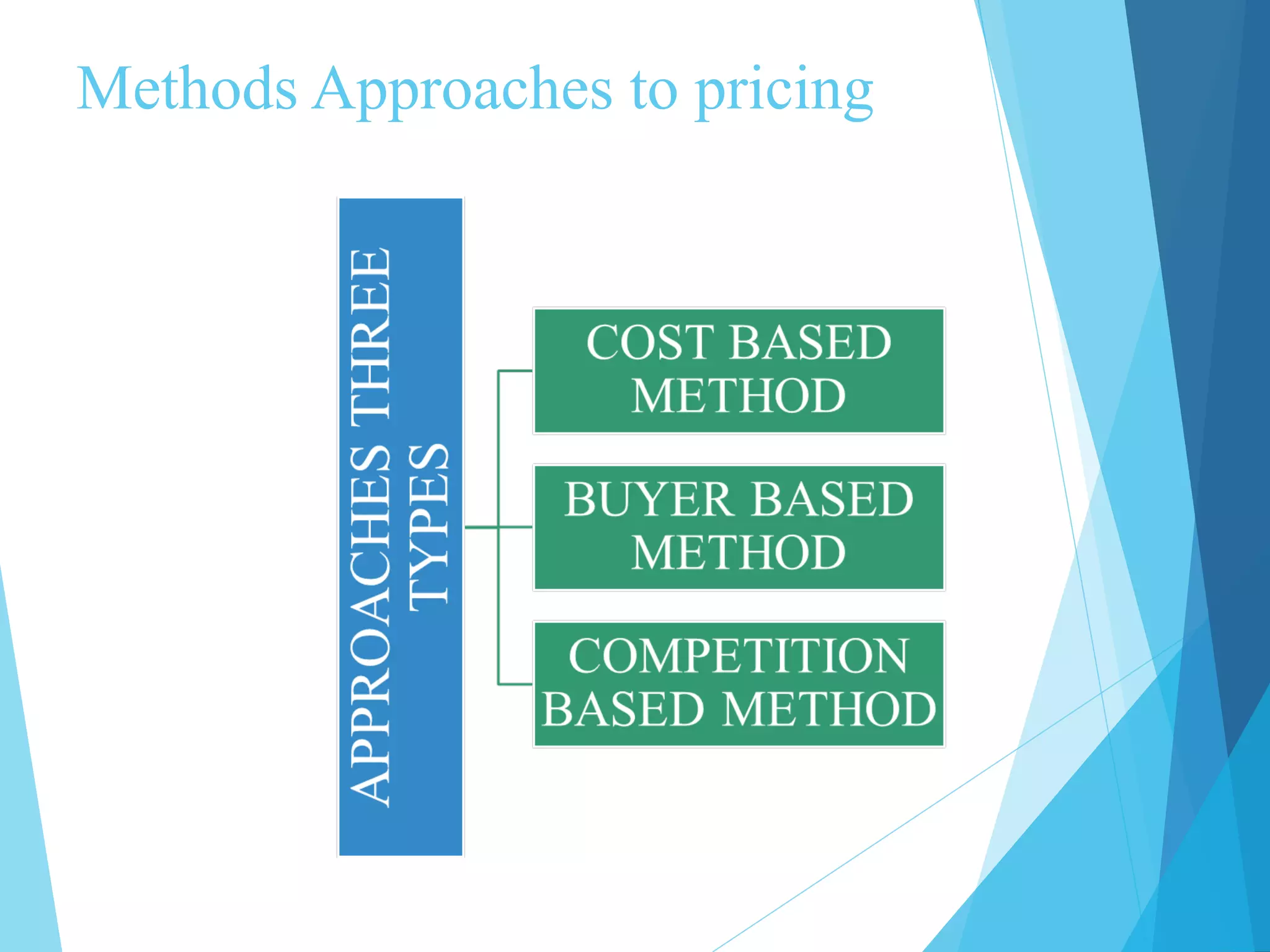
The document discusses various pricing strategies and approaches. It defines price and pricing, and lists factors that influence pricing decisions such as objectives, costs, competitors' prices, and consumer perceptions. It then describes several pricing methods including cost-plus pricing, break-even analysis, target profit pricing, going-rate pricing, and sealed-bid pricing. It also discusses buyer-based pricing where value instead of costs determines price. Finally, it provides examples of three specific pricing strategies: price penetration, price skimming, and the loss leader approach.