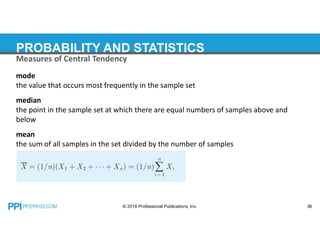
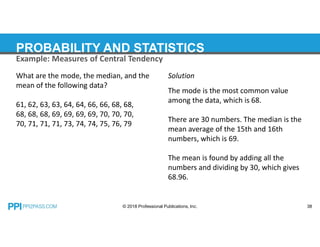
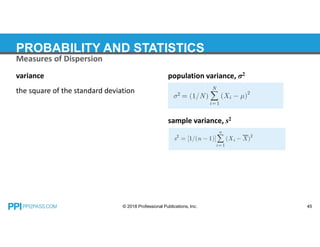
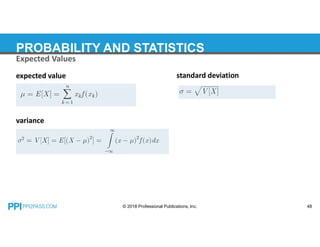
This document provides an overview of topics covered in a probability and statistics course for an FE exam prep, including combinations and permutations, sets, measures of central tendency such as mode, median and mean, measures of dispersion like standard deviation and variance, expected values, probability distributions, and hypothesis testing. Examples are provided for calculating the mode, median, mean and weighted mean of data sets and for determining population variance and standard deviation.