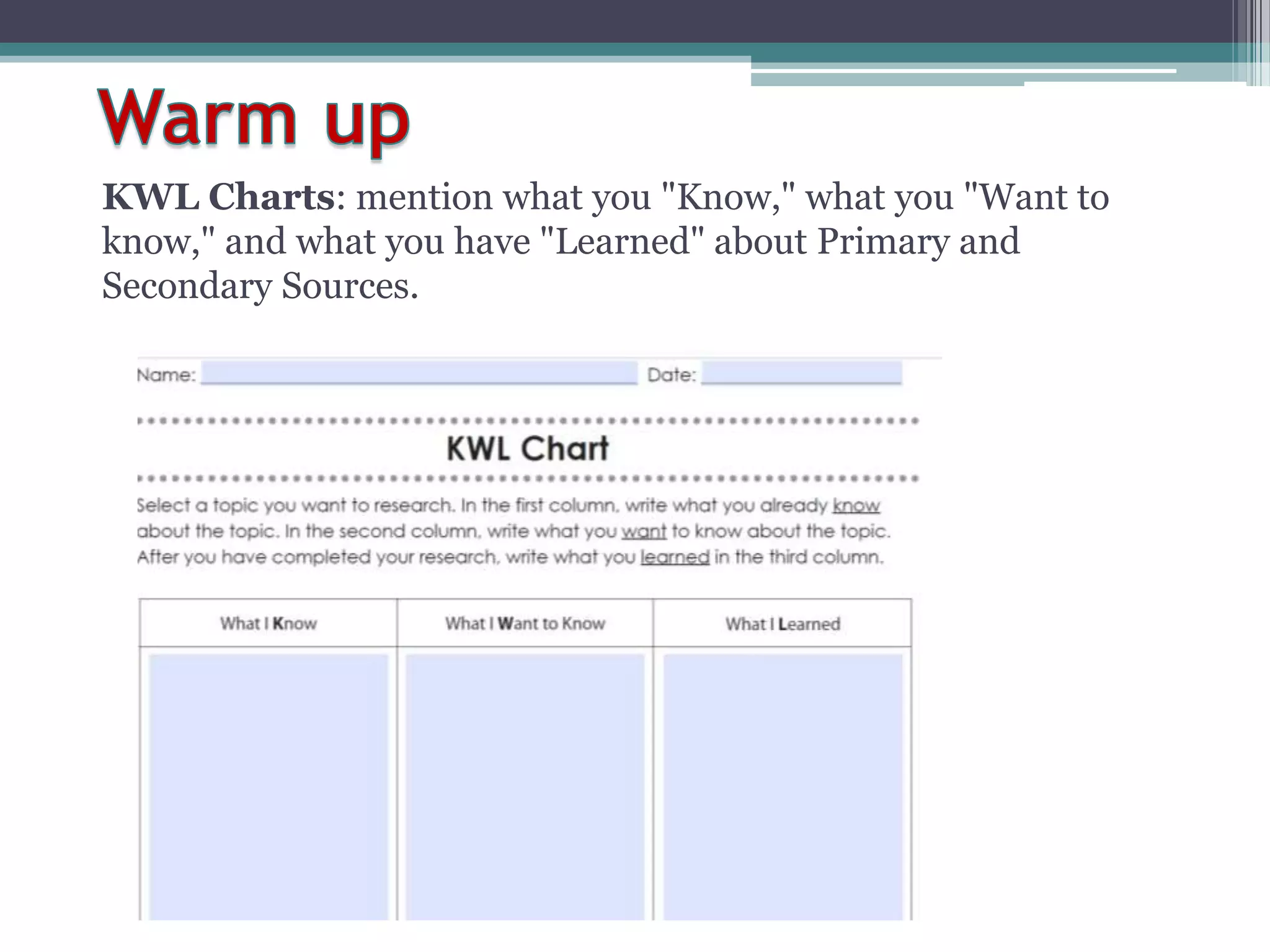
Primary sources are original documents or artifacts created during the time period being studied that provide first-hand accounts. Secondary sources are analyses or interpretations created after the event based on primary sources. While primary sources provide unfiltered perspectives, they lack context and completeness. Secondary sources help provide context and interpretation but rely on the perspectives of their authors. Both have advantages and disadvantages depending on the type of understanding and information needed. Students should use both primary and secondary sources when researching to gain different insights.