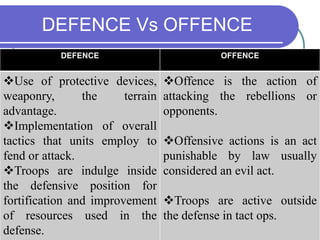
This document discusses the concept of "the offensive is the best form of defense" in a military context. It begins with introductions to key concepts like military strategy, offensive actions, and different types of offenses. It then covers different types of defenses and compares offense and defense. Other topics include counteroffensives, risk strategies, and dirty wars. The aim is to analyze whether the offensive is the best form of defense through studying these military strategies and concepts. It concludes that both offense and defense are important but offensive actions may be more effective and provide benefits to the population as well as security forces.