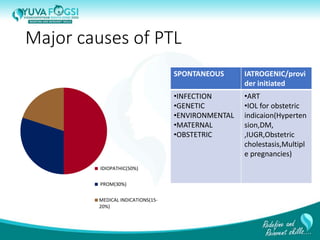
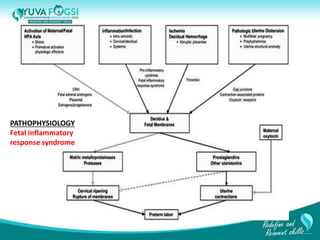
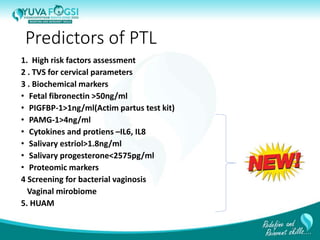
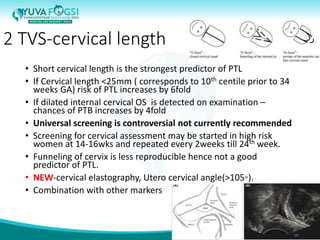
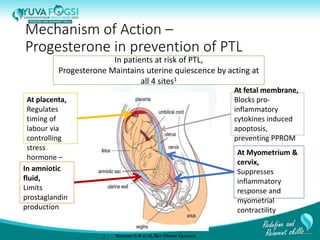
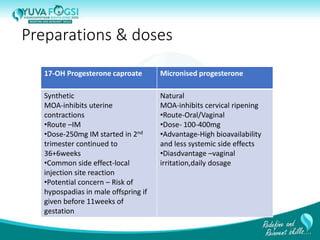
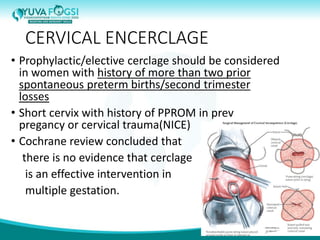
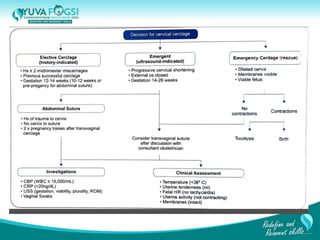
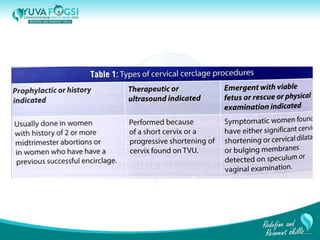
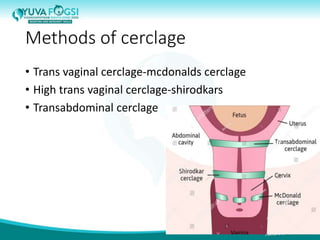
This document discusses prediction and prevention of preterm labour. It begins by defining preterm labour as contractions before 37 weeks of gestation. It then discusses the major causes of preterm labour and the pathophysiology. Several predictive variables and tests are examined, including cervical length screening, fetal fibronectin levels, and various biochemical markers. Prophylactic progesterone supplementation and cervical cerclage are explored as prevention methods for women at high risk of preterm labour, such as those with a prior preterm birth or short cervix. However, the document concludes that while research has identified several predictive factors, no single marker can accurately predict preterm labour on its own.