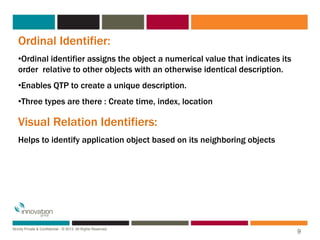
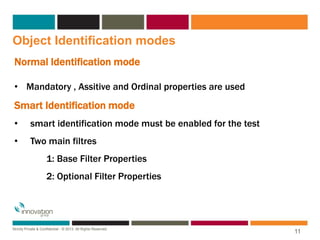
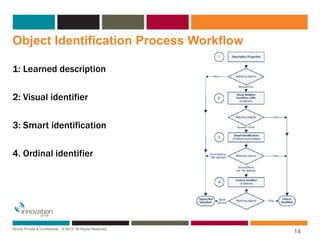
The document discusses object identification in QTP, including the types of objects like test objects and runtime objects. It describes how QTP learns about objects using mandatory properties, assistive properties, and ordinal identifiers to form a learned description. It also outlines the object identification process workflow where QTP first tries to identify objects using the learned description, then visual identifiers, smart identification, and finally ordinal identifiers. The document introduces the object repository as the storage place for object information in QTP and describes ways to add objects and the types of object repositories like local and shared.