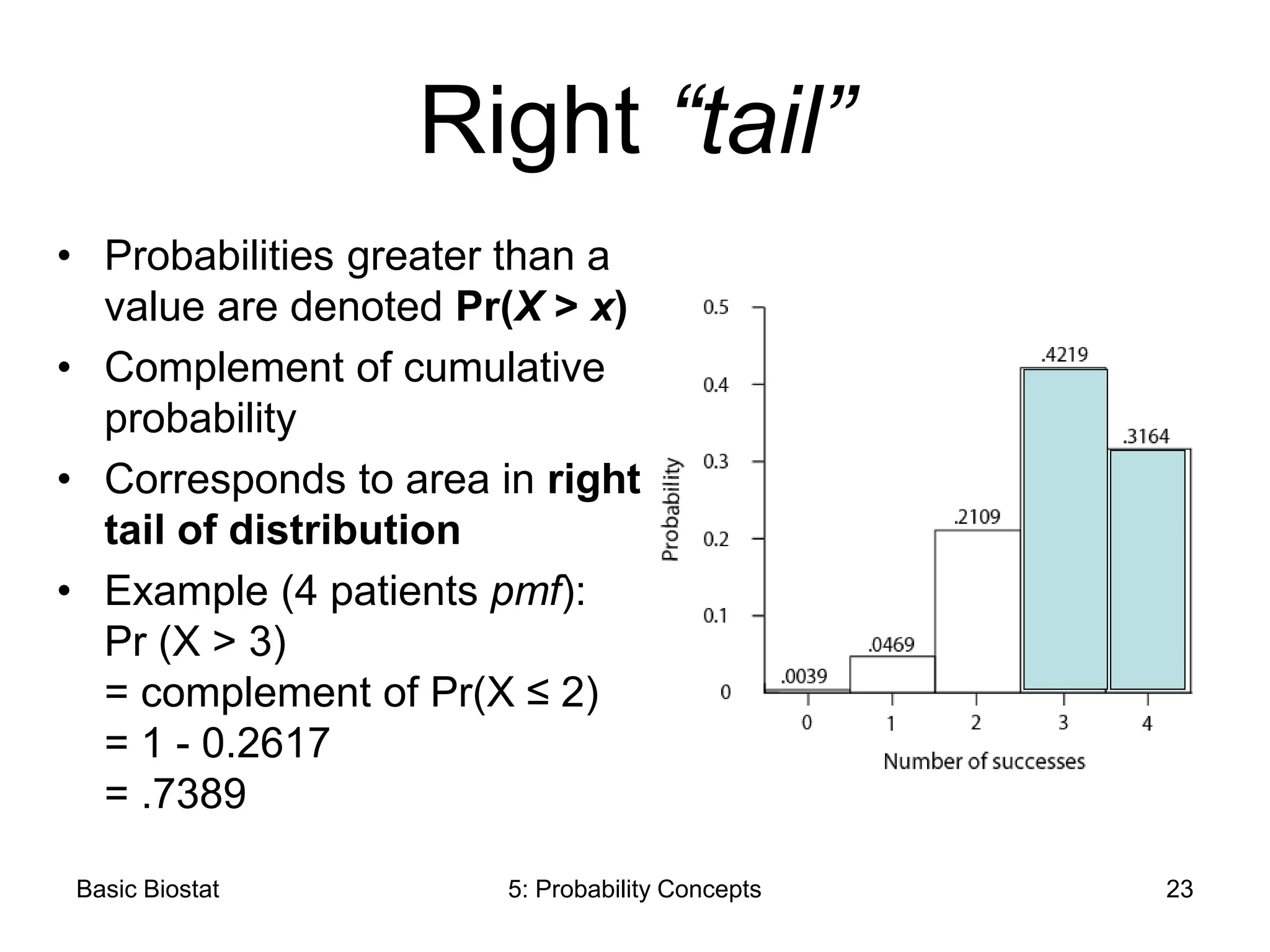
Example:
Discrete Random Variable
• Treat 4 patients with a
drug that is 75% effective
• Let X ≡ the [variable]
number of patients that
respond to treatment
• X is a discrete random
variable can be either 0,
1, 2, 3, or 4 (a countable
set of possible outcomes)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gerstmanpp05-240402045858-71c4c9d1/75/Probability-and-statistics-Understanding-7-2048.jpg)