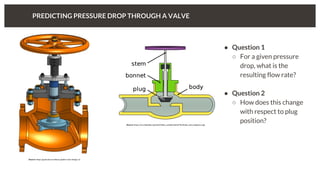
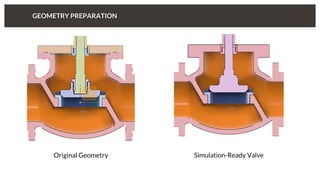
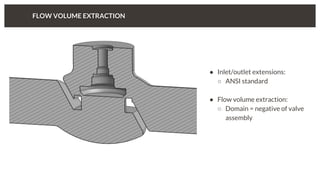
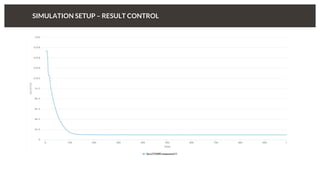
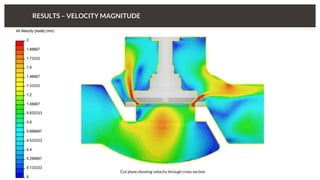
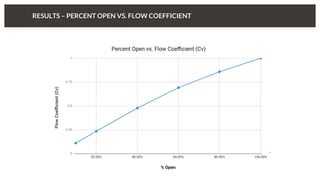
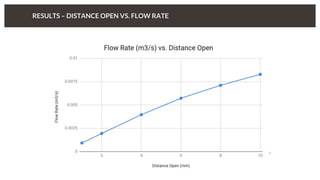
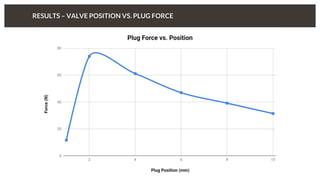
The document discusses predicting pressure drop through a valve and the relationship between pressure drop and flow rate. It outlines the setup and parameters for simulations, including boundary conditions and mesh refinements at various valve positions. Additionally, it includes details on the flow coefficient and the effects of valve opening on flow characteristics.