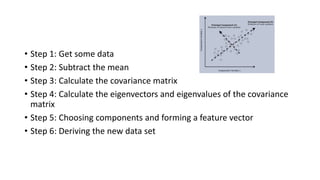
Principal component analysis (PCA) is a statistical technique used to reduce the dimensionality of large datasets by converting a set of observations of possibly correlated variables into a set of linearly uncorrelated variables called principal components. The first principal component accounts for as much of the variability in the data as possible, and each succeeding component accounts for as much of the remaining variability as possible. PCA is performed by calculating the eigenvectors and eigenvalues of the covariance matrix derived from the original dataset.