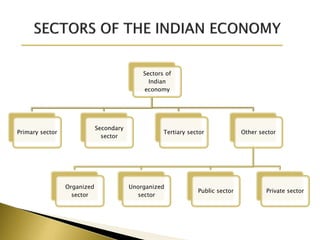
The Indian economy is the third largest in the world based on purchasing power and is projected to become the third largest economy by 2035 after the US and China. It will grow to 60% the size of the US economy. The history of the Indian economy can be broadly divided into three phases - pre-colonial, colonial, and post-colonial. Currently, the Indian economy is slowing with GDP growth at 4.8% in the first quarter of 2013, but the government is introducing reforms and increasing capital investment and social spending to boost growth going forward.