This document provides an introduction to key concepts in artificial intelligence including uncertainty, probability, possible worlds, unconditional and conditional probability, Bayes' rule, random variables, probability distributions, independence, Bayesian networks, and approximate inference techniques like sampling and likelihood weighting. It defines key terms and provides examples to illustrate probabilistic reasoning and how to compute probabilities and inferences in Bayesian networks.








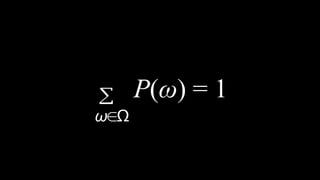







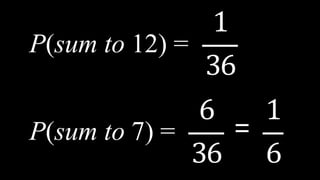


























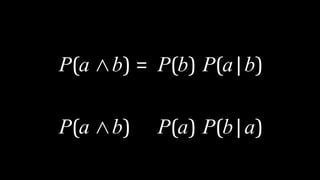



































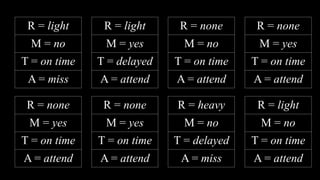
![Appointment
{attend, miss}
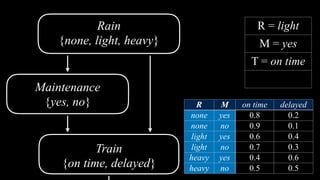
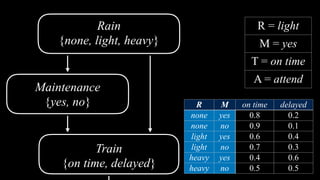
Train
{on time, delayed}
Maintenance
{yes, no}
Rain
{none, light, heavy}
P(Appointment | light, no)
= α P(Appointment, light, no)
= α [P(Appointment, light, no, on time)
+ P(Appointment, light, no, delayed)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/probabilisticreasoningai-230512212556-ed618672/85/PROBABILISTIC-REASONING-AI-pptx-81-320.jpg)